37 twin paradox spacetime diagram
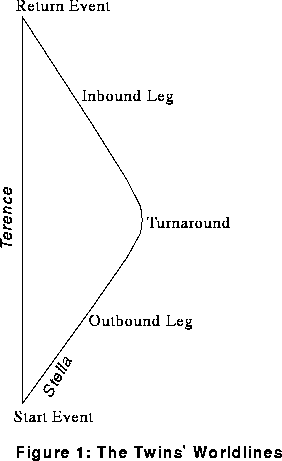
The Twin Paradox has nothing to do wit h gravi tation, nor has it anythi ng to do wit h the spacetime curvature postulated in GR. As we 'll see in section IV, ... Consider the space-time diagram in Figure 1. In this di agram, line t is the time axi s, according to Earth Twin, while s is the space axis (or: Twin Paradox. Recall the "twin paradox" that we discussed in section 15 of the lecture notes: Alice and Beth are twins. Beth travels to a far away star in a high-speed spaceship while Alice remains at home on Earth. Due to time dilation, Alice observes time to be flowing slower on Beth's spacethip than on the Earth, while Beth observes time to ...
Twin Paradox Spacetime Diagram (calculus not required) Below I will present some arguments below that the spacetime diagrams produced by the non-inertial observer are distinctly different from those by an inertial observer. While there are a lot of words to setup the diagrams, you can jump to the end to see main argument.
Twin paradox spacetime diagram
In this video, I show how to use space-time diagrams to understand the famous twin "paradox" in special relativity. Beyond just using the diagram to calculat... Correct application of the Minkowski space-time diagrams will show that there is no real paradox in the twin paradox and within the framework of special relativity there is no real age difference between the twins when they meet again. 2. The frame-jumping explanation The Minkowski diagram has been considered as the tool to help people obtain In the animation the spacetime diagram is divided by the two lightlines into 4 equal sectors. Two of these are labelled "Timelike intervals", two "Spacelike intervals". Choose any value for v and plug in these value-pairs for d and t: d = 5 t = 3, d = 6 t = -1, d = -5 t = 4, d = -6 t = -3. ... 9 The twin paradox .
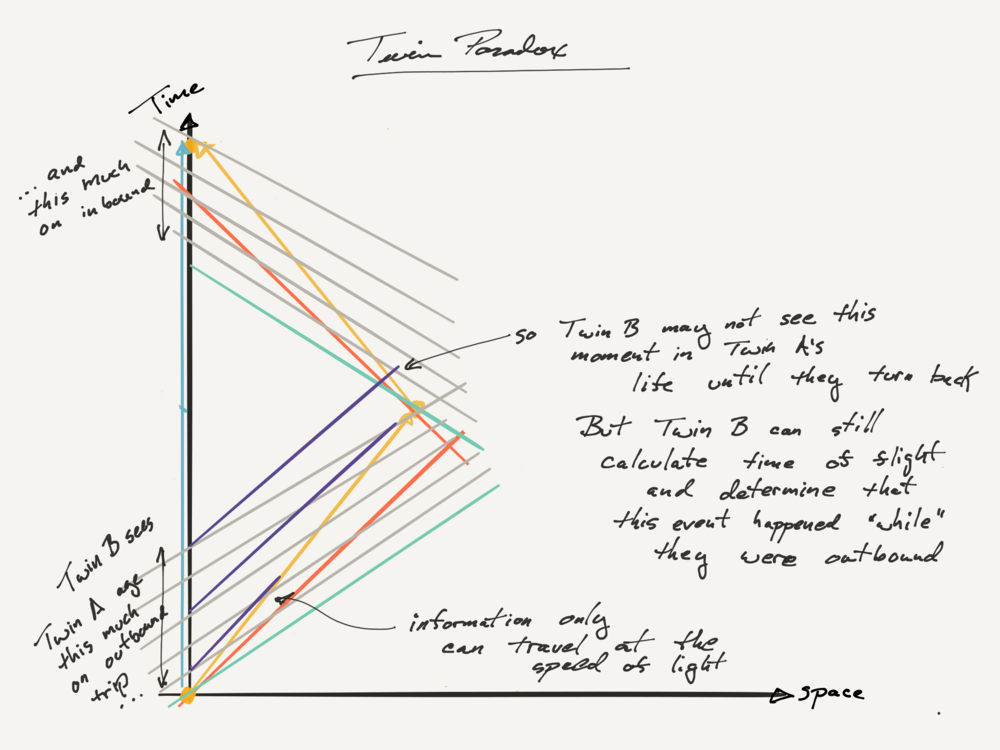
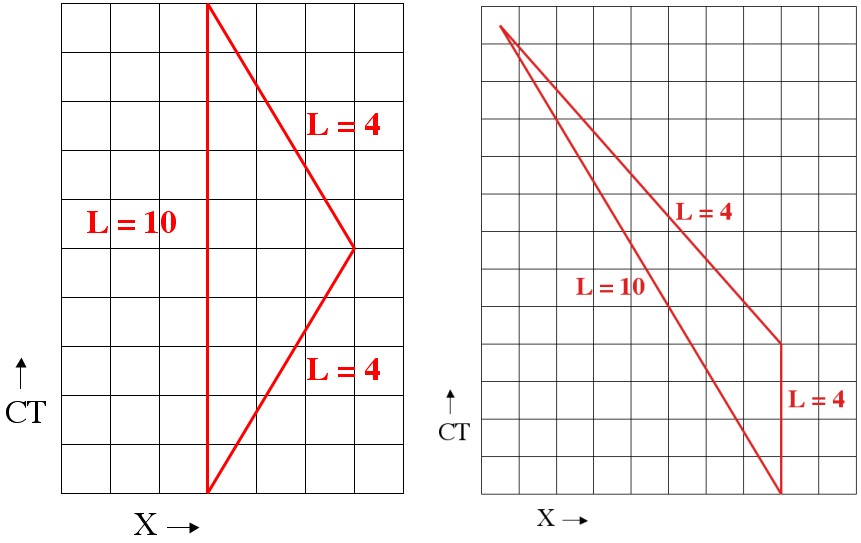
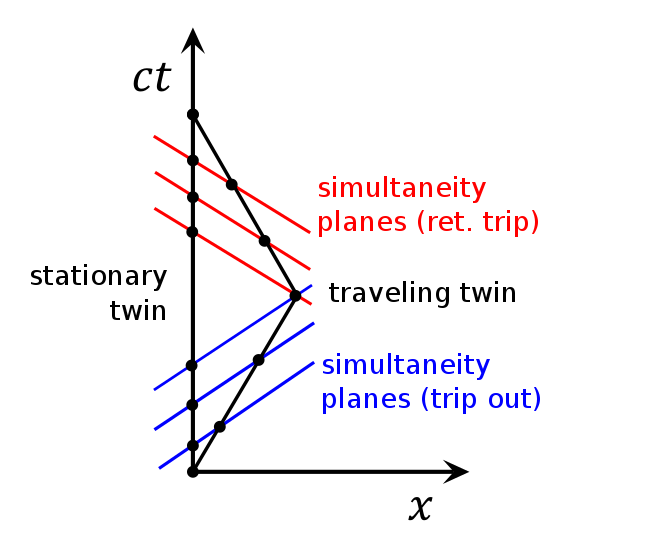
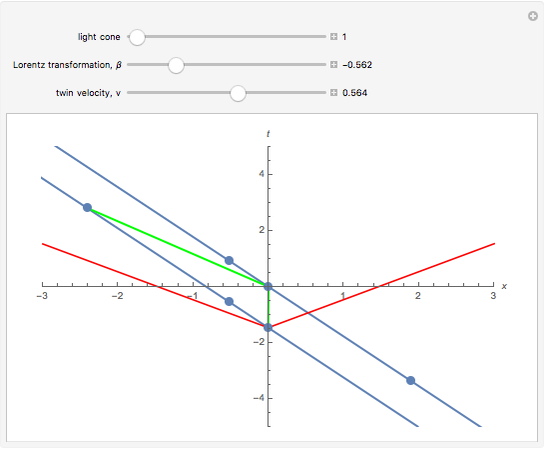
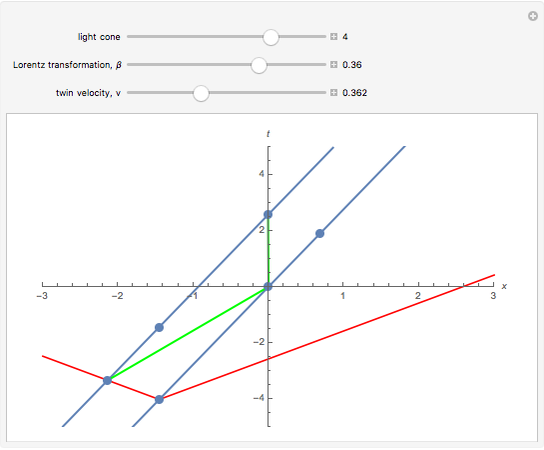
Twin paradox spacetime diagram. In the spacetime diagram below, we are basically replicating the same twin paradox example used throughout this discussion. According to the inertial frame, the space twin travels at velocity [v=+0.6c] for 5 years, then 'instantaneously' turns around and travels back at velocity [v=-0.6c] for 5 years. Spacetime diagrams. One of the most illuminating ways of understanding the resolution of the so-called "twin paradox" is by analyzing carefully drawn, detailed spacetime diagrams for specific choices of trip distance and velocity. I have done so below for a trip of three lightyears undertaken at a speed of 3/5 c (giving a relativistic factor γ ... At some point, Twin A needs to age 19.8 years according to Twin B for the paradox to resolve itself. How does that happen? You can see the resolution in a clever way using spacetime diagrams. What a spacetime diagram does is show how particular observers divide up space and time. The best one can do with a space-time argument in the context of the twin paradox is to note that one party, when changing inertial frames, will observe a jump in the reading of the clock time of the other party, using the 'lattice of clocks' method dictated by Einstein's particular clock synchronization.
In physics, the twin paradox is a thought experiment in special relativity involving identical twins, ... The x-t (space-time) diagrams at left show the paths of light signals traveling between Earth and ship (1st diagram) and between ship and Earth (2nd diagram). These signals carry the images of each twin and his age-clock to the other twin. Twin paradox through spacetime diagram: Lets try to analyse how we might work out the twin paradox using spacetime diagrams, in order to get a feel of how to work with the diagrams. First, however, we will need to introduce a few quantitative details to aid our treatment of the problem. Nevertheless, in formulations of the twin paradox in curved spacetime, where the twins will fall freely along space-time geodesics between meetings. Non-Space-Time Approach to Twin Paradox Theory An out-and-back twin paradox adventure could include the transition of a clock reading from one astronaut to the next, effectively removing the impact ... • Spacetime diagrams • Worldlines • The twin paradox Applications and skills: • Representing events on a spacetime diagram as points • Representing the positions of a moving particle on a spacetime diagram by a curve (the worldline) • Representing more than one inertial reference frame on the same spacetime diagram
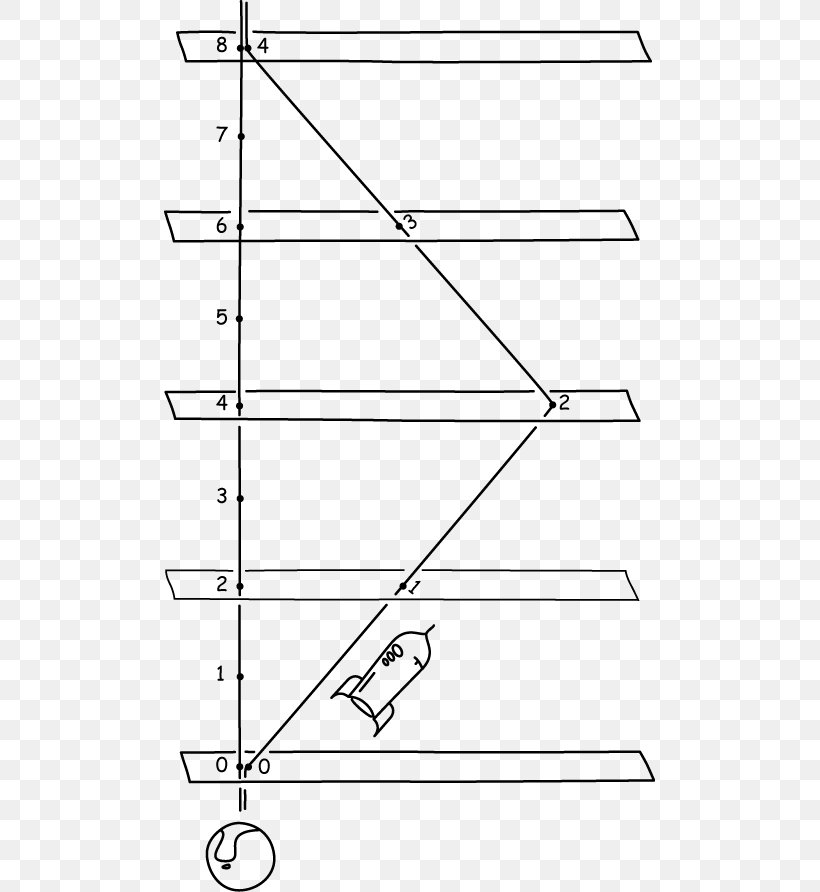
English: Spacetime diagram illustrating the twin paradox. The proper time from O to C to B is less than the proper time from O to A to B. Spacetime diagram - Twin paradox Thread starter jaumzaum; Start date Feb 12, 2013; Prev. 1; 2; First Prev 2 of 2 Go to page. Go. Feb 14, 2013 #26 PAllen. Science Advisor. 8,516 1,779. Let me remind to look at my post #8, where I describe carefully how the diagram looks for Pam at rest in a typical coordinate chart. This description is based on ... 22. I was studying the twin paradox (of Einstein special relativity) and everything was working well until I get to the traveler's spacetime diagram. First let me introduce the paradox for you to understand the diagram. Pam is the twin sister of Joe. Pam goes out Earth in 2007 in a spaceship with v = 0.6c (velocity that Jim measures) for a 3 ... The much-cited twin paradox consists of three stages: (1) the traveling twin takes off; (2) he turns around; and (3) he arrives back home. Those three events are connected by the green line segments. In this simulation imagine that the traveling twin is moving between two walls or space stations with the path marked in blue. The presence of these two space stations suggests three more observable;;
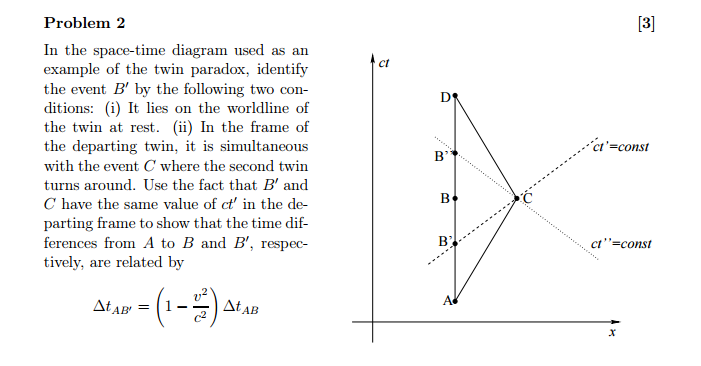
(b) You’regoing to resolve this paradox using a Spacetime diagram and Lorentztransformations. Draw a single spacetime diagram showing the entire trip in the reference frame of Blake. Your diagram should show the world lines of both twins. Label all events and show the space and time axes of the fft frames. Update your spacetime diagram
The twin paradox uses the symmetry of time dilation to produce a situation that seems paradoxical. In the introductory film clip, we saw that time was dilated when observed from frames of reference with a constant relative velocity v. There is an animation and analysis below, but let's introduce it with a cartoon.
The Twin Paradox: The Spacetime Diagram Explanation. This entry borrows heavily from the original FAQ entry for the Twin Paradox, by Kurt Sonnenmoser. However, it has also been extensively modified, so he is not responsible for any sloppiness or infelicities. Minkowski said, "Henceforth Space by itself, and Time by itself, are doomed to fade away into mere shadows, and only a kind of union of the two will preserve an independent reality."
Geometric Resolution of the Twin Paradox in Special Relativity Nicholas Mecholsky 7/13/11 1 Spacetime ets (i.e., acceleration), then at any instant, they are an equally valid origin for a different I am going to try to resolve the twin paradox coordinate system. and some relativity issues using the geome- ct try of spacetime diagrams.
Minkowski Spacetime Diagrams Instructions. These are the instructions for my script-based spacetime diagram generator. Using a script-based system provides for a lot more options than could be easily accommodated with a graphical user interface (GUI). ... This is a variant of the famous twin paradox. A ship traveling at 80% c passes Earth ...
The Twin Paradox: The Spacetime Diagram Analysis. This entry borrows heavily from the original FAQ entry for the Twin Paradox, by Kurt Sonnenmoser. But it has also been extensively modified, so he is not responsible for any sloppiness or infelicities.
The Simultaneity Spacetime Diagram model was written for the study of special relativity the Lorentz transformation using spacetime diagrams and is a supplemental simulation for an article by Sebastien Cromier and Richard Steinberg "The Twin Twin Paradox: Exploring Student Approaches to Understanding Relativistic Concepts" in the The Physics ...
Answer (1 of 5): There's no single diagram since the traveling twin can go at different speeds, accelerate and decelerate differently. The only thing important is that the twins take different paths thru spacetime. Here's the simplest form for a traveler who accelerates instantaneously (e.g. very...
sent from each twin to the other. This, especially when drawn on a spacetime diagram, can make it more clear exactly how the twins perceive each other’s aging. While a Doppler analysis of timing signals can be informative for the traditional twin paradox (see figure 1), it will not help very much in the problem discussed later on in this paper.
Page 4 of 4 The Twin \Paradox" in a Space-Time Diagram t (yr) x (ly) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 1 yr 0 1 2 3 4 2 yr 3 yr 4 yr 5 yr 6 yr 7 yr 8 yr 4.75 yr 4.5 yr 4.25 yr 8 ...
A metric tensor of space-time is expressed in this equation: g uv = [- 1 00 00 1000 00 10 001] As mentioned earlier, space-time is flat everywhere. Interactive Minkowski Diagram. In physics, twin paradox space is the thought experimentation in special relativity consisting of identical twins.
This problem is known as the twin paradox. Spacetime Diagram explanation of the Twin Paradox The answer to this question is that for the astronaut to return to the Earth, he/she must change direction and thereby switch from one inertial frame to another, and that breaks the symmetry between the two observers.
Although this diagram belongs above the one above, I'll leave it down here because this is "later" in the story of the Twin Paradox. When they approach, one Doppler Triangle is ZVS, with future-directed light-signal VS. The Doppler factor is SZ/VZ=1/2. (Comparing reception period to transmission period.)
34.2 The Pole in the Barn: Spacetime Diagrams. This demonstration shows how the "pole in the barn paradox" plays out in a spacetime diagram. Choose the relative speed of the pole (the yellow line segment) and the barn (the blue line segment). Hit start to watch the pole move through the barn, or adjust the time slider to control its motion ...
In the animation the spacetime diagram is divided by the two lightlines into 4 equal sectors. Two of these are labelled "Timelike intervals", two "Spacelike intervals". Choose any value for v and plug in these value-pairs for d and t: d = 5 t = 3, d = 6 t = -1, d = -5 t = 4, d = -6 t = -3. ... 9 The twin paradox .
Correct application of the Minkowski space-time diagrams will show that there is no real paradox in the twin paradox and within the framework of special relativity there is no real age difference between the twins when they meet again. 2. The frame-jumping explanation The Minkowski diagram has been considered as the tool to help people obtain
Why Does The Twin Paradox Assume The Stationary Twin Will Become Older Than The Moving Twin Due To Time Dilation There Are No Absolute Speeds Speed Is Relative And Either Twin Could
In this video, I show how to use space-time diagrams to understand the famous twin "paradox" in special relativity. Beyond just using the diagram to calculat...















0 Response to "37 twin paradox spacetime diagram"
Post a Comment