41 bowen's reaction series diagram
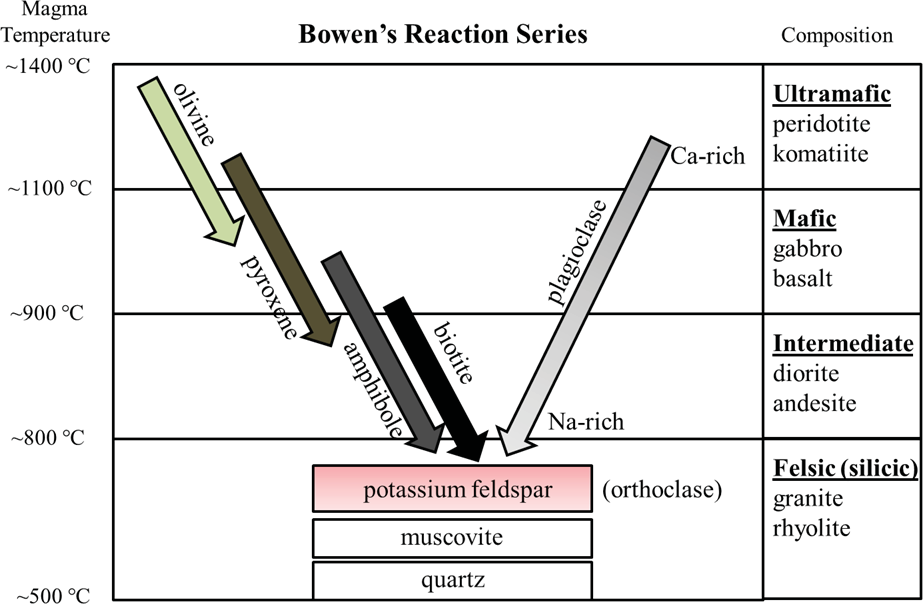
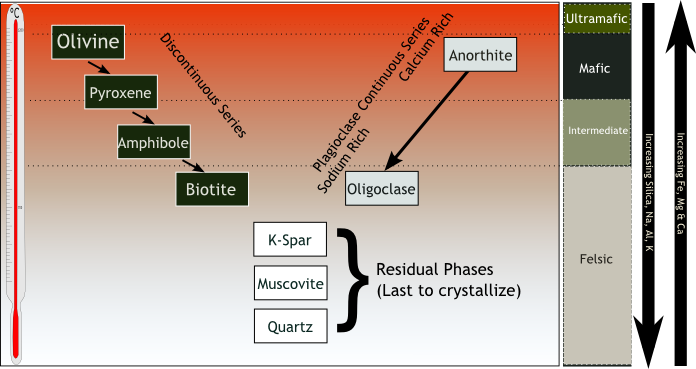
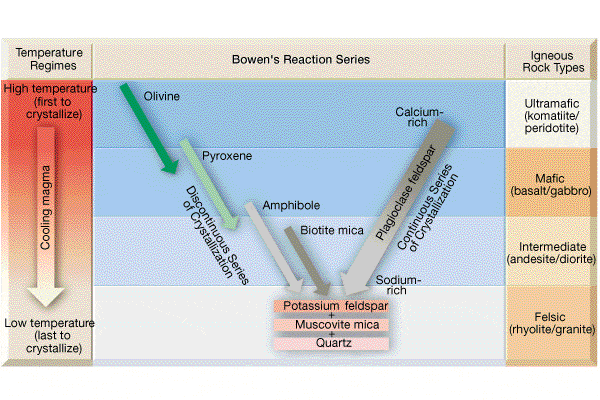
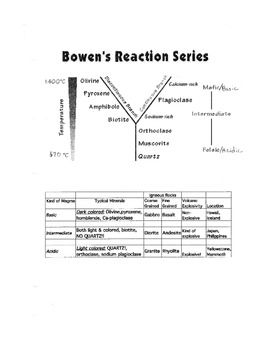
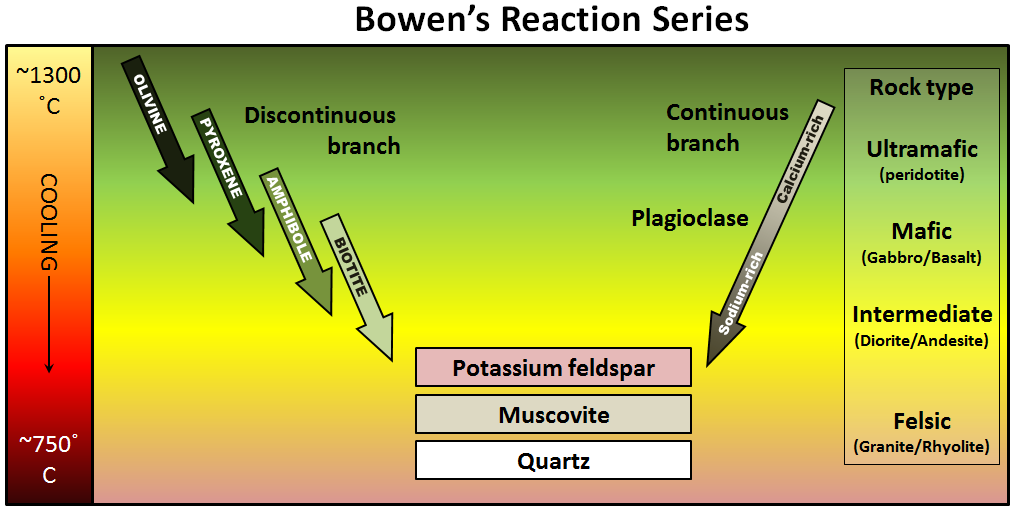
Minerals in the Earth's Crust. There are more than 3000 known minerals (the number is still growing), but of these only about 20 are very common, and only 9 of these constitute 95% of the crust.These 9 minerals are all silicates, and are also called the rock forming minerals.They can be subdivided into two groups, the mafic and felsic minerals according to the principal rocks types they mainly ... Figure 5: Bowen's reaction series showing the sequence of minerals that would be formed and removed during fractional crystallization of a melt.
Continuous reaction series. As temperature falls, calcic plagioclase feldspar reacts continuously with the magma to become increasingly sodium-rich. Mafic rock. Composed of calcic plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene and olivine, this is the rock produced by the crystallization of a basaltic magma if no crystals are removed from the melt.
Bowen's reaction series diagram
Look at the diagram of Bowen's Reaction Series on the next page. The Discontinuous Reaction Series The left-hand side of Bowen's Reaction series. These are a group of mafic or iron- magnesium bearing minerals - olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. If the chemistry of the melt is correct, these minerals react discontinuously to form the ... Bowen's Reaction Series Norman L. Bowen, an experimental petrologist in the early 1900s, realized this from his determinations of simple 2- and 3-component phase diagrams, and proposed that if an initial basaltic magma had crystals removed before they could react with the liquid, that the common suite of rocks from basalt to rhyolite could be produced. This is summarized as Bowen's Reaction ... 4.2 Bowen’s Reaction Series. Bowen’s Reaction Series. Minerals that crystallize at higher temperatures are at the top (olivine) and minerals that crystallize at lower temperatures are at the bottom (quartz). (Source Colivine, modified from Bowen, 1922) Olivine, the first mineral to crystallize in a melt.
Bowen's reaction series diagram. 3 Bowen’s Reaction Series. 3. Bowen’s Reaction Series. Elizabeth Johnson. Drag each word to the correct location on the Bowen’s Reaction Series diagram. Please note that you can expand this image to fill the screen by clicking on the blue arrows on the right side of the diagram. 5 Aug 2020 — Bowen's Reaction Series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. The low end of the temperature ... Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano.In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and ... What is the charge on Iron (Fe)? +2. When two single chains of Pyroxene bond together, what is formed? Amphibole. What is the order of minerals made during Bowen's reaction series? Olivine --> Pyroxene --> Amphibole --> Biotite. What is forming as Olivine is forming in the magma? Calcium Plagioclase.
Within the field of geology, Bowen's reaction series is the work of the Canadian petrologist Norman L. Bowen, who summarized, based on experiments and observations of natural rocks, the sequence of crystallization of common silicate minerals from typical basaltic magma undergoing fractional crystallization (i.e. crystallization wherein early-formed crystals are removed from the magma by ... Bowen’s reaction series is based on observations and experiments of natural rocks, the crystallization sequence of typical basaltic magma change as they cool. It is a sorting tool according to the temperature at which they crystallize common magmatic silicate minerals. Bowen’s Reaction Series describes temperatures at which different common silicate minerals change from liquid to solid ... Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic.Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. ... reaction series and the continuous reaction series. Look at the diagram of Bowen's Reaction Series on the next page. The Discontinuous Reaction Series The left-hand side of Bowen's Reaction series. These are a group of mafic or iron-magnesium bearing minerals - olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. If the chemistry of
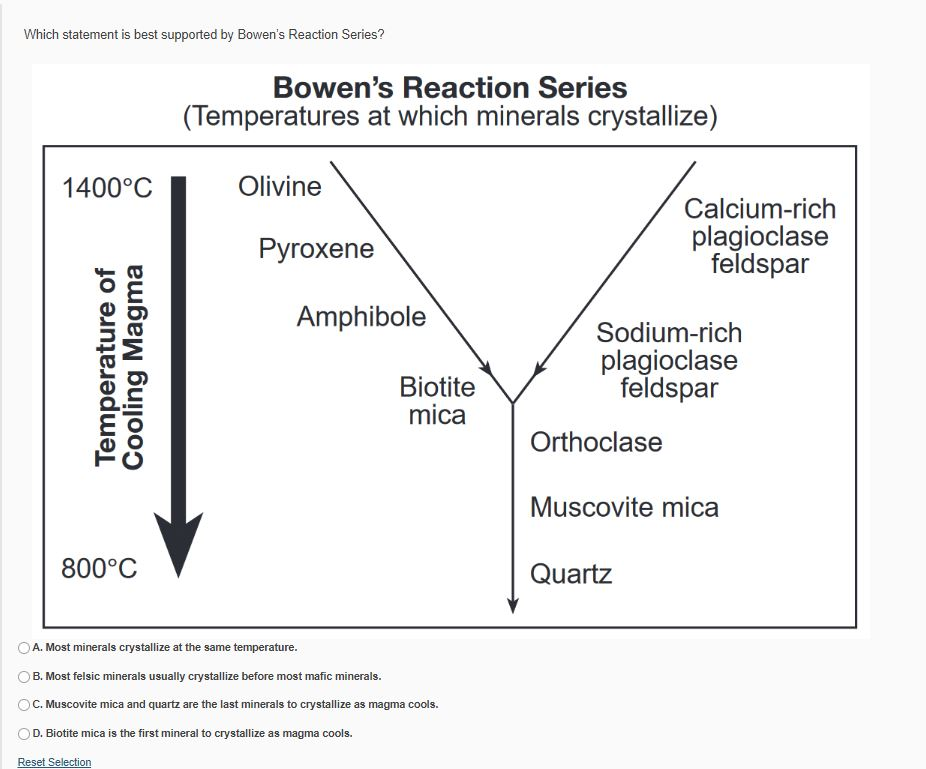
Bowen's reaction series is a means of ranking common igneous silicate minerals ... Minerals on the left part of the "Y" of the diagram are what are called.2 pages Lower Series. As these minerals form, they do NOT react with the remaining melt, they simply cool to become solid. In summary, Bowen’s Reaction Series comprises 3 series: 1. The left side of the diagram shows the Discontinuous Series. Minerals crystallize and change from one mineral to the next in discrete steps as the liquid magma cools. 2. This diagram shows magnetic stripes on either side of the mid-ocean ridge. The number of different ages of stripes represented in this diagram is 6. Correctly complete this sentence using the numbers provided. Volcanoes, ridge, trench, island arc. For the plate boundary labeled with a 3, choose all of the features that occur. Use the legend below for the symbols on the map. volcanoes ... Bowen's Reaction Series describes the temperatures at which different common silicate minerals change from the liquid to solid phase (or from the solid to liquid). The Bowen reaction series is a description of how magma's minerals change as they cool. It’s a means of ranking common igneous silicate minerals by the temperature at which they crystallise.
Bowen S Reaction Series Diagram Who Doesn T Love Bowen S Reaction Series Air American Samoa Bowen S Reaction Series Diagram
Bowen's reaction series can be defined as the crystallization sequence of magma as cooling occurs. It has two parts, the discontinuous series and the continuous series. It has two parts, the ...
Start studying Geology 107: Homework #4. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The Bowen reaction series is a description of how magma 's minerals change as they cool. The petrologist Norman Bowen (1887–1956) carried out decades of melting experiments in the early 1900s in support of his theory of granite. He found that as a basaltic melt slowly cooled, minerals formed crystals in a definite order.
Earth science lab mineral identification sample 3
The remarkable thing that Bowen found concerned the discontinuous branch. At a certain temperature a magma might produce olivine, but if that same magma was ...Missing: diagram | Must include: diagram
Bowen determined that specific minerals form at specific temperatures as a magma cools. At the higher temperatures associated with mafic and intermediate magmas ...
Overview Of Igneous Rocks Introductory Physical Geology Laboratory Manual First Canadian Edition V 3 Jan 2020
4.2 Bowen’s Reaction Series. Bowen’s Reaction Series. Minerals that crystallize at higher temperatures are at the top (olivine) and minerals that crystallize at lower temperatures are at the bottom (quartz). (Source Colivine, modified from Bowen, 1922) Olivine, the first mineral to crystallize in a melt.
Bowen's Reaction Series Norman L. Bowen, an experimental petrologist in the early 1900s, realized this from his determinations of simple 2- and 3-component phase diagrams, and proposed that if an initial basaltic magma had crystals removed before they could react with the liquid, that the common suite of rocks from basalt to rhyolite could be produced. This is summarized as Bowen's Reaction ...
Look at the diagram of Bowen's Reaction Series on the next page. The Discontinuous Reaction Series The left-hand side of Bowen's Reaction series. These are a group of mafic or iron- magnesium bearing minerals - olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. If the chemistry of the melt is correct, these minerals react discontinuously to form the ...





























0 Response to "41 bowen's reaction series diagram"
Post a Comment