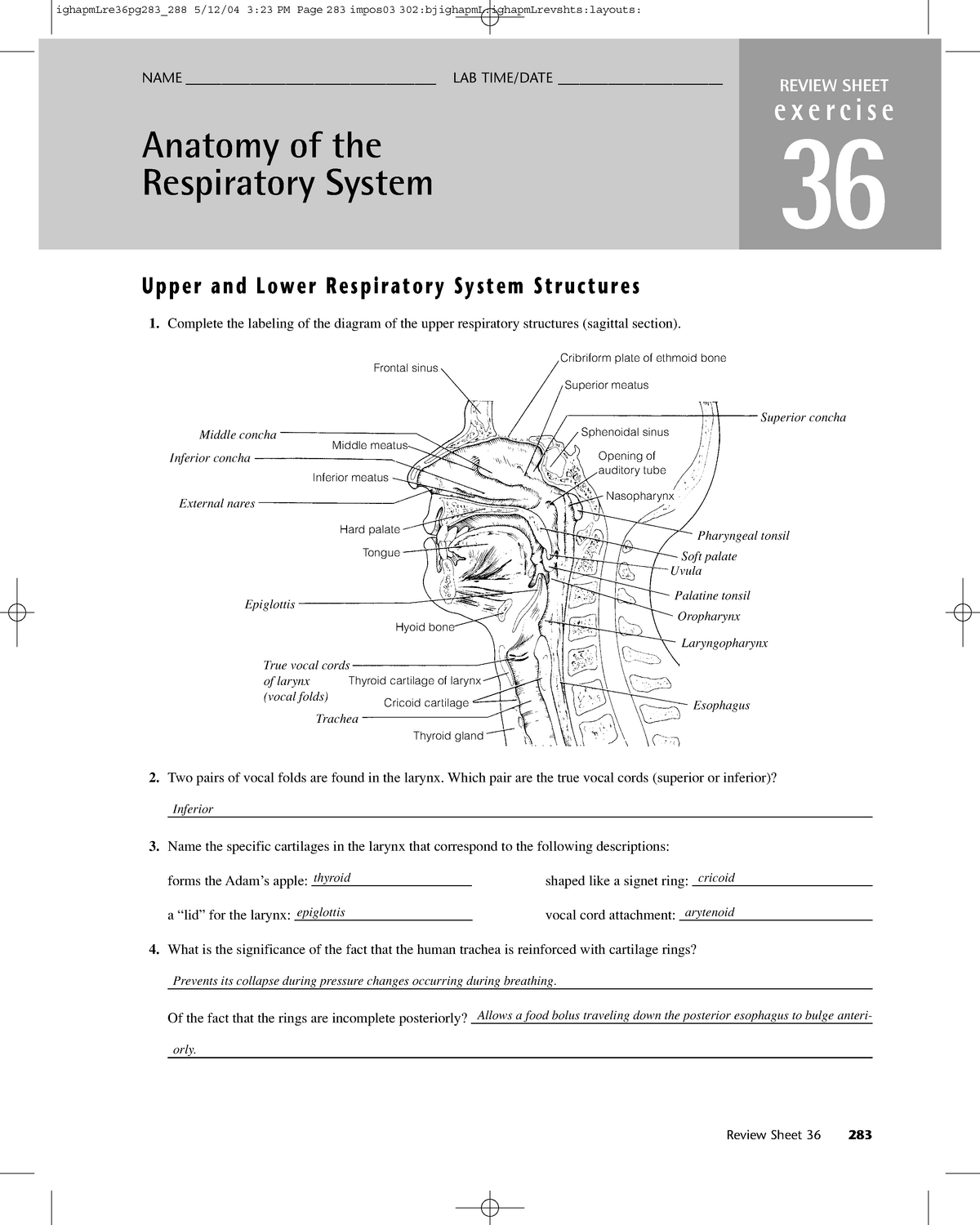
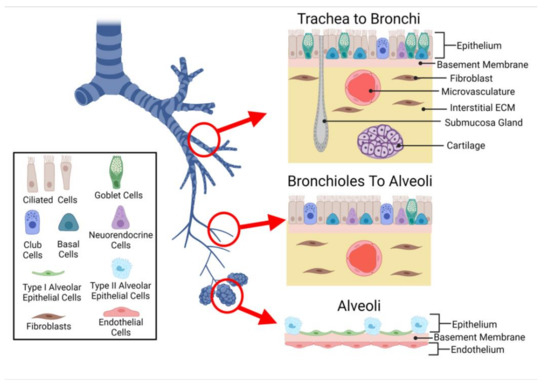
38 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
(the diagram shows B cells in a lymph node. A B cell is shown binding to an antigen to its B cell receptor. Next, the sensitized B cell presents the antigen via MHC class II to a TH cell, which is shown secreting cytokines. Then, the B cell divides repeatedly and gives rise to plasma cells and memory B cells) parts, epithelial tissues form the inner lining and external lining of body parts. To summarize, the apical pole faces the surface, while the basal pole is attached to the connective tissue located below the epithelium. Types of epithelial tissue. There are 3 different types of epithelial tissue: squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
Put the following in order: 1. Alveolar Duct 2. Bronchiole 3. Tertiary Bronchus 4. Gas Exchange 5. Alveolar Sac 6. Nasopharynx 7. Secondary Bronchus 8. Trachea 9. …

On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
Thick regions, where the epithelium is separated from the endothelium by fibers or other cells, can be associated with either aerocytes or gCap cells. AT1 cell, alveolar type 1 epithelial cell; AT2 cell, alveolar type 2 epithelial cell. Micrographs in top left, middle, and bottom panels are shown without pseudocoloring in Fig. 2g- -i. i. Inflammation of non-gingival periodontal tissues (i.e. the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone) Alveolar mucositis: Inflammation of alveolar mucosa (i.e., mucosa overlying the alveolar process and extending from the mucogingival junction without obvious demarcation to the vestibular sulcus and to the floor of the mouth) Sublingual mucositis: Feb 09, 2016 · Periodontal disease represents a group of oral inflammatory infections initiated by oral pathogens which exist as a complex biofilms on the tooth surface and cause destruction to tooth supporting tissues. The severity of this disease ranges from mild and …
On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium. 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16. Jul 30, 2020 · Figure 1 is a diagram showing the main parts of the airway and lung. The airway consists of the oral and nasal cavities, which connect to the voice box (larynx), which connects to the windpipe (trachea). Note in the diagram that the windpipe splits into two air passages called bronchi, one going to each lung (right and left main bronchi). May 28, 2021 · A comprehensive database of more than 35 histology quizzes online, test your knowledge with histology quiz questions. Our online histology trivia quizzes can be adapted to suit your requirements for taking some of the top histology quizzes. The epithelium of the alveoli, contains two main types of cells: type I pneumocytes: large flattened cells - (95% of the total alveolar area) which present a very thin diffusion barrier for gases. type II pneumocytes (making up 5% of the total alveolar area, but 60% of cells). These cells secrete 'surfactant' which decreases the surface tension ...
52. The broadest basis for classifying epithelium into subgroups is a. keratinized or not keratinized b. squamous, cuboidal or columnar c. simple or stratified d. absorptive or secretory e. lining or glandular 53. Regarding simple columnar epithelium which statement is least descriptive? a. may be keratinized b. may exhibit a microvillous border On the diagram below, identify the alveolar duet, respiratory bronchioles, terminal bronchiole, alveoli, and alveolar sa. Examining Prepared Slides of Tracheal and Lung Tissue 14. The tracheal epithelium is ciliated and has goblet cells. What is the function of each of these modifications? cilia: goblet cells: 15. Review Sheet 23 302 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16. Among permanent teeth, 16 are found in the maxilla and 16 in the mandible, for a total of 32.The dental formula is 2.1.2.3 2.1.2.3.Permanent human teeth are numbered in a boustrophedonic sequence.. The maxillary teeth are the maxillary central incisors (teeth 8 and 9 in the diagram), maxillary lateral incisors (7 and 10), maxillary canines (6 and 11), maxillary first premolars (5 and 12 ...
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek περί, perí – 'around'; and ὀδούς, odoús – 'tooth', genitive ὀδόντος, odóntos) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them.The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum ... Jan 11, 2017 · Tuberculosis is a public health problem worldwide, including in the United States—particularly among immunocompromised patients and other high-risk groups. Tuberculosis manifests in active and latent forms. Active disease can occur as primary tuberculosis, developing shortly after infection, or postprimary tuberculosis, developing after a long period of latent infection. … Types of Epithelial Tissue. There are three types of epithelial cells, which differ in their shape and function. Squamous- thin and flat cells Cuboidal- short cylindrical cells, which appear hexagonal in cross-section Columnar- long or column-like cylindrical cells, which have nucleus present at the base On the basis of the number of layers present, epithelial tissue is divided into the simple ... The basal epithelium consists of myoepithelial cells, which generate the outer layer of the gland, and a small population of stem cells, which supply the different cell types. The luminal epithelium forms ducts and secretory alveoli and contains populations of cells defined by their hormone receptor status.

Streptococcus Pneumoniae Inhibits Purinergic Signaling And Promotes Purinergic Receptor P2y2 Internalization In Alveolar Epithelial Cells Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Question: iagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the brane respira Elastic fiber Connective tissue fibers Monocyte . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text
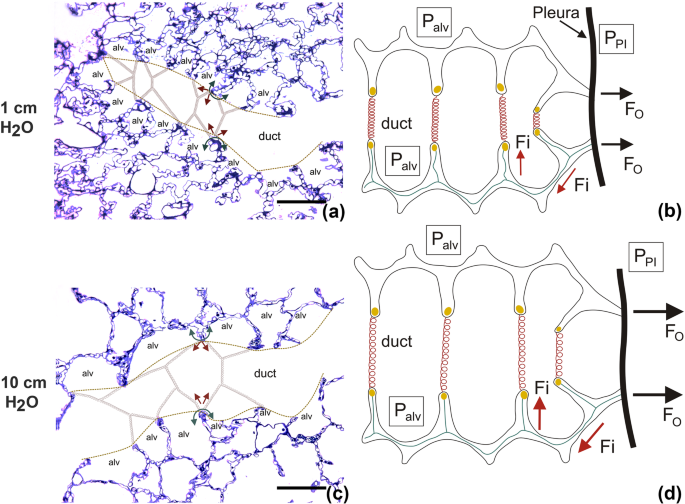
The Micromechanics Of Lung Alveoli Structure And Function Of Surfactant And Tissue Components Springerlink
In summary, the following things can be said about the alveolar shape and structure: Largely polyhedral shape. Open at one end, like a cup. Walls of the alveoli are composed of the pulmonary capillary sheet. Alveolar surfaces are covered in a thin (200nm) layer of surfactant which acts as the interface with the gas.

Sectional View Of Alveoli With A Pulmonary Capillary Is Shown Below Identify The Right Match In Context To The Options Given Below Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Nta Neet Set 63 E03 036 Q01 Png Width 80
Feb 09, 2016 · Periodontal disease represents a group of oral inflammatory infections initiated by oral pathogens which exist as a complex biofilms on the tooth surface and cause destruction to tooth supporting tissues. The severity of this disease ranges from mild and …
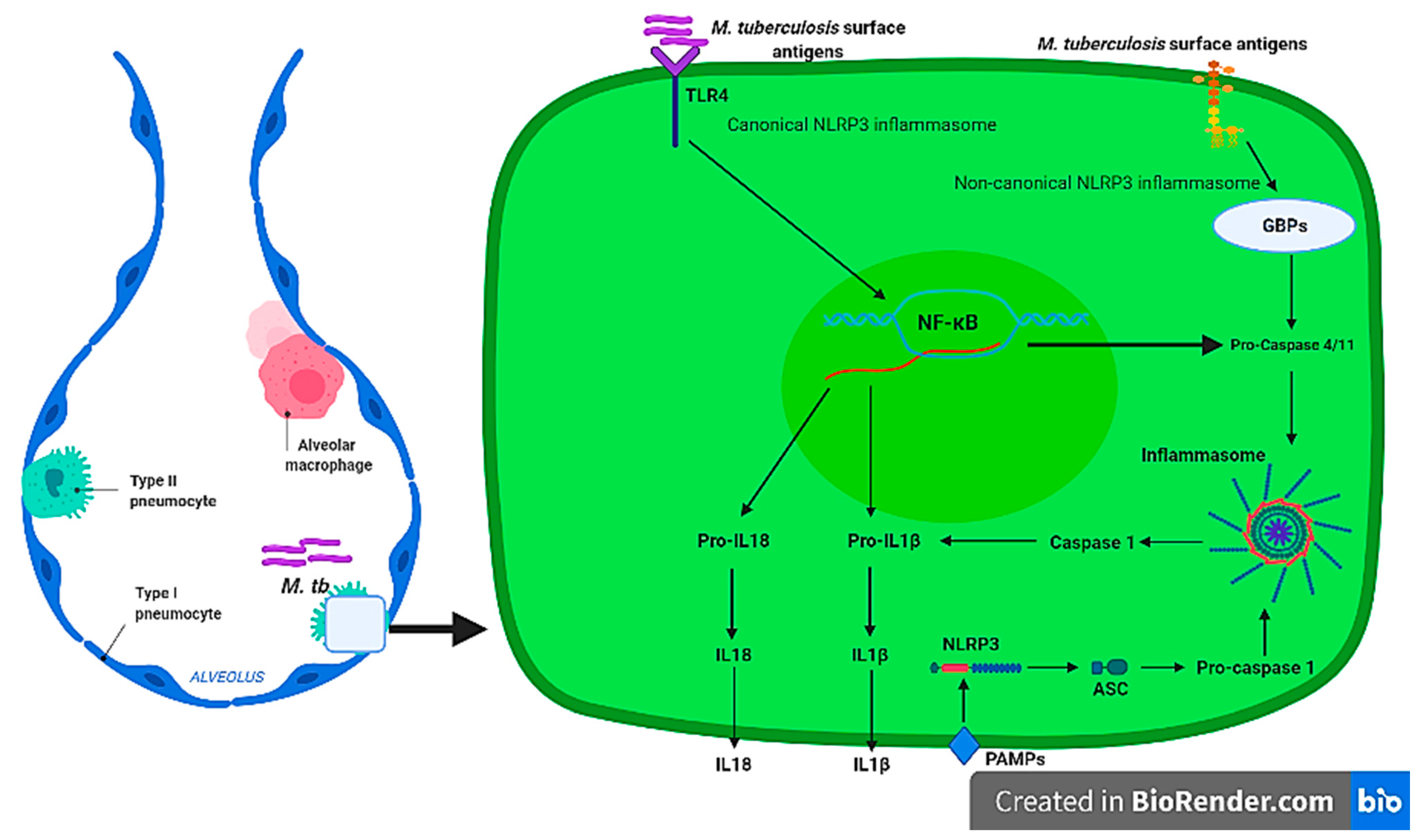
Ijms Free Full Text Exploring The Use Of Medicinal Plants And Their Bioactive Derivatives As Alveolar Nlrp3 Inflammasome Regulators During Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection Html
Inflammation of non-gingival periodontal tissues (i.e. the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone) Alveolar mucositis: Inflammation of alveolar mucosa (i.e., mucosa overlying the alveolar process and extending from the mucogingival junction without obvious demarcation to the vestibular sulcus and to the floor of the mouth) Sublingual mucositis:

Alveolar Wars The Rise Of In Vitro Models To Understand Human Lung Alveolar Maintenance Regeneration And Disease Evans 2020 Stem Cells Translational Medicine Wiley Online Library
Thick regions, where the epithelium is separated from the endothelium by fibers or other cells, can be associated with either aerocytes or gCap cells. AT1 cell, alveolar type 1 epithelial cell; AT2 cell, alveolar type 2 epithelial cell. Micrographs in top left, middle, and bottom panels are shown without pseudocoloring in Fig. 2g- -i. i.
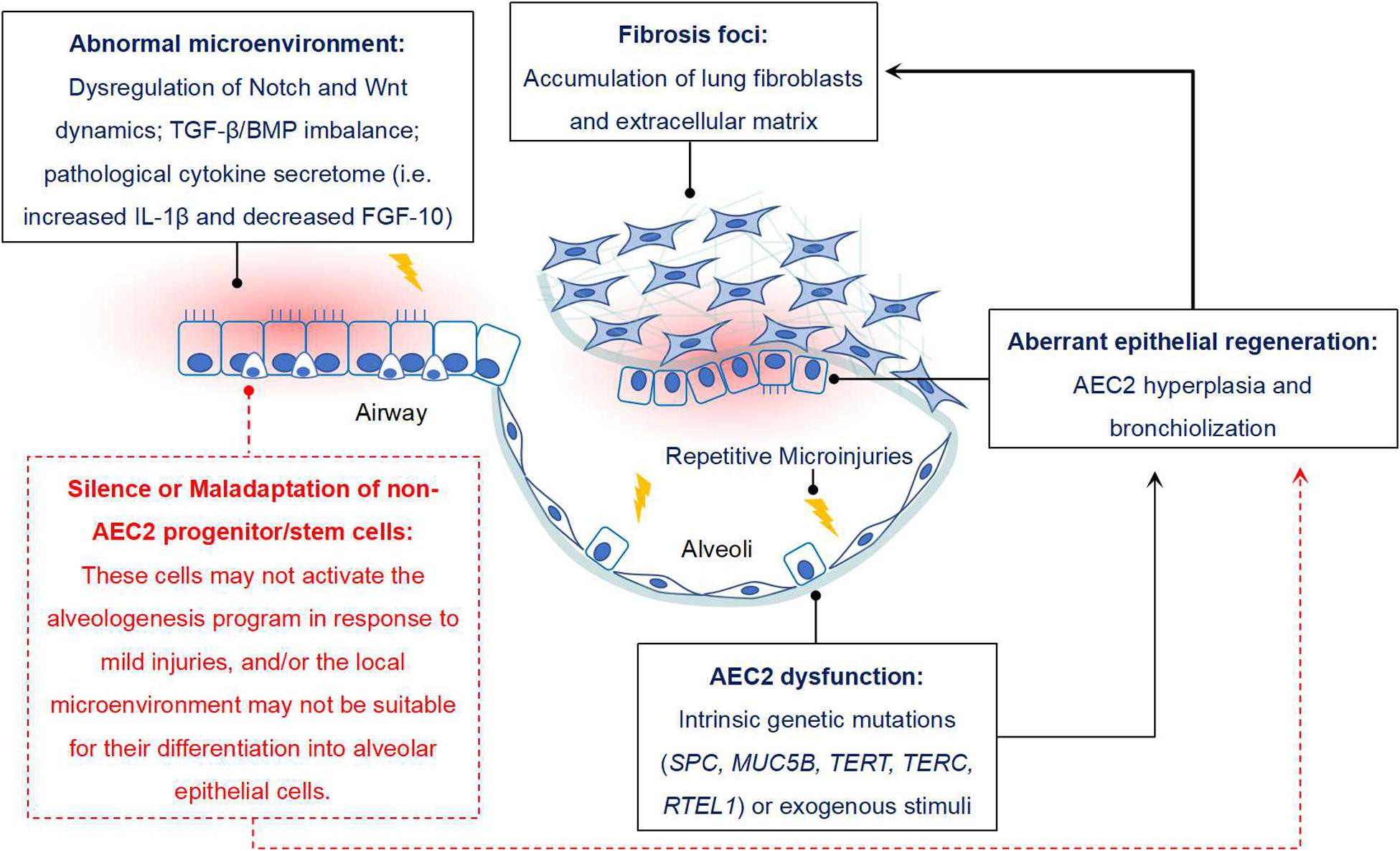
Frontiers New Perspectives On The Aberrant Alveolar Repair Of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Cell And Developmental Biology
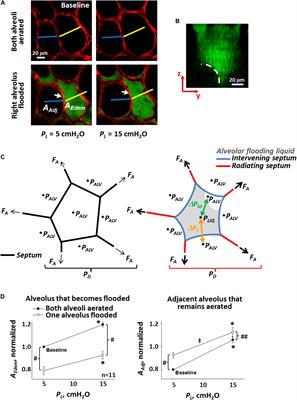
Frontiers The Contribution Of Surface Tension Dependent Alveolar Septal Stress Concentrations To Ventilation Induced Lung Injury In The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Physiology
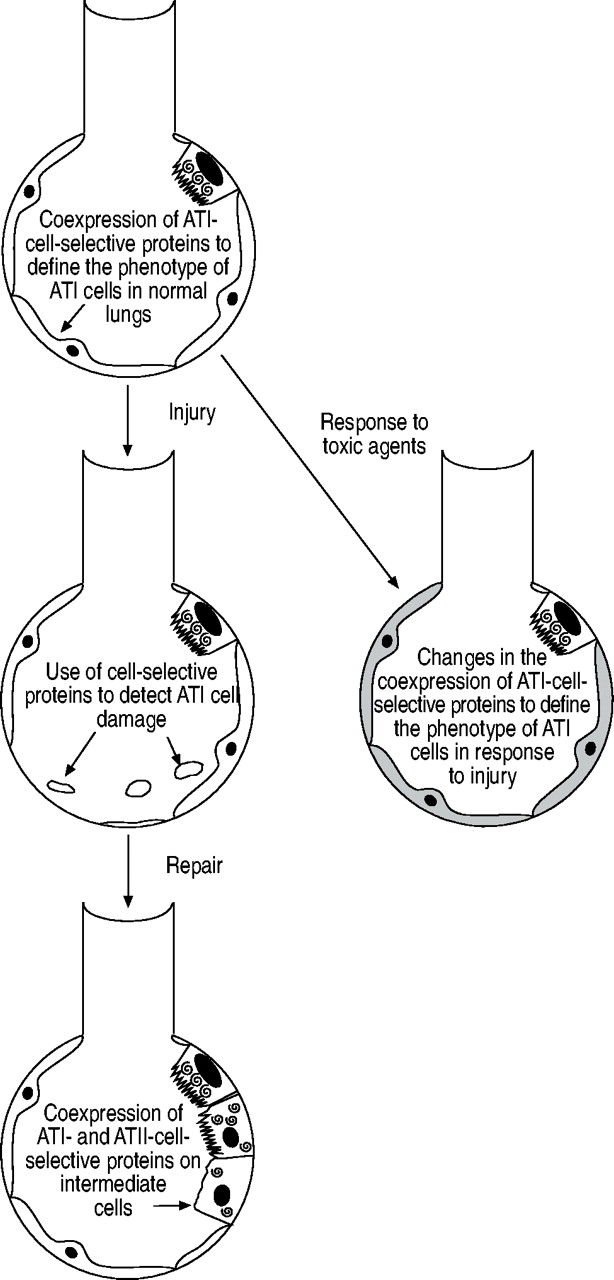
The Use Of Alveolar Epithelial Type I Cell Selective Markers To Investigate Lung Injury And Repair European Respiratory Society

The Use Of Alveolar Epithelial Type I Cell Selective Markers To Investigate Lung Injury And Repair European Respiratory Society

The Use Of Alveolar Epithelial Type I Cell Selective Markers To Investigate Lung Injury And Repair European Respiratory Society

Crosstalk Between Alveolar Macrophages And Alveolar Epithelial Cells Fibroblasts Contributes To The Pulmonary Toxicity Of Gefitinib Sciencedirect

Alveolar Progenitor Cells And The Origin Of Lung Cancer Sainz De Aja 2021 Journal Of Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library

Treatment Of Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome Plea For Rescue Therapy Of The Alveolar Epithelium Thorax
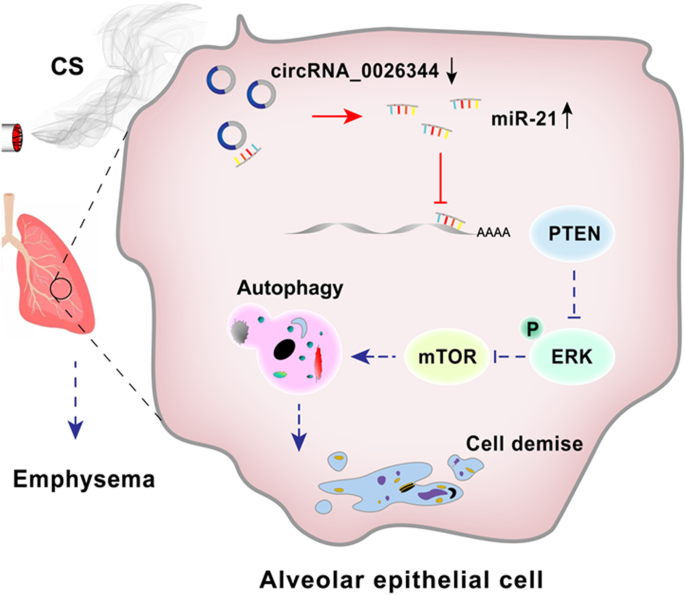
Circrna 0026344 Via Mir 21 Is Involved In Cigarette Smoke Induced Autophagy And Apoptosis Of Alveolar Epithelial Cells In Emphysema Springerlink

Long Term Culture Of Distal Airway Epithelial Cells Allows Differentiation Towards Alveolar Epithelial Cells Suited For Influenza Virus Studies Ebiomedicine
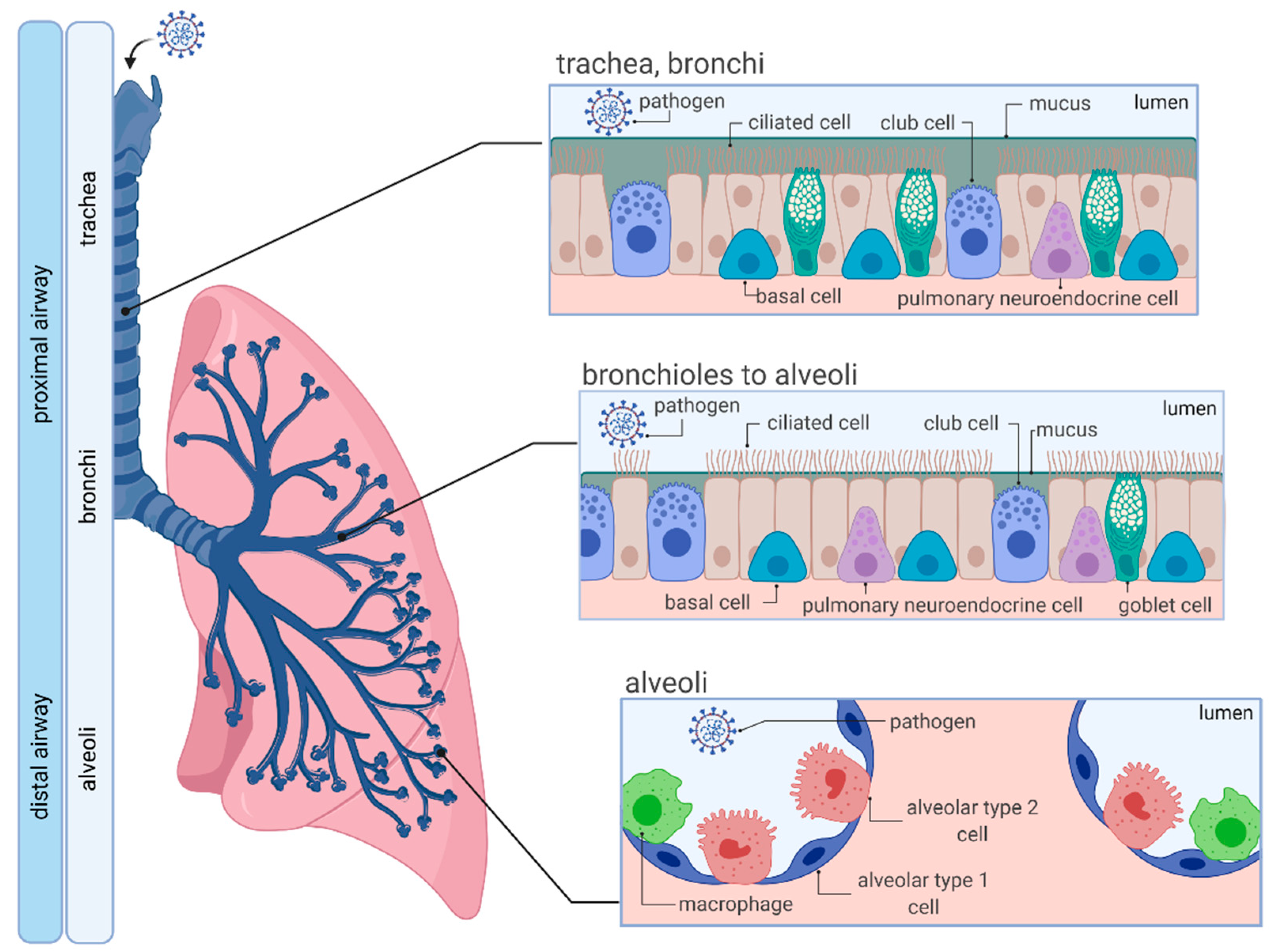
Viruses Free Full Text In Vitro Lung Models And Their Application To Study Sars Cov 2 Pathogenesis And Disease Html
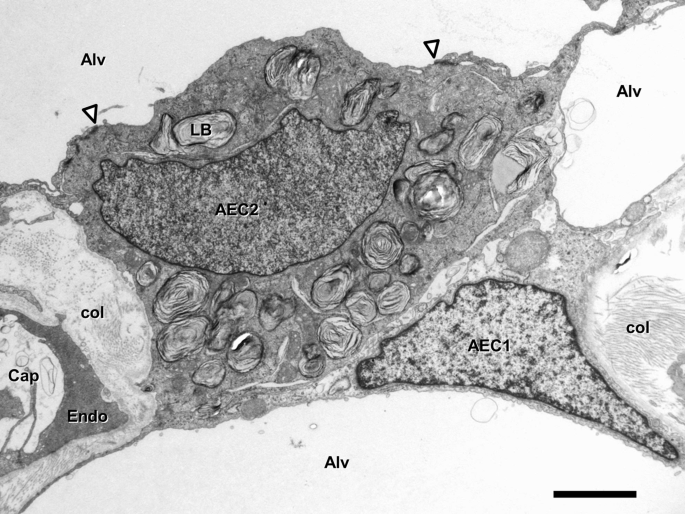
The Micromechanics Of Lung Alveoli Structure And Function Of Surfactant And Tissue Components Springerlink

31 Appropriately Label All Structures Provided With Leader Lines On The Diagrams Below Labels For You









:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/alveolar-sac/j761cjMMZrj6LkMNQf1srw_Alveolar_sac.png)



0 Response to "38 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium"
Post a Comment