42 square planar orbital diagram
C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic orbitals. D) Electrons placed in antibonding orbitals stabilize the ion/molecule. E) All of the above are true. Square-Planar Complexes The crystal field theory can be extended to square-planar ... Electrons are added to a subshell with the same value of the spin quantum number until each orbital in the subshell has at least one electron. ... , or d 3 configurations can therefore be described by the following diagrams. When we try to add a fourth ...
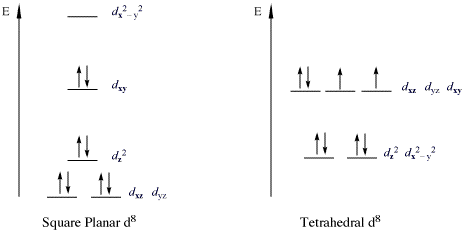
Square planar complexes have a four tiered diagram (i.e. four different sets of orbitals with different energies). If it has a two tiered crystal field splitting diagram then it is tetrahedral. But this assumes you have the crystal field splitting diagram of the complex.
Square planar orbital diagram
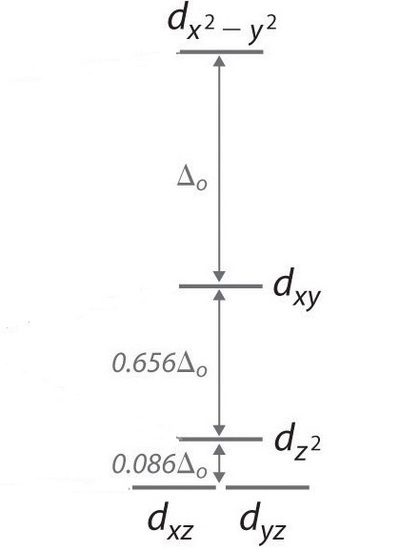
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Consequently, the d x2-y 2 remains unoccupied ... Nov 17, 2021 · In the XeF4 MO diagram, it is quite clear that the structure of the compound is square planar. It has a distance of 1.95 A° between the Xe and F. This is particularly explained by the valence bond theory, as the two non-bonding electrons from 5p are promoted to the 5d orbital. the result is called a square planar shape. The bond angles between equatorial positions is 90°. 1). Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CO3 2 ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ ...
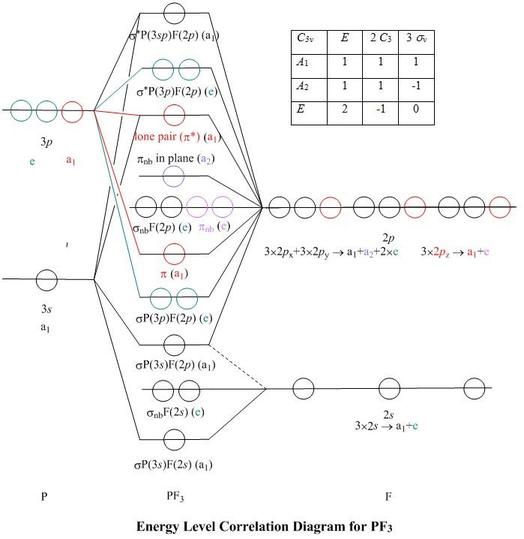
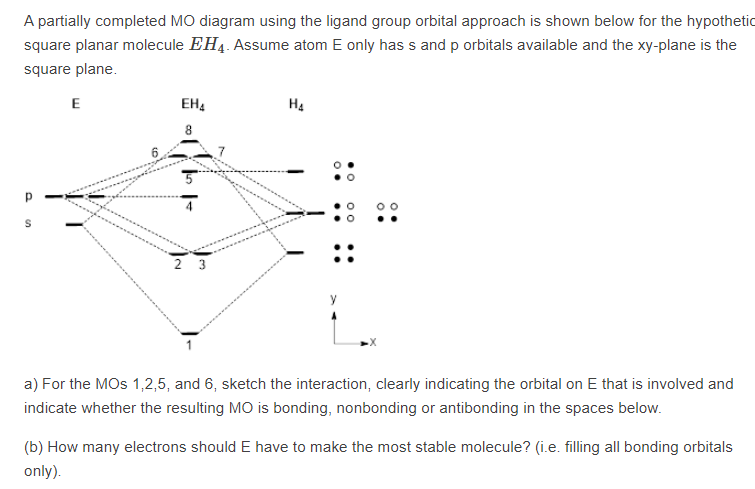
Square planar orbital diagram. This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H(1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C. -35-(b) The P.E.S. results are consistent with the MO scheme. Only the Bn(x) MO is strictly nonbonding, while the F(z) MO is weakly bonding, as indicated by the vibrational fine structureon its P.E.S. band. (c) Rather than two lone pairs in approximately sp3 hybrids, the MO scheme suggests a single region of electron density protruding from the back side of the molecule. Produce the molecular orbital diagram of the hypothetical square-planar CH4 molecule. Then produce the MO diagram for the tetrahedral CH_4 molecule. Make sure you organize MO energies in the tetrahedral version so that it has four C-H bonds. Why exactly is the planar CH_4 molecule unstable relative to the tetrahedral arrangement? The BH 3 molecule is trigonal planar and we will make the C 3 principal axis of symmetry the z axis, with the x and y axes in the plane of the molecule. The y axis (arbitrary) will be along one of the B-H bonds. Molecular Orbital Theory - D3h Character Table D3h E 2C 3 3C 2 σh 2S 3 3σv A1' 1 1 1 1 1 1 A2' 1 1 -1 1 1 -1 E' 2 -1 0 2 -1 ...
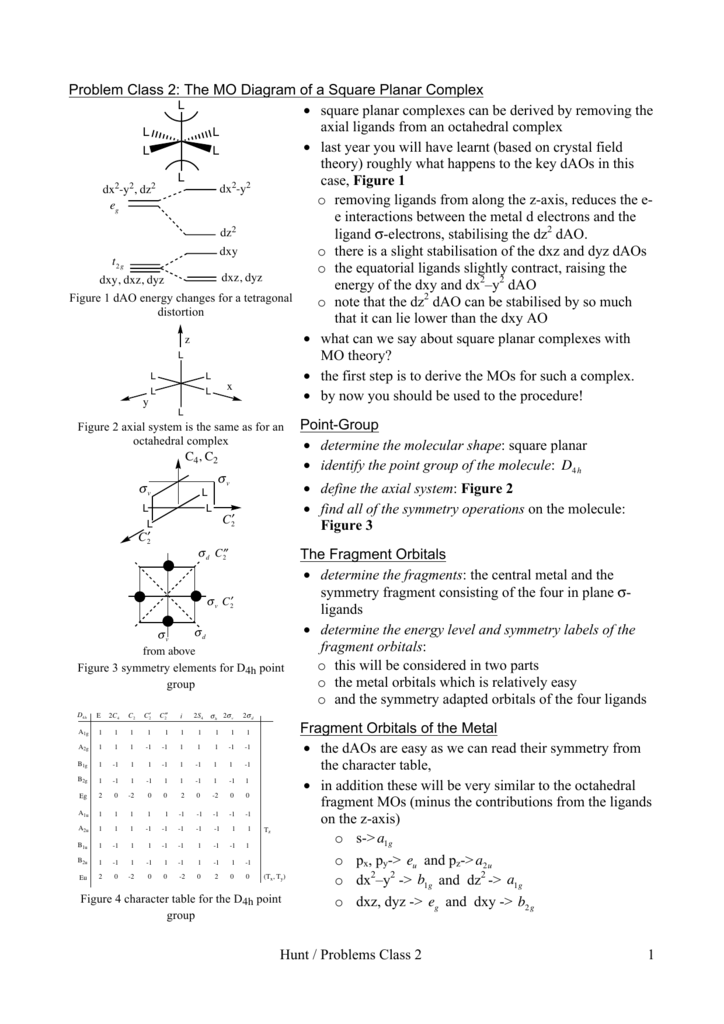
In this video, I have explained the detailed molecular orbital diagram for square planar complexes. Formation of sigma lgo and pi lgo have been discussed in ... Difficult to use other than octahedral, square planar, tetrahedral. Deal with a variety of possible geometries and with a mixture of ligand. →Angular Overlap Model The strength of interaction between individual ligand orbitals and metal d orbitals based on the overlap between them. Use the character table of square planar metal complexes, ML4 (point group D4h) to answer the following questions: (total 25 marks) (a) determine the orbitals symmetries of the central metal atom. (b) draw symmetry labelled molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Given that the four (4) sigma-ligand group orbitals (0-LGOs) symmetries are aig, big, and eu. A good general rule is that if you have either square planar or tetrahedral, a low-spin complex generally forms square planar, and a high-spin complex generally forms tetrahedral. Platinum is not an exception to that statement. To see why, we should consider nickel, which is in the same group, whose complexes are tetrahedral sometimes and square planar other times.
Bond Square planar Tetrahedral ... Orbital patterns: 2 orbitals: 1 bonding, 1 antibonding 3 orbitals 1 bonding, 1 non-bonding, 1 antibonding ... (details depend on relative energies) Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and ... In the square planar structure, 2s and 2p orbitals of the carbon atom does not point in the direction of the 1s orbital of hydrogen. For the square planar structure, the methane molecule should have sp 3 d 2 hybridization. For this, there must be one s-orbital, three p-orbitals, and two d-orbitals. May 10, 2021 · In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is ... A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals.
• MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection.
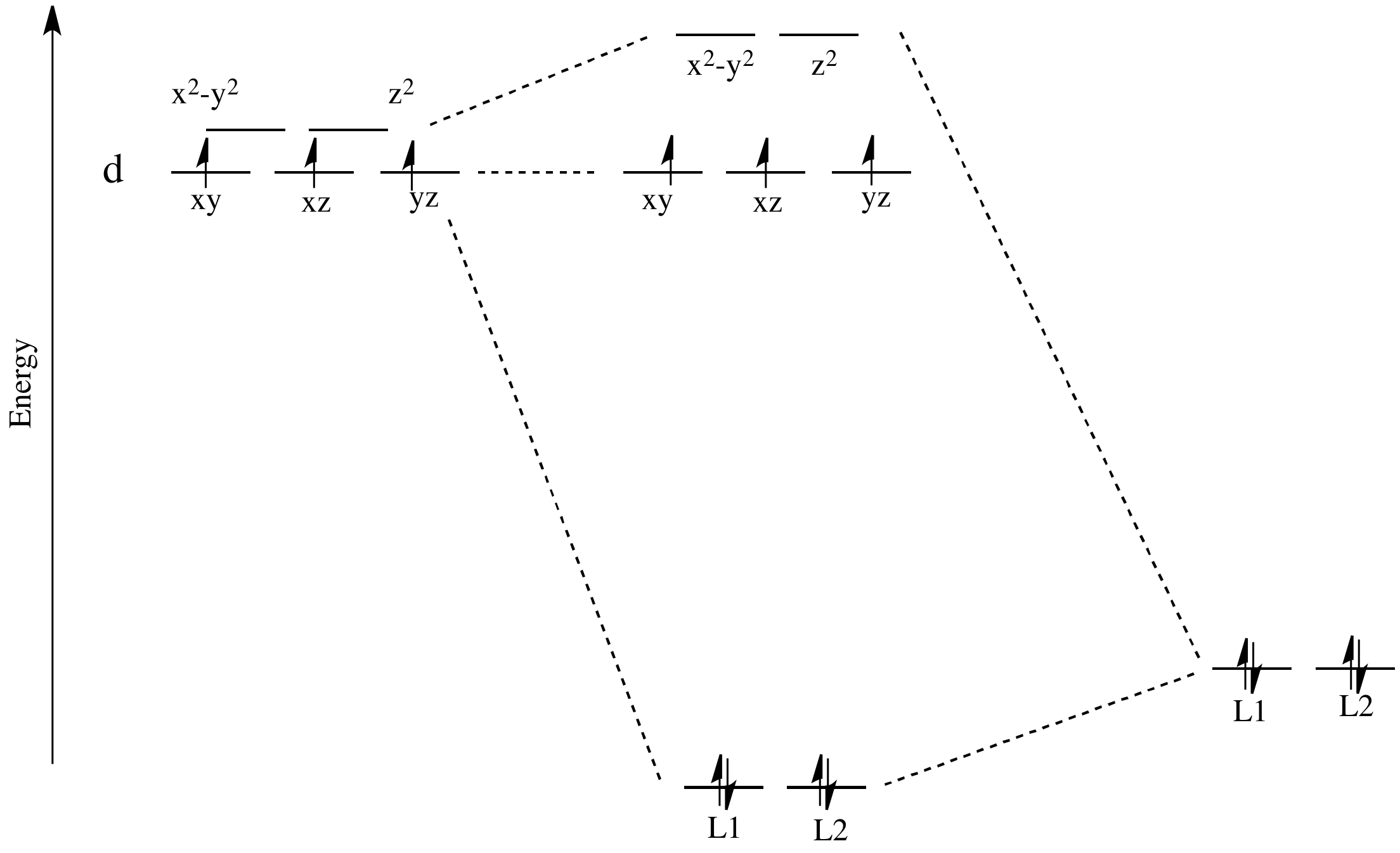
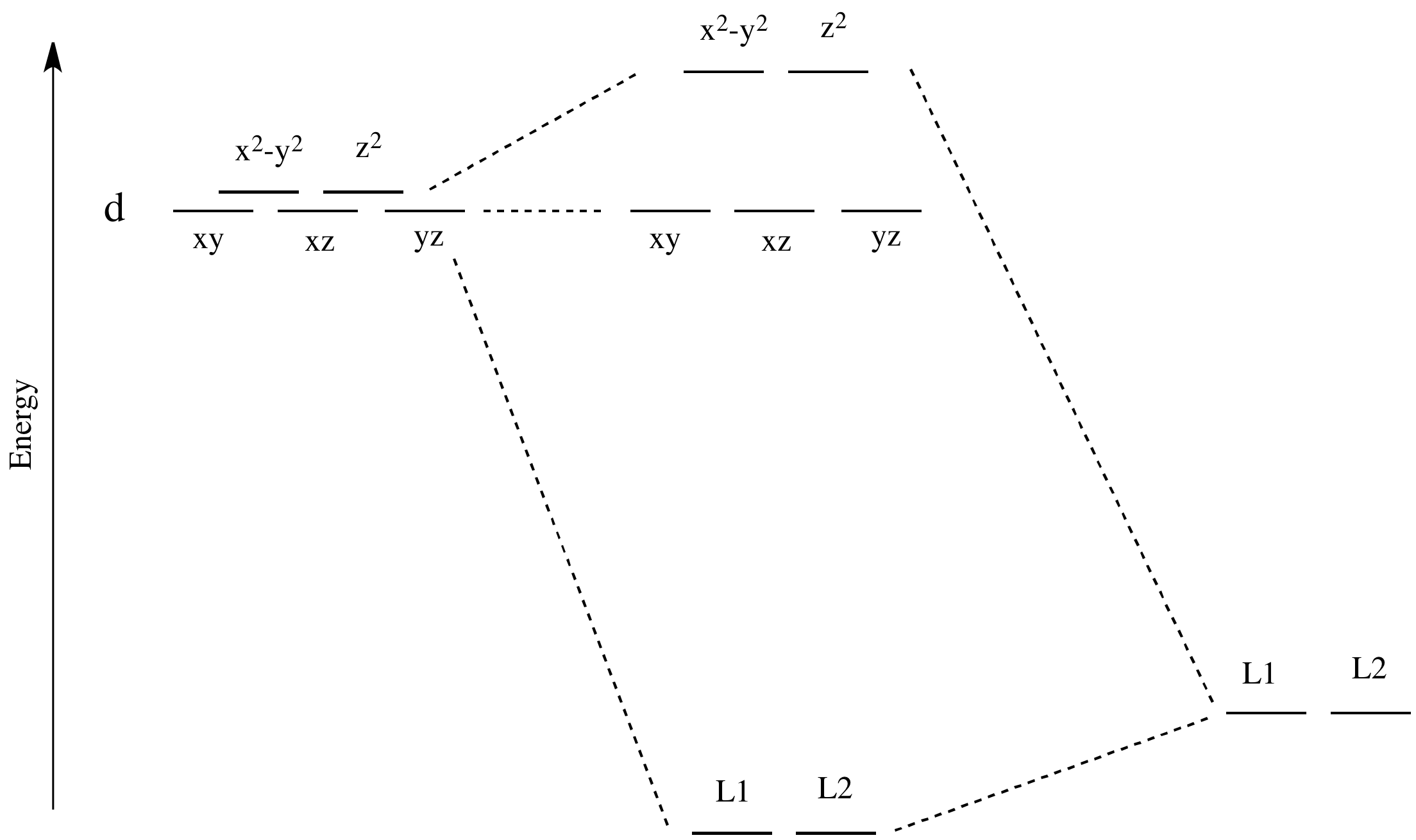
Square Planar Complexes Consider a CFT diagram of a tetragonal elongation taken to its extreme: tetragonal elongation removal of z ligands eg t2g b2g dxydxzdyz eg dz2 dx2-y2 dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 a1g b1g b2g eg dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 a1g b1g ∆1,sp Octahedral Square Planar Δ> Π
Solved Generate The Mo Diagram For Ch4 As Square Planar And Ch4 As Tetrahedral Why Does Ch4 Not Exist As A Swaure Planar But It Does As A Tetrahed Course Hero
Square Planar D Orbital Splitting Diagram. Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model that describes the breaking of degeneracies of electron In a tetrahedral crystal field splitting, the d-orbitals again split into two groups, with an energy difference of Δtet. The lower energy Square planar and other complex geometries can also be described by CFT.
A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti-bonding. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . ... (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4(Td), CH4(D4h) and Cyclopropane using ...
The orbital splitting diagram for square planar coordination can thus be derived from the octahedral diagram. As ligands move away along the z-axis, d-orbitals with a z-component will fall in energy. The d z2 orbital falls the most, as its electrons are concentrated in lobes along the z-axis.
The extreme case of a tetragonal distortion is to form a true square planar complex in which the ligands along the z-axis are completely removed. In this case, the d z 2 orbital drops even lower in energy, and the molecule has the following orbital splitting diagram.
Solved Q Use Group Theory To Construct A Qualitative Mo Molecular Orbital Diagram For Ah4 Square Planar D4h Orbital Energy S P D A 17 1 Course Hero
D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. What we gain in the bonding sigma MO, we lose in the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. There is no advantage for two helium atoms to join together in a molecule, and so they remain as isolated atoms (note
As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. Here is an energy level diagram showing ...
The molecule $\ce{[PdCl4]^2-}$ is diamagnetic, which indicates a square planar geometry as all eight d electrons are paired in the lower-energy orbitals. However, $\ce{[NiCl4]^2-}$ is also $\mathrm{d^8}$ but has two unpaired electrons, indicating a tetrahedral geometry. Why is $\ce{[PdCl4]^2-}$ square planar if $\ce{Cl}$ is not a strong-field ...
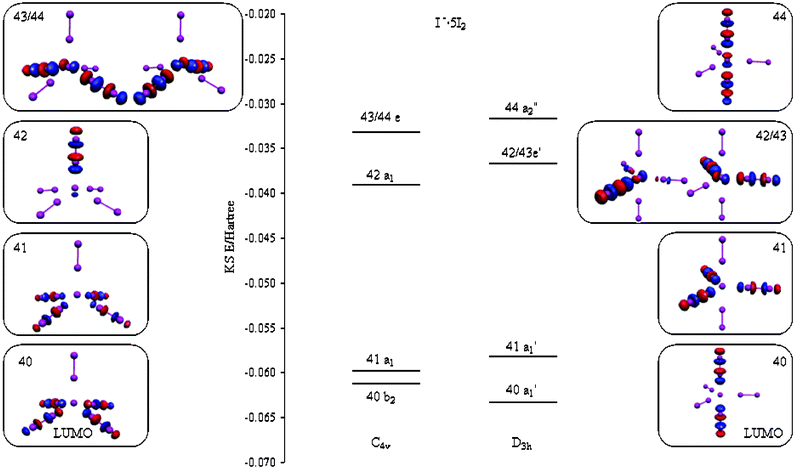
Square Pyramidal Bonding Of I 2 Molecules At The I Nodes Of A Polyiodide Infinite Pseudo Cubic 3d Network Crystengcomm Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 B415415k
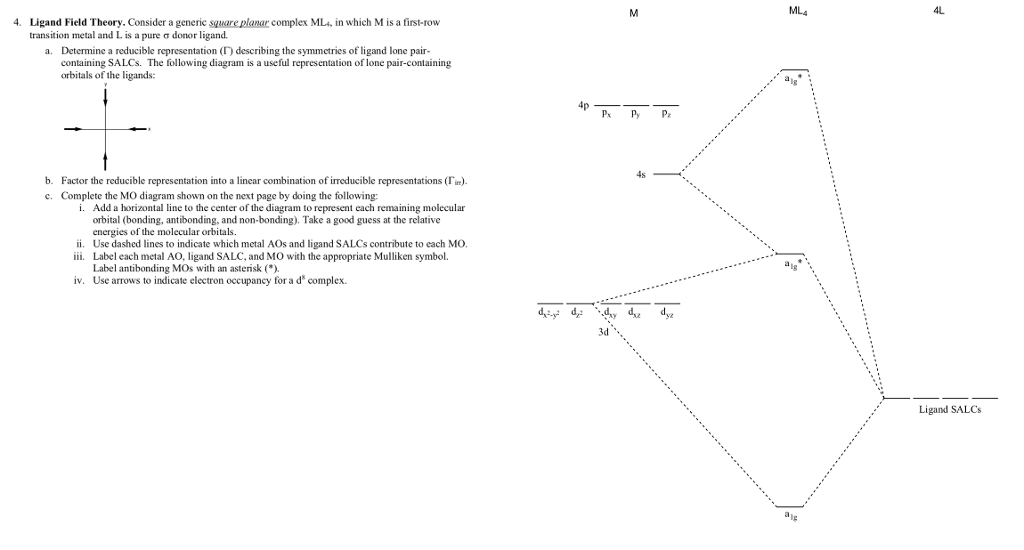
Question 2. a. π-bonding perpendicular to the plane. Point Group = D 4h. The vectors lie along a C 2 rotation axis, there the p orbitals can be separated into one set of four perpendicular to the plane and one set of four parallel to the plane.. Recall that d block elements use ns, np and (n-1)d orbitals for bonding, and that (n-1)d orbitals are lower in energy than ns and np orbitals.
Here, a square planar crystal field is obtained by replacing the cyanide ligands with negative point charges. Under the influence of this field, the d orbitals of the metal ion are split into four different energy levels. Here, the d x 2 − y 2 orbital is the
The next step is to start drawing an orbital diagram. The five d-orbitals should initially be on one level corresponding to the ionisation energy of nickel(II). The virtual 4s and 4p orbitals somewhat higher. The π-type ligand group orbital should be on a level corresponding to the ionisation energy of ammonia, the σ-type ones slightly below.

In Crystal Field Theory Why Do All The Metal Electrons Enter The D Orbitals And Not The S Orbital Chemistry Stack Exchange
Square planar low-spin: no unpaired electrons, diamagnetic, substitutionally inert. Includes Ni 2+. Example: [Ni(CN) 4] 2−. Ionic radii. The spin state of the complex affects an atom's ionic radius. For a given d-electron count, high-spin complexes are larger. d 4. Octahedral high spin: Cr 2+, 64.5 pm.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar Complexes The crystal field theory fails to explain many physical properties of the transition metal complexes because it does not consider the interaction between the metal and ligand orbitals. The molecular orbital theory
the result is called a square planar shape. The bond angles between equatorial positions is 90°. 1). Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CO3 2 ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ ...
Nov 17, 2021 · In the XeF4 MO diagram, it is quite clear that the structure of the compound is square planar. It has a distance of 1.95 A° between the Xe and F. This is particularly explained by the valence bond theory, as the two non-bonding electrons from 5p are promoted to the 5d orbital.
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Consequently, the d x2-y 2 remains unoccupied ...
















0 Response to "42 square planar orbital diagram"
Post a Comment