40 bn molecular orbital diagram
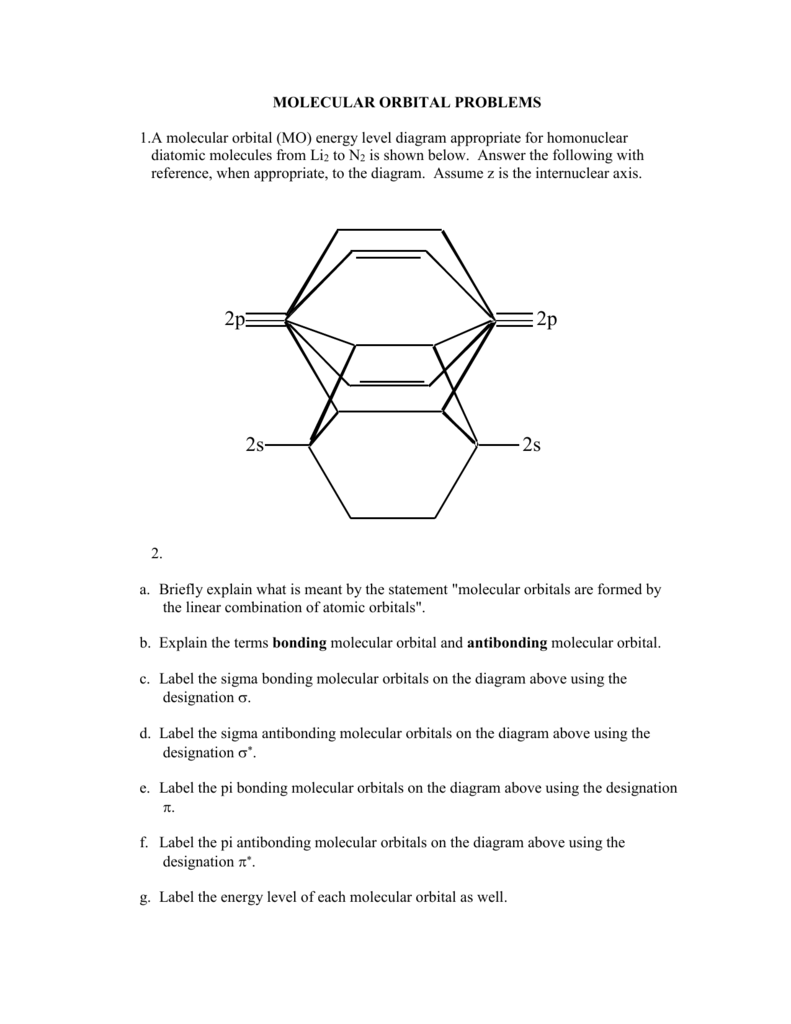
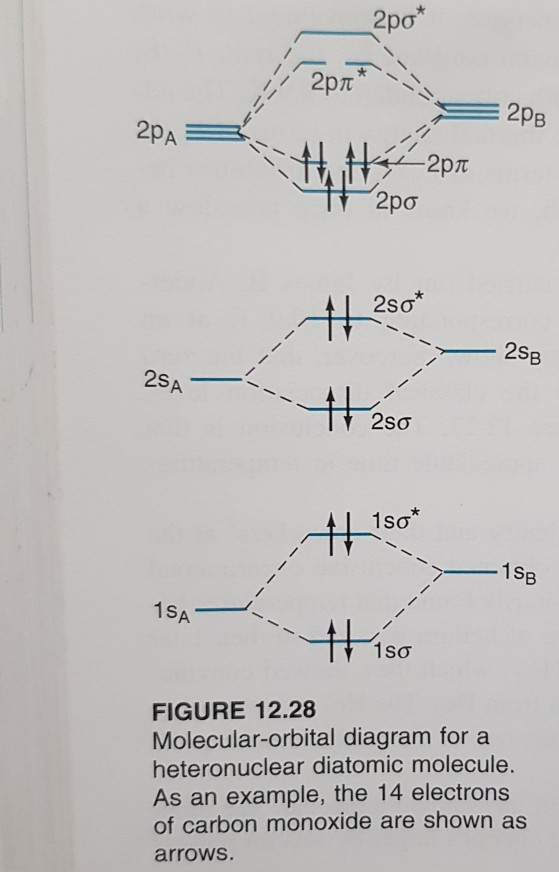
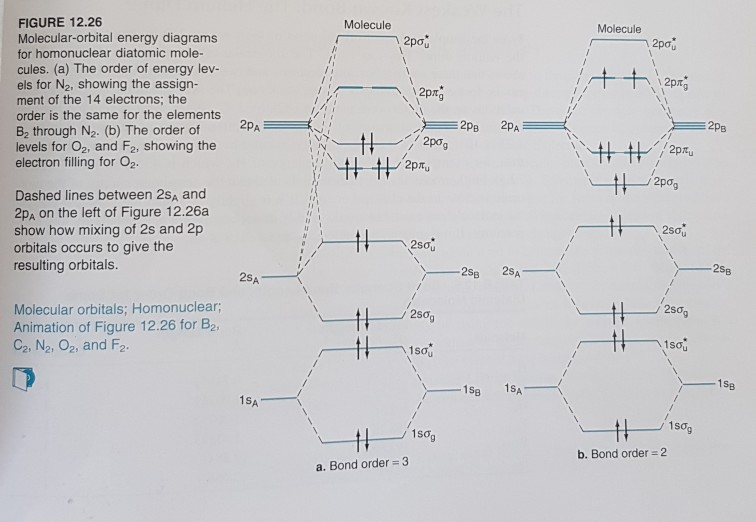
Construct a molecular orbital description of the bonding in this species. 13. Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine the number of unpaired electrons in (a) O 2 -, (b) O 2 +, (c) BN, and (d) NO -. Also give the bond order for each species in the question. 14. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Understanding the influence of adsorption sites to the electronic properties of adsorbed molecules on two-dimensional (2D) ultrathin insulator is of essential importance for future organic-inorganic hybrid nanodevices. Here, the adsorption and electronic states of manganese phthalocyanine (MnPc) on a single layer of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) have been comprehensively studied by low ...

Bn molecular orbital diagram
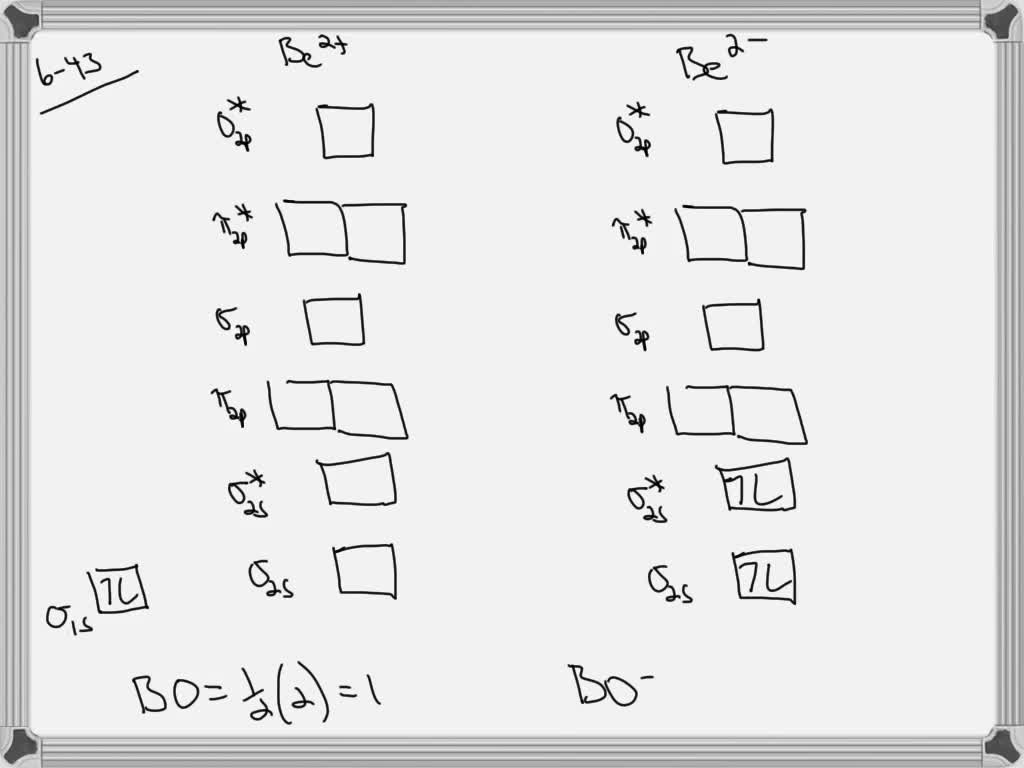
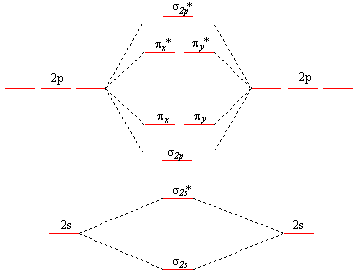
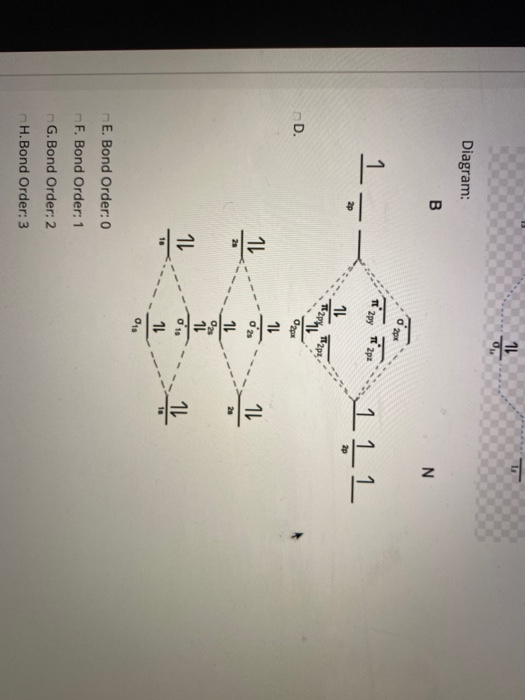
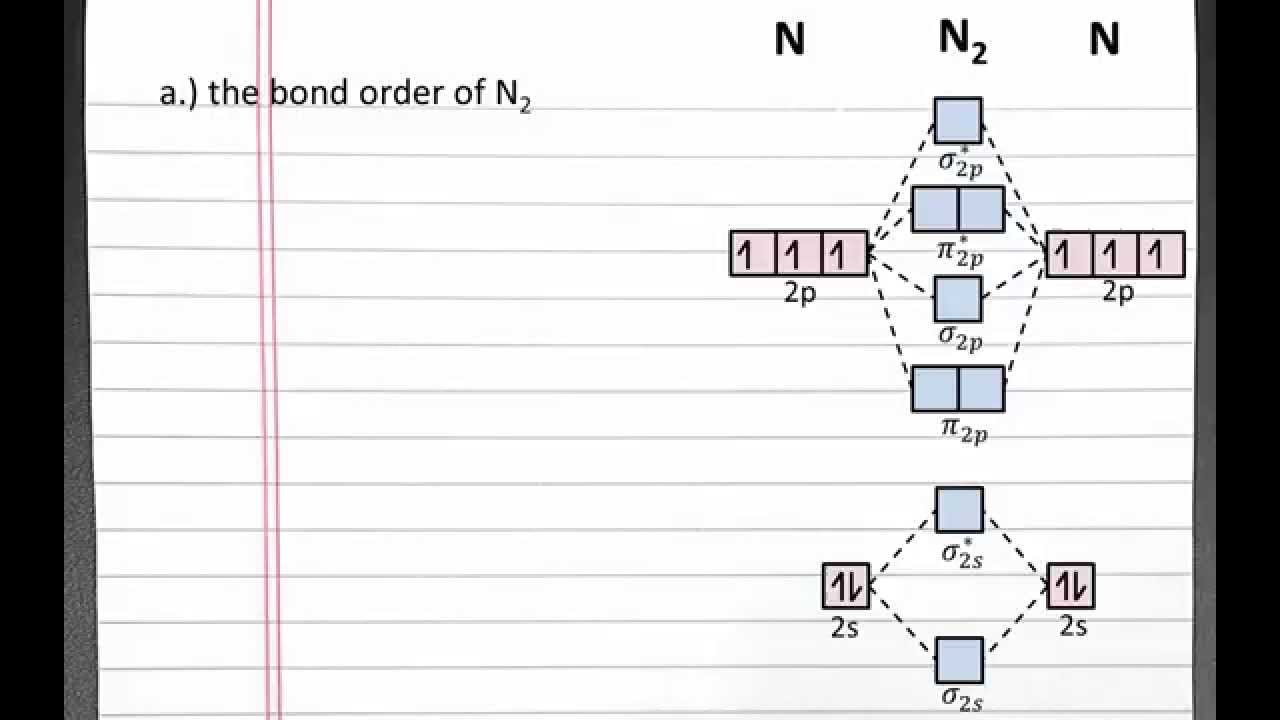
Answer. This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN. Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. The molecular orbital diagram for ClO - is given below: The basis orbitals for Cl are 3s and 3p and for O are 2s and 2p. Z* for O 2s and 2p orbitals are similar so the AOs start at nearly the same energy. For the Cl 3s and 3p orbitals the two Z* values are quite different so the initial energies are more separated. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Bn molecular orbital diagram. Oct 26, 2016 · Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Each time you get a combination of two atomic orbitals you get a bonding molecular orbital and an anti-bonding molecular orbital (from constructive and destructive interference respectively). Take Be 2 as an example: Spoiler: Show. each pair of mixing s-orbitals give rise to 1 bonding (lower energy) and 1 antibonding (higher energy)sigma MO. Answer: I think you can safely assume to start off with the molecular orbital diagram of the Nitrite anion (NO₂¯) and then remove an electron from it: What will be the molecular orbital diagram for nitrite ion? The outcome, i.e. the molecular orbital diagram for Nitrogen dioxide NO₂, should loo... Write the molecular orbital configuration of the diatomic molecule BN. What is the bond order of BN? Is the substance diamagnetic or paramagnetic? Use the order of energies that was given for homonuclear diatomic molecules.
Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Therefore the b electron configuration will be 1s22s22p1. Lower energy subshells fill before higher energy subshells. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. In this example problem, we show how to fill a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule and use molecular bond theory to compare bond order, bond st... Molecular orbitals are different from the atomic orbitals. Complete answer: - In the question it is given to draw the molecular orbital diagram for BN molecules.-We should know the atomic number of the atoms involved in the bonding to draw the orbital diagram. - The atomic number of Boron is 5 means the number of electrons in boron are 5.
¤ Molecular Orbital diagram of COhttps://youtu.be/8mufOTgvagU¤Molecular Orbital diagram of NO , NO+, NO-https://youtu.be/gKxzUfEJyNA¤ S-P mixing OF ORBITALS ... Core orbitals are omitted. Marks 8 Using arrows to indicate electrons with their appropriate spin, indicate on the above diagram the ground state occupancy of the atomic orbitals of O and H, and of the molecular orbitals of OH. In the provided boxes on the above diagram, label the molecular orbitals as n, σ, σ∗, π, π∗, etc. The molecular orbital electron configuration given below is for what neutral homonuclear diatomic molecule? CH क Пар N b.N c. C, d. BN 2 e. B, 11. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Bs. The number of electrons in the #p, molecular orbital is a1 1.2 03 d. 4 e zero 12. Draw the molecular orbital dingram for C. The number of electrons in ... Construct Molecular Orbital Diagram and determine unpaired electrons in O2- , O2+ , BN , NO- Determining Unpaired electrons The number of unpaired electrons can have consequences on the behavior ...
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. In contrast to VSEPR and valence bond theory which describe bonding in terms of atomic orbitals, molecular orbital theory visualizes bonding in relation to molecular orbitals, which are orbitals that surround the entire molecule. The purpose of MO theory is to fill in the gap for some behavior that ...
Molecular orbitals in Carbon ... 10.5: Molecular Orbital Theory ... Molecular Orbital Theory by ... MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM Reviewed by Umasa on 14:33 Rating: 5. Share This: Facebook Twitter Google+ Pinterest Linkedin. Hiç yorum yok:
This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p . You have now 2 electrons left, and two orbitals ...
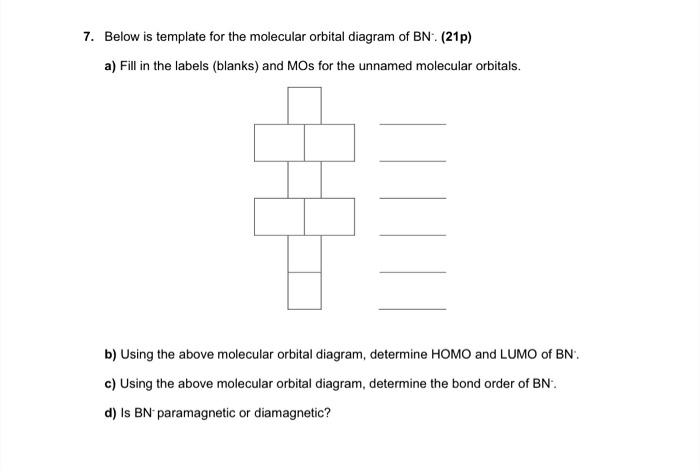
(a) Consider the gaseous molecule {eq}BN^- {/eq}. Construct the molecular orbital diagram that is consistent with the known order of filling of molecular orbitals in the second period and with {eq ...
Solved I Draw Molecular Orbital Of Bn Ii What Condition Will Sp Mixing Occur For Heteroatoms Can You List Some Examples Thanks
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. (b) (8 pts) Show the molecular orbital diagram for BN (boron nitride), calculate its bond order and compare its stability to BC (boron carbide) - which is paramagnetic? Which is diamagnetic? 02 75 Thy 1 x 2p 2p 2p 2p 027 27 TIX Tty Tly 023* 28 2s 2s 2s O 1s 1s Os Os.
Answer (1 of 5): Boron nitride has several solid state structures. The most stable is hexagonal and resembles graphite with B and N in alternating positions. Less stable is cubic spalerite structure) that resembles diamond. Another is wurtzite structure. The bonding between B and N is covalent. F...
1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule B. 2. For full credit on MO diagrams, • label increasing energy with an arrow next to the diagram. • pay attention to whether the question asks for valence electrons or all electrons.

Which Of The Following Statements About The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H 2 Is False A There Is A Non Zero Bond Order B There Is One Filled Bonding Orbital C Two Atomic
(a) Consider the gaseous molecule BN-. At home, construct the molecular orbital diagram that is consistent with the known order of filling of molecular orbitals in the second period and with BN- being stable and paramagnetic. What is the bond order of BN-? (c) What ion of BN is isoelectronic with N2? (d) Do you expect your answer to part c to be less stable, more stable, or equally stable as ...
Property Name Property Value Reference; Molecular Weight: 24.82: Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count: 0: Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
Nov 20, 2014 · ActiveOldestVotes. 5. $\begingroup$. This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN. Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy.
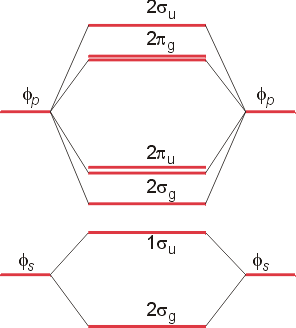
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
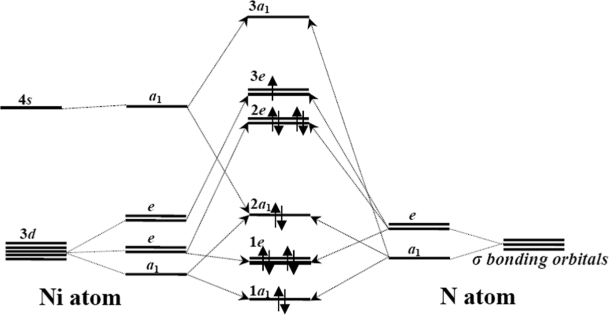
Atomic Orbital Diagram; Carbon Orbital Diagram; MO Theory; HE2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; S2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; MO Diagram of No; O2 MO Diagram; H2O MO Diagram; Cl2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; For Ph5; NH3 MO Diagram; BN Molecular Orbital Diagram; HF MO Diagram; For BH3; MO Diagram for Carbon; For Li2; SP3 Orbital Diagram; For Carbon ...
Which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part B 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Drag the formulas to the appropriate magnetic bin . chemistry. What two conditions necessary for molecules to be polar? Her's my answer pls check.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
The molecular orbital diagram for ClO - is given below: The basis orbitals for Cl are 3s and 3p and for O are 2s and 2p. Z* for O 2s and 2p orbitals are similar so the AOs start at nearly the same energy. For the Cl 3s and 3p orbitals the two Z* values are quite different so the initial energies are more separated.
Answer. This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN. Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy.

Coproduction Of Styrene And Benzaldehyde Over A Boron Nitride Supported Monomeric Moox Catalyst Sciencedirect

Oneclass Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram And Determine The Bond Order And The Number Of Unpaired Elec
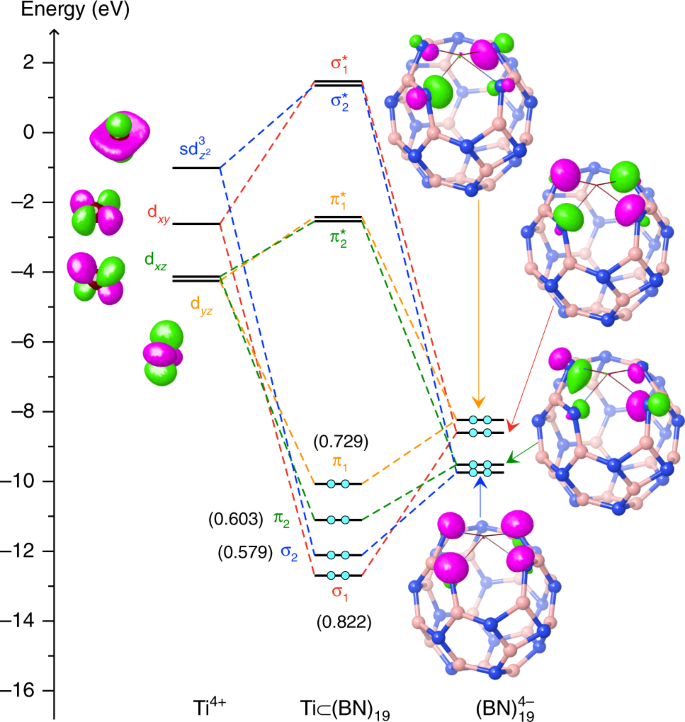
Modification Of Boron Nitride Nanocages By Titanium Doping Results Unexpectedly In Exohedral Complexes Nature Communications















0 Response to "40 bn molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment