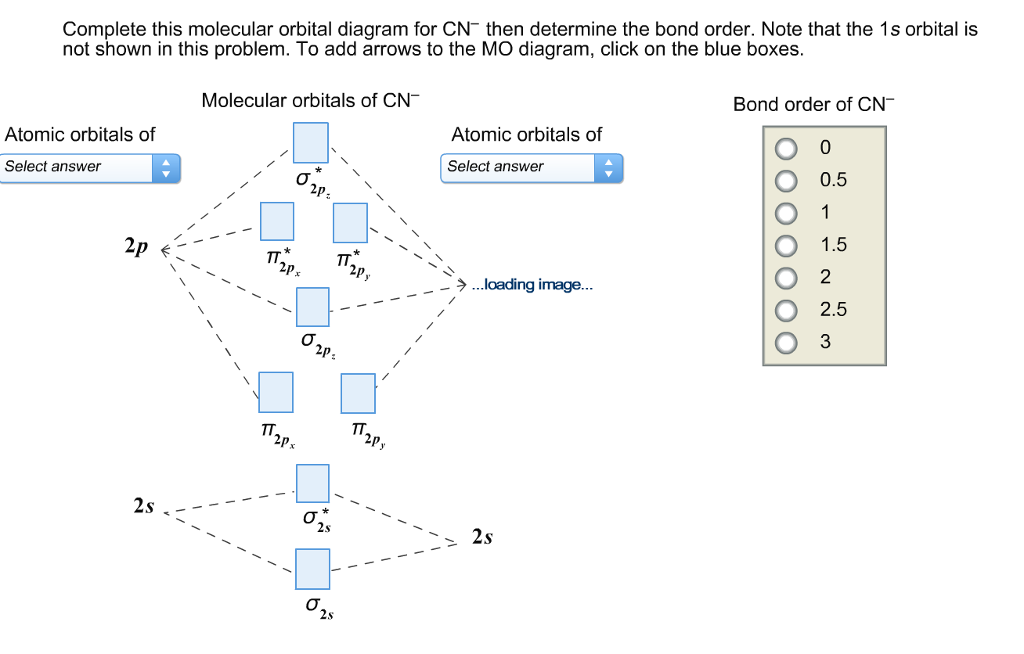
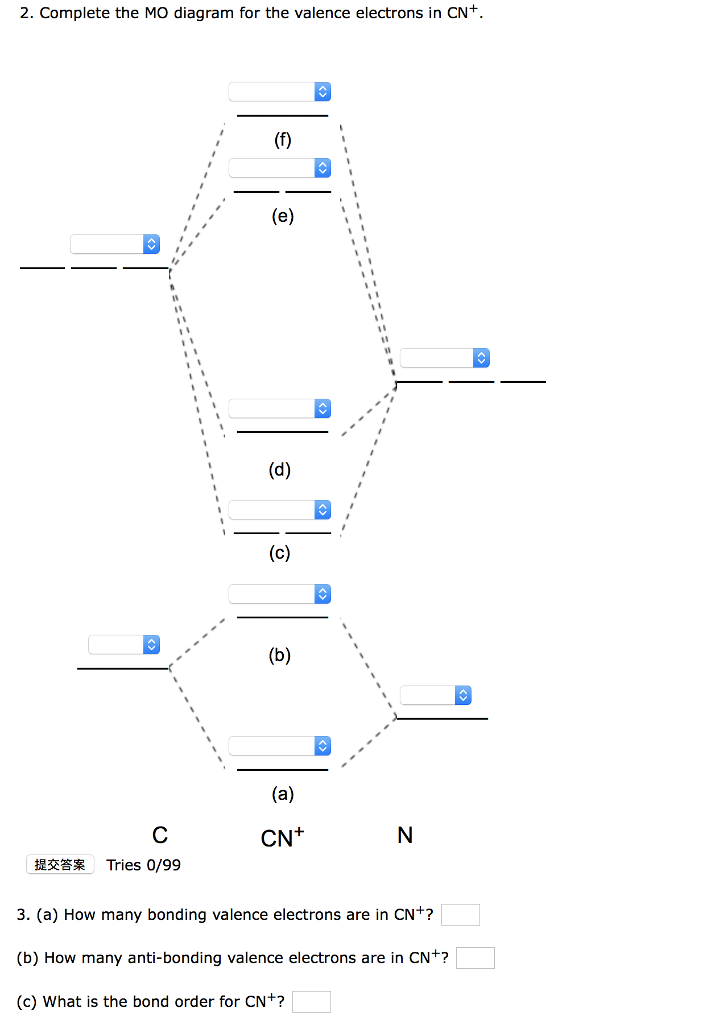
38 complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn
Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn. Posted on December 21, 2018 December 20, 2018. Sponsored links. Related posts: Recirculating Hot Water System Diagram. Lexus Gs 350 Parts Diagram. Intake Manifold Gasket Diagram. Human Anatomy Torso Diagram. John Deere 826 Snowblower Parts Diagram. Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
The molecular orbital diagram of NO shown in the figure below also applies to the following species. Write the molecular orbital electron configuration of each, indicating the bond order and the number of unpaired electrons. (a) CN (b) CO-(c) BeB-(d) BC +
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn
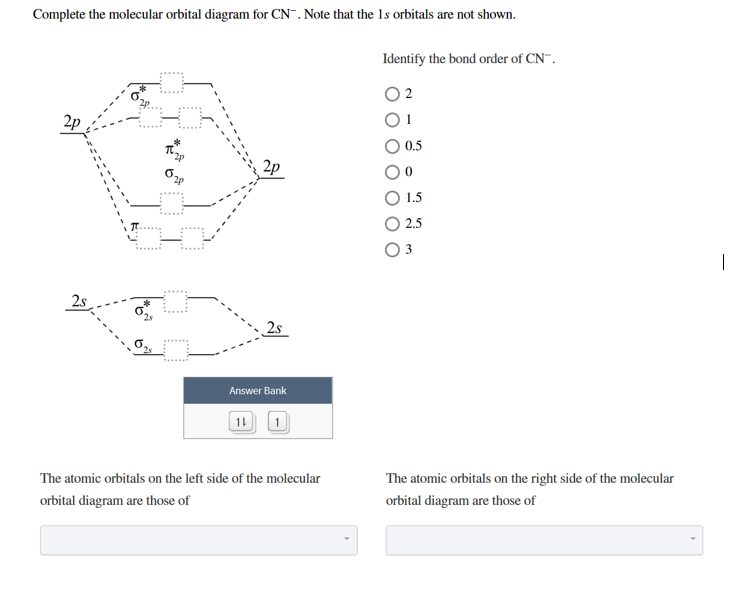
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN-. a. Label the elements and add the electrons where appropriate. b. Determine the bond order of CN-. c. Will the bond between the C and the N be strengthened or weakened by the removal of 1 electron? 2s 2p 2s 2p AO's MO's AO's s s* s s* p p p* p* Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is ... The extra electron in CN-occupies a σ-orbital. This is a bonding orbital and so Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. image.png. Bond order of CN-.1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
FREE Expert Solution. We’re being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence ... Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn then determine the bond order. Right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic. Where the indicates an anitbonding molecular orbital that is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals that combine to form it. But there are many more molecules. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. Answer to Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN– then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown i...
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN¯. О 1.5 2p ´2p 2p 2 1 0.5 2.5 3 2s 2s 2.s Answer Bank 11 1 The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of orbital diagram are those of 9. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11. Get homework help fast! Search through millions of guided step-by-step solutions or ask for help from our community of subject experts 24/7. Try Study today. Source 1: wikianswers.com Rating: General Information colorless gas WebMO Calculations: used to produce chemical compounds, especially polymers formerly used as a disinfectant for preserving biological specimens carcinogenic to humans Formaldehyde (H2CO) Molecular Orbitals Source
Watch the video solution for the question: Complete this molecular orbital diagram for C...
Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Orbit Not Shown In This Problem To Add Arrows To The Mo Diagram Click On The
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
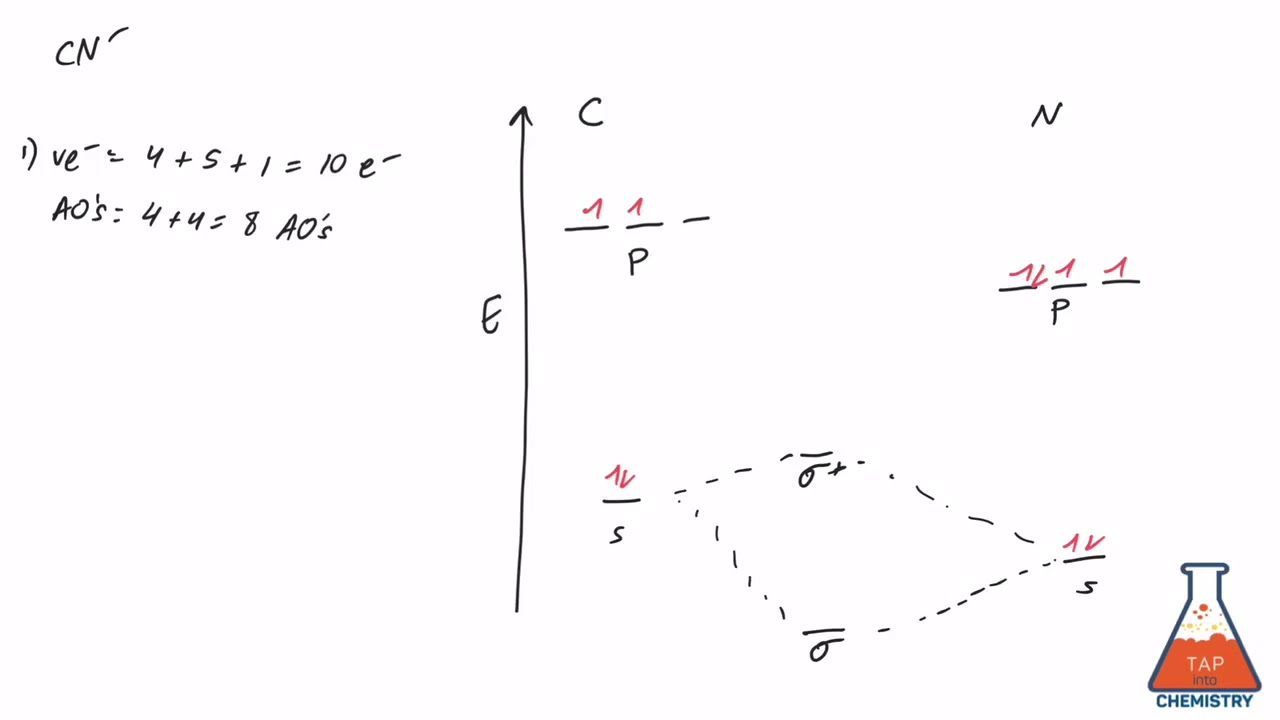
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ...
Education portal for Homework help, IIT JEE, NEET. Post questions you can’t solve, Past exam questions with answers, large question bank. Improve concepts using videos, connect with students and teachers globally. Build your reputation.
Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond order, and write the MO electron configuration with an ...
Tania Havenga. University of South Africa. Here is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. http ...
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
Theoretical chemistry research group focusing on development of methods, and calculations in the areas of ionic liquids, photochemistry and catalysis
🚀To book a personalized 1-on-1 tutoring session:👉Janine The Tutorhttps://janinethetutor.com🚀More proven OneClass Services you might be interested in:👉One...
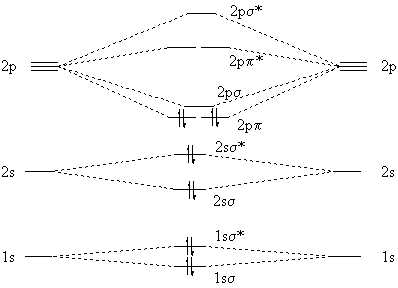
together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This ...
Solved Compare The Mo Diagram Of Pt Cn 4 2 And Pt Pyridine 4 2 Assume The Pyridine Molecules Are All Flat In The Xy Plane Pyridine Is A Pi Acce Course Hero
January 4, 2021 - Part (b) in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) is the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for He2+. This ion has a total of three valence electrons. Because the first two electrons completely fill the σ1s molecular orbital, the Pauli principle states that the third electron must be in the \( \sigma ...
Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).
Education portal for Homework help, IIT JEE, NEET. Post questions you can't solve, Past exam questions with answers, large question bank. Improve concepts using videos, connect with students and teachers globally. Build your reputation.
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
FREE Answer to Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN– then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s...
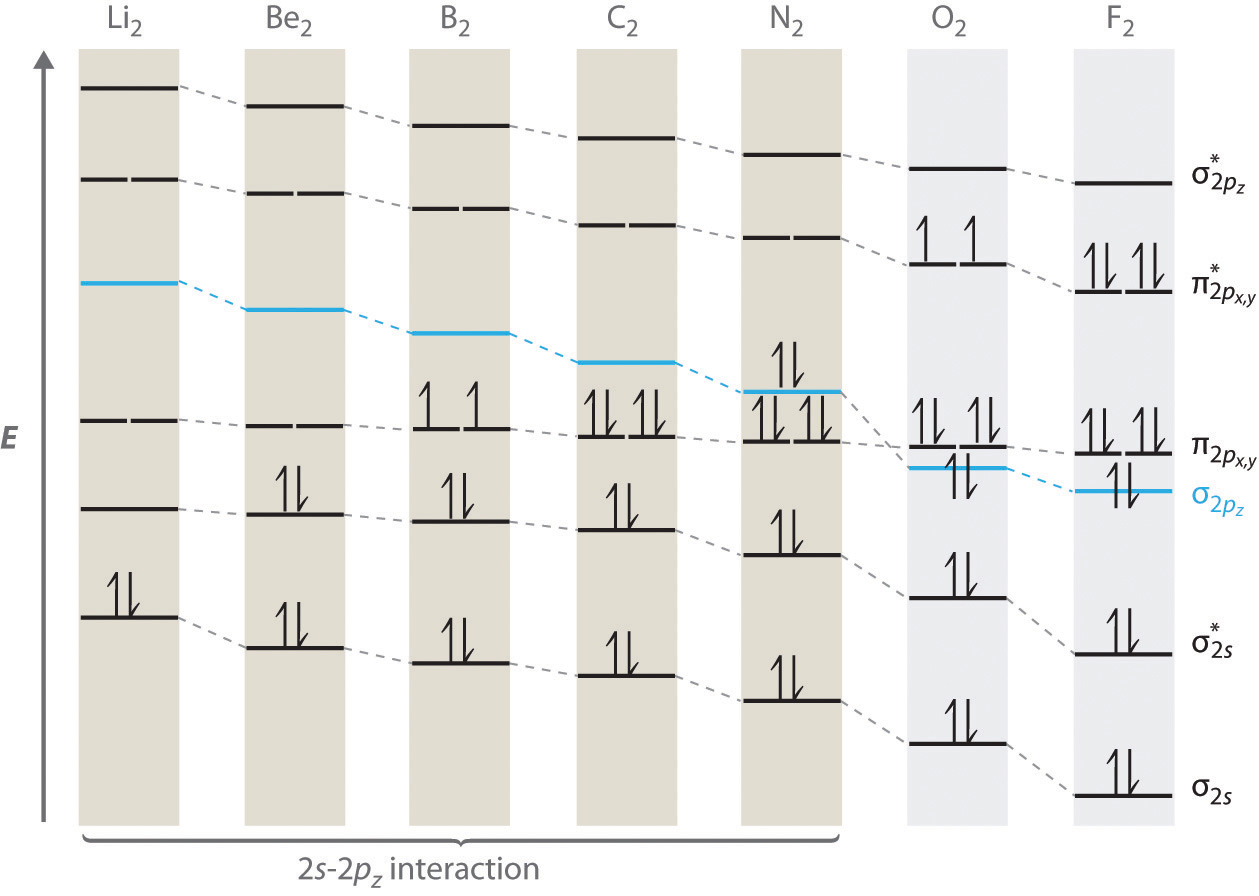
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Bond order of CN O 0 O 0.5 Molecular orbitals of CN Atomic orbitals of Atomic orbitals of Select answer Select answer O 1.5 2 2Py oading image.
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN - then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos

Can You Please Describe The Mo Diagram Of Cn I Could Not Find The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Brainly In
Answer (1 of 5): The total number of electron of CN- ion is ( 6+7+1) = 14 . According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration of CN - ion is as follows, From the above electronic configuration , it has been found that , the number of bonding electron is 10 and the the number of...
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagrams For The Following Diatomic Molecules Polyatomic Ions Indicate Their Bond Orders And Rank Them In Order Of Increasing Bond Strength A Cn B Co C F 2 D N 2
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is ... The extra electron in CN-occupies a σ-orbital. This is a bonding orbital and so
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN-. a. Label the elements and add the electrons where appropriate. b. Determine the bond order of CN-. c. Will the bond between the C and the N be strengthened or weakened by the removal of 1 electron? 2s 2p 2s 2p AO's MO's AO's s s* s s* p p p* p*
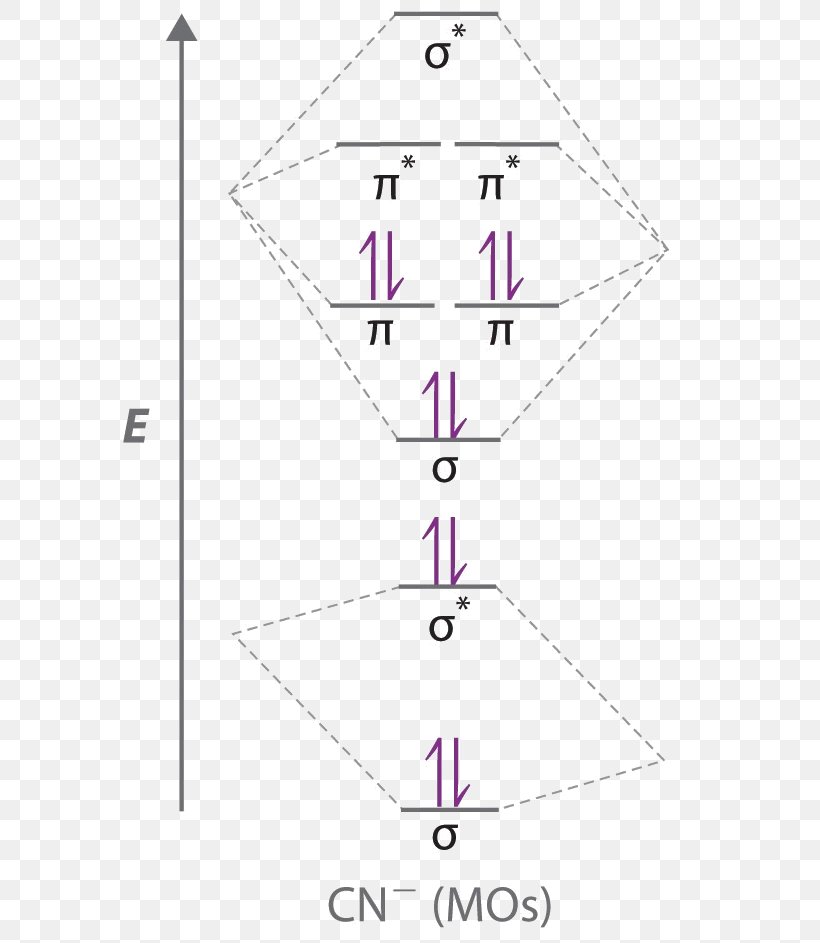
Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Cyanide Png 631x943px Diagram Anion Area Atomic Orbital Bond Order Download

Which Atom Bears The Negative Charge In Cyanide I Am Confused By The Mo Diagram Chemistry Stack Exchange






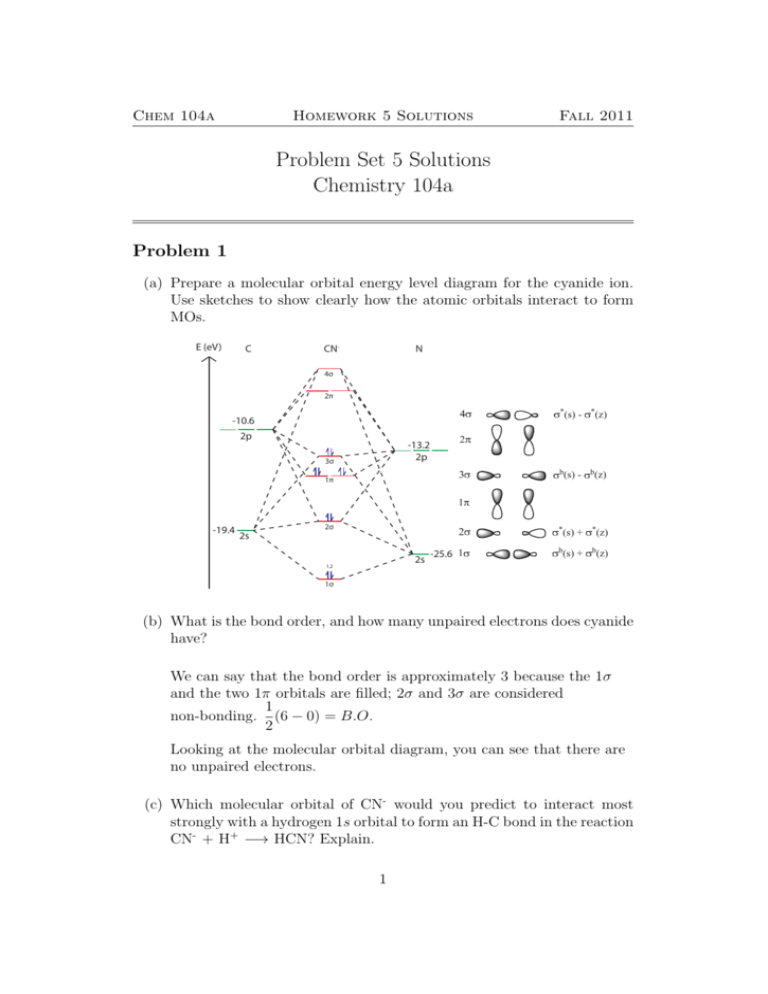
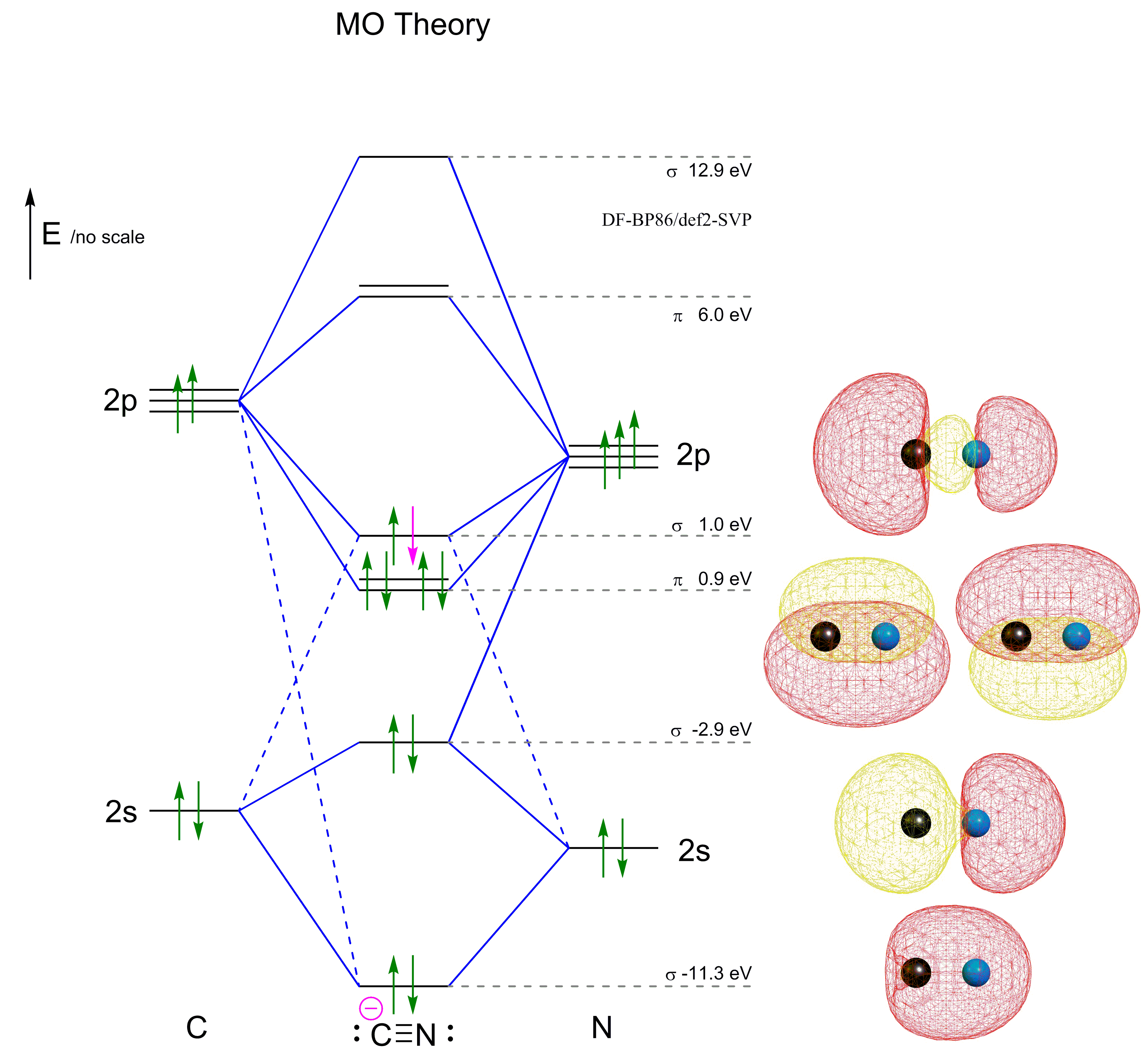

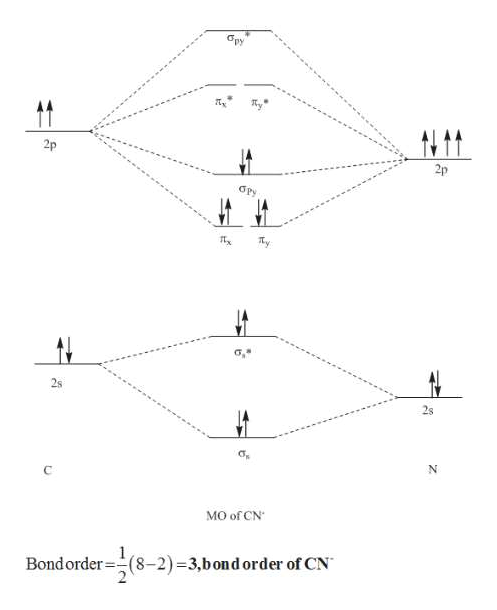





0 Response to "38 complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn"
Post a Comment