37 bayes theorem tree diagram
Bayesian classification is based on Bayes' Theorem. Bayesian classifiers are the statistical classifiers. Bayesian classifiers can predict class membership probabilities such as the probability that a given tuple belongs to a particular class. Baye's Theorem. Bayes' Theorem is named after Thomas Bayes. There are two types of probabilities − Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. Next lesson. Conditional Probability (video lessons, examples and Step 1: Write out the Conditional Probability Formula in terms of the problem Step 2: Substitute in the values and solve. Example: Susan took two tests. ... How to Use Bayes' Theorem to Find ...
The expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment. Expected value is a key concept in economics, finance, and many other subjects. By definition, the expected value of a constant random variable. X = c {\displaystyle X=c} is. c {\displaystyle c} .

Bayes theorem tree diagram
Bayes' theorem; Boole's inequality; Venn diagram; Tree diagram; v; t; e; A diagram representing a two-state Markov process, with the states labelled E and A. Each number represents the probability of the Markov process changing from one state to another state, with the direction indicated by the arrow. For example, if the Markov process is in ... Bayes' theorem; Boole's inequality; Venn diagram; Tree diagram; In probability theory, the sample space (also called sample description space or possibility space) of an experiment or random trial is the set of all possible outcomes or results of that experiment. The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ...
Bayes theorem tree diagram. Learn Probability for Statistics, Data Science, Business decisions and Bayes Theorem for Machine Learning with Exercises 2022 Ultimate Probability A-Z™: for Machine Learning. Get Black Free Day. What you'll learn. Learn probability theory from scratch; You will learn Different types of distributions: Normal, Binomial, Poisson... In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; recently Bayes–Price theorem: 44, 45, 46 and 67 ), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, Bayes' theorem allows ... The concept of conditional probability is primarily related to the Bayes’ theorem Bayes' Theorem The Bayes theorem (also known as the Bayes’ rule) ... Finally, conditional probabilities can be found using a tree diagram. In the tree diagram, the probabilities in each branch are conditional. Sep 02, 2021 · Comparability : Let and be the elements of a poset , then and are said to comparable if either or .Otherwise, and are said to be incomparable. Example – In the poset (where is the set of all positive integers and is the divides relation) are the integers 3 and 9 comparable? Are 7 and 10 comparable? Solution – 3 and 9 are comparable since i.e. 3 divides 9.
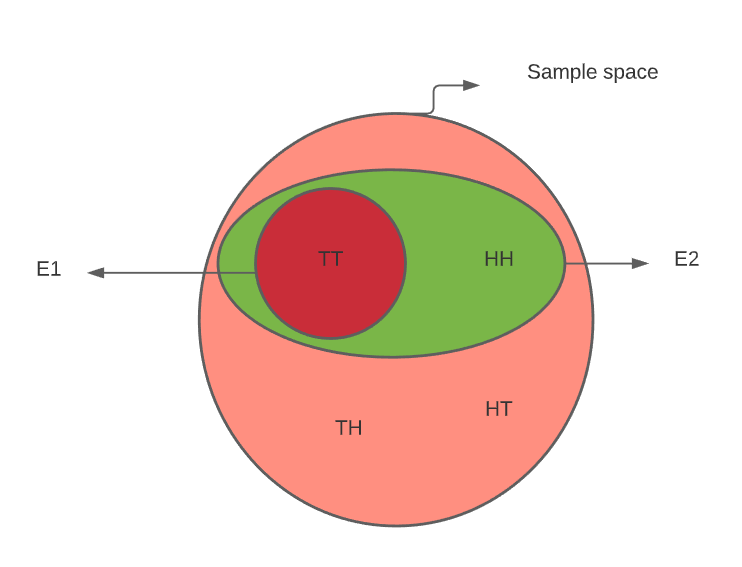
Venn Diagram Statistical Mechanics Thermodynamics Venn Diagram Physics Quantum Mechanics Introduction To Conditional Probability And Bayes Theorem For Data Science Professionals Venn Diagram Examples Venn Diagram Conditional Probability Algebra 3 Venn Diagrams Unions And Intersections Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Examples Venn Diagram Worksheet Probability Calculator With Formulas To Solve In ... Conditional Probability, Independence and Bayes' Theorem Conditional Probability, Independence and Bayes' Theorem. Class 3, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom. 1 Learning Goals. 1. Know the definitions of conditional probability and independence of events. 2. Be able to compute conditional probability directly from the definition. 3. Bayes Theorem Binomial Distribution Poisson Distribution Normal Distribution Skewness and Kurtisos T - Distribution Decision Tree of Probability Who is this course for: Those starting from scratch in probability Current students studying probability Professional in the field of Data Science Professionals in the banking industry In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; recently Bayes-Price theorem: 44, 45, 46 and 67 ), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if the risk of developing health
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one ... Using a tree diagram to work out a conditional probability question. If someone fails a drug test, what is the probability that they actually are taking drugs? ... Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. Practice: Calculate conditional probability. Hasse Diagrams. It is a useful tool, which completely describes the associated partial order. Therefore, it is also called an ordering diagram. It is very easy to convert a directed graph of a relation on a set A to an equivalent Hasse diagram. 38 bayes theorem tree diagram; 40 creating a web diagram is a tool for; 38 kenwood dnx690hd wiring diagram; 37 2005 ford taurus 3.0 serpentine belt diagram; 42 khan academy phase diagram; 41 1994 dodge dakota wiring diagram; 41 how to diagram direct objects; 38 quadrajet electric choke wiring diagram; 41 refer to the diagram. if actual ...
Ppt Discrete Mathematics Bayes Theorem And Expected. Cs 441 discrete mathematics for cs m. hauskrecht cs 441 discrete mathematics for cs lecture 21 milos hauskrecht [email protected] 5329 sennott square probabilities: expected value m. hauskrecht probability basics sample space s: space of all possible outcomes event e: a subset of outcomes probability: a number in [0,1] we can associate with ...
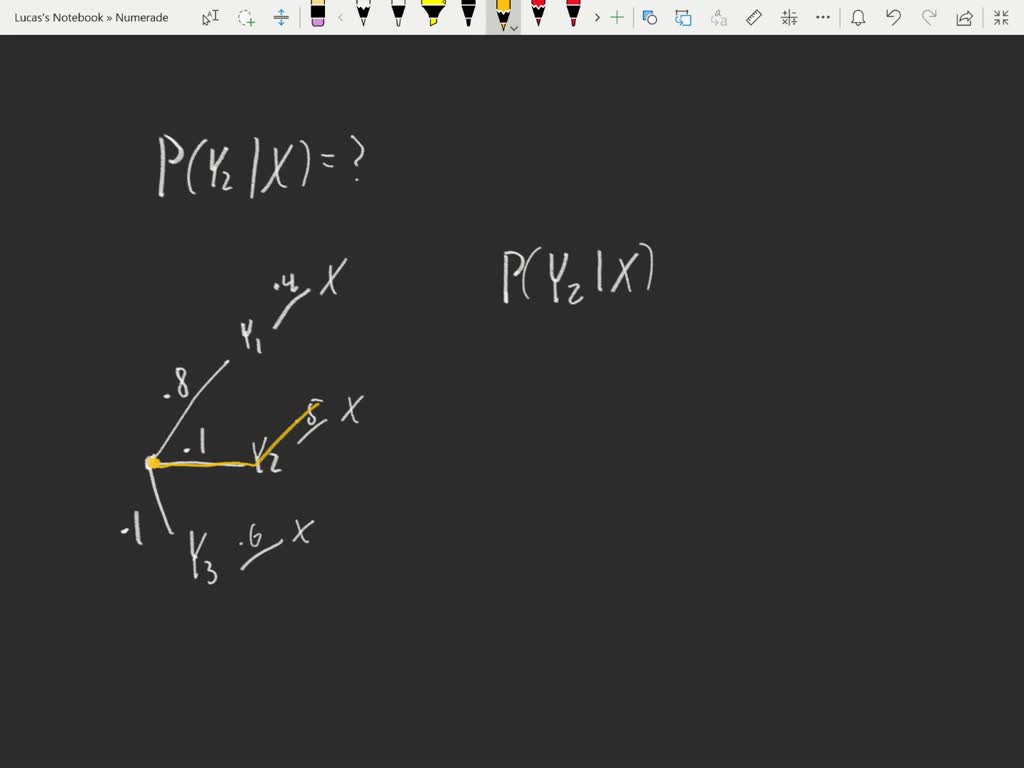
Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. ... Calculate conditional probability. Conditional probability and independence. Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events ...
home • meta search • • meta search •
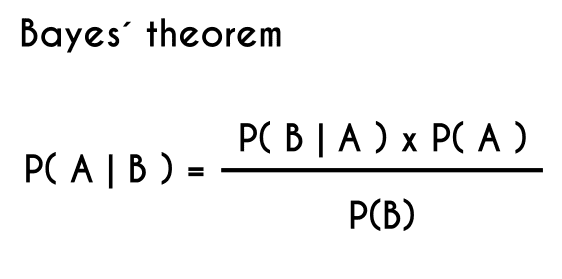
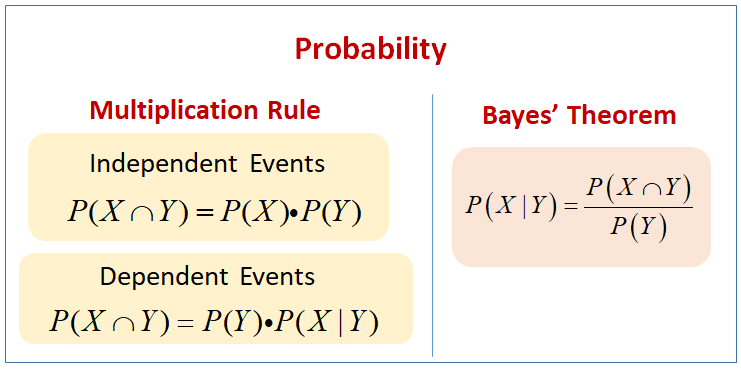
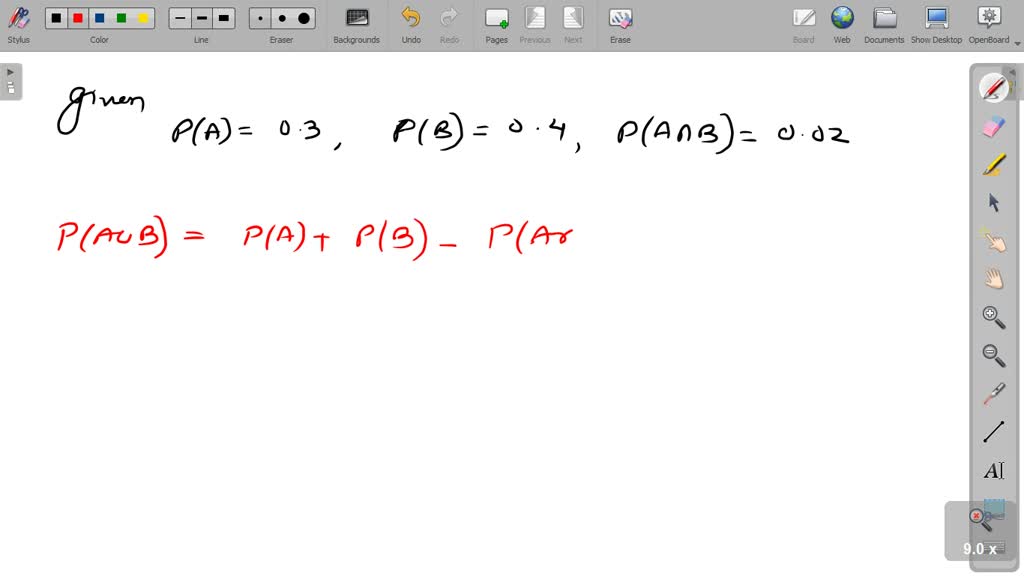
Bayes' Theorem. Bayes' Theorem finds the probability of an event occurring given the probability of another event that has already occurred. Bayes' theorem is stated mathematically as the following equation: where A and B are events and P(B) ≠ 0. Basically, we are trying to find probability of event A, given the event B is true.
35 1.6 The Law of Total Probability and Bayes' Formula 43 1.6.1 Bayes' ... The theorem generalizes to stationary stochastic processes. So anyone who ... A tree diagram is a tool in the fields of general mathematics, probability,
Consider the population consisting of the values 1 3 4. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Grade 11 probability work work 1 Algebra 2 name date Lectures on elementary probability Taking a chance Finding probability using tree diagrams and outcome tables Chapter probability bayes theorem Tree diagrams probability. Tes classic free licence.
My approach:-. 4 cases possible for A and B based on one saying Truths and Lies (TT,TF,FT,FF) Case 1:- Both speaking truth and it is really a queen = 3/5 * 2/3 * 4/52. Case 2 and 3:- One person saying truth and other lie will not be possible as it would lead to an inconsistency because it is given that both agree it to be queen. Case 4:-Both ...
Probability Problems (video lessons, examples and solutions) In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; recently Bayes-Price theorem: 44, 45, 46 and 67 ), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event.
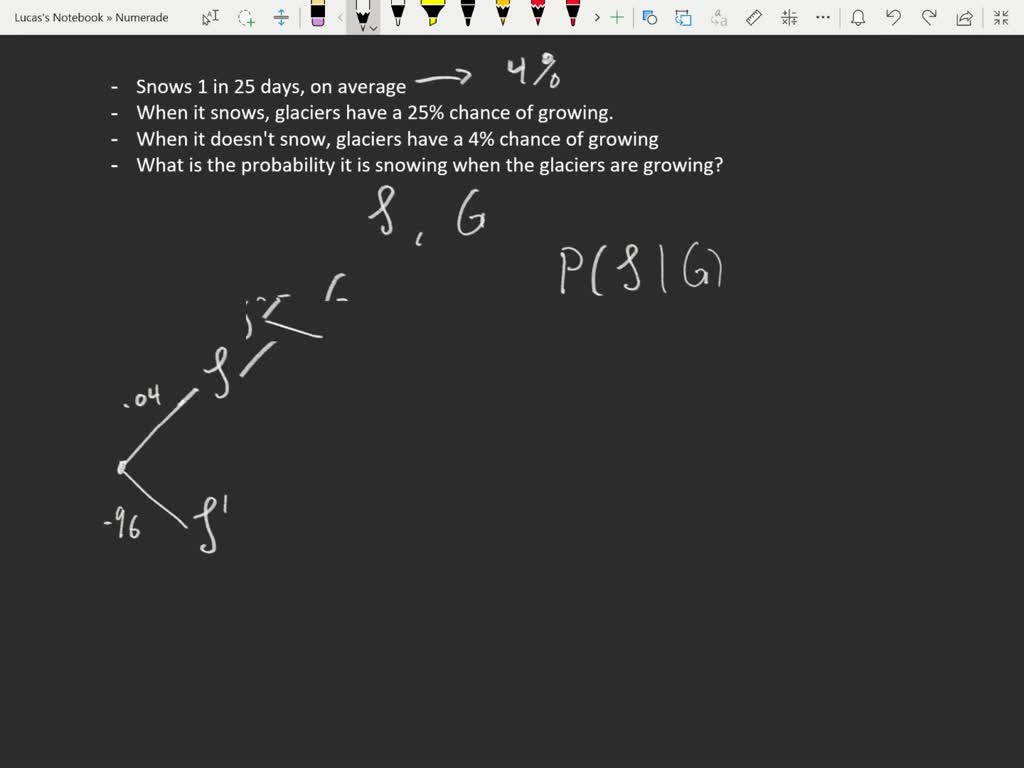
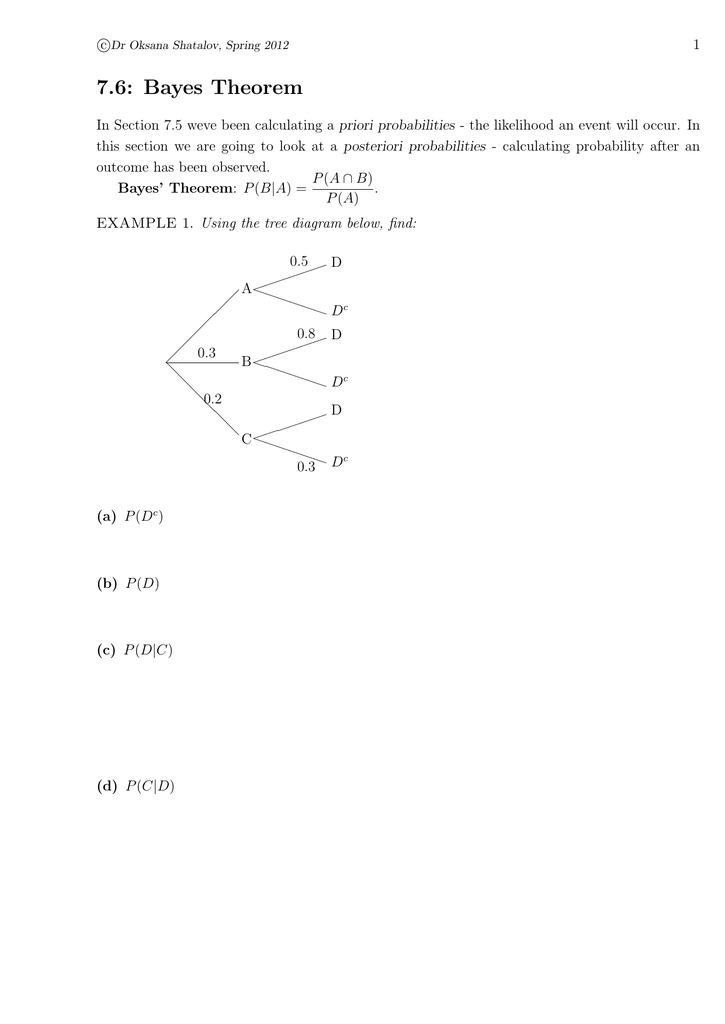
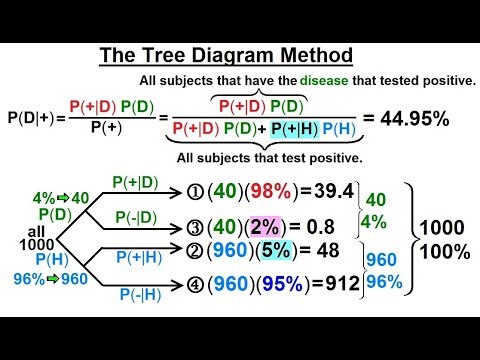
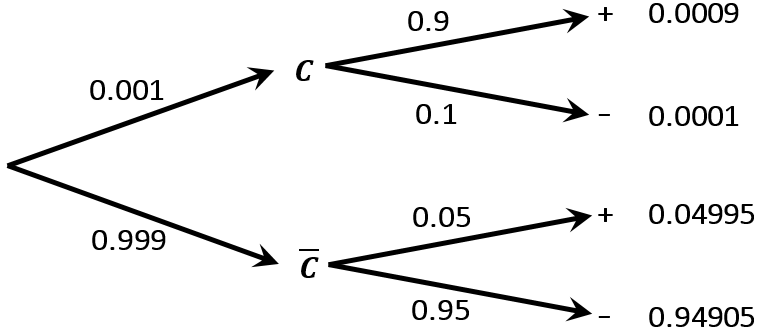
the tree diagram. Please do so when you try to do them, or when you read the solutions {draw the diagram to try to follow what’s happening. 2. solutions Exercise 1. A doctor is called to see a sick child. The doctor has prior information that 90% of sick children in that neighborhood have the u, while the other 10% are sick with 1
Statement. The law of total probability is a theorem that, in its discrete case, states if {: =,,, …} is a finite or countably infinite partition of a sample space (in other words, a set of pairwise disjoint events whose union is the entire sample space) and each event is measurable, then for any event of the same probability space:
Bayes' theorem; Boole's inequality; Venn diagram; Tree diagram; A computer-simulated realization of a Wiener or Brownian motion process on the surface of a sphere. The Wiener process is widely considered the most studied and central stochastic process in probability theory.
6. We can now validate Chebyshev’s theorem that: At least 75% of the data must lie within 2 standard deviations from the mean. The observed proportion for the data within 84.47 +/- (2X27.21) or within 30.05 to 138.89 = sum of relative frequencies within 30.05-138.89 = 1 or 100%.
The Bayes’ theorem is given by . Bayes’ theorem can be derived from the multiplication law . Bayes’ Theorem can also be written in different forms . Bayes' Theorem Formulas The following video gives an intuitive idea of the Bayes' Theorem formulas: we adjust our perspective (the probability set) given new, relevant information.
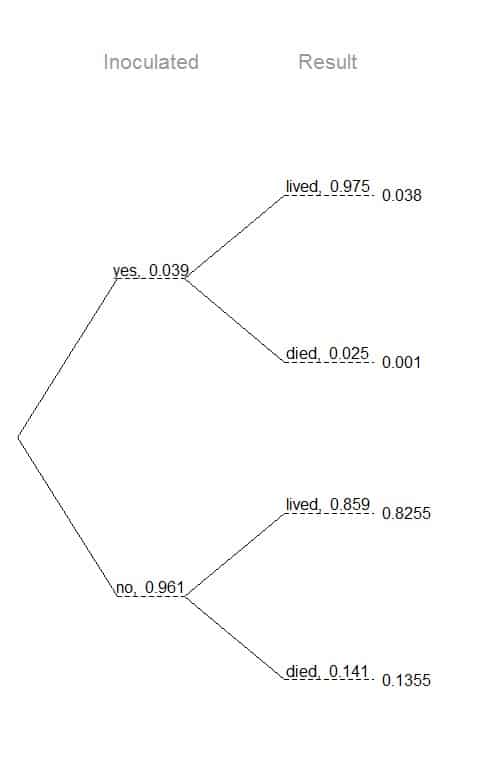
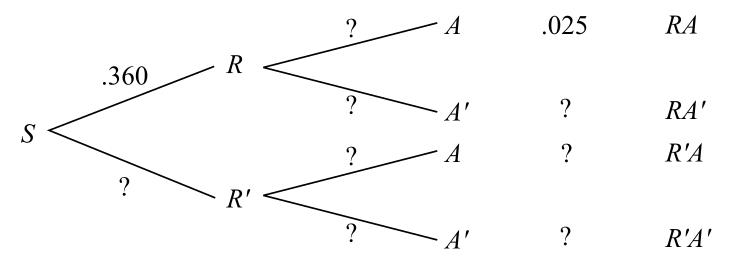
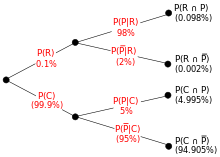
Probability. Elementary Intermediate 1. Introduction to Probability 1.1 Sample space and tree diagram 1.2 Union of sets and Venn diagrams 1.3 Mutually exclusive events 1.4 De Morgan's laws 1.5 Independent and dependent events 1.6 Conditional probability 1.7 Bayes' theorem with tree diagrams 1.8 Bayes theorem extended 2.
probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. Next lesson. Conditional Probability, Independence and Bayes' Theorem Conditional probability: Abstract visualization and coin example Note, A ⊂ B in the right-hand figure, so there are only two colors shown. The formal definition of conditional probability
Tree diagrams for conditional probabilities Tree diagram for conditional probabilities Probability Question Ace Computer store Fault Tree Problem: Calculating probabilities. Probability tree Conditional Probability question Simple Probability - Bayes Theorem and Venn Diagrams Probabilities and conditional probabilities.
The Monty Hall problem is a brain teaser, in the form of a probability puzzle, loosely based on the American television game show Let's Make a Deal and named after its original host, Monty Hall.The problem was originally posed (and solved) in a letter by Steve Selvin to the American Statistician in 1975. It became famous as a question from reader Craig F. Whitaker's letter quoted in Marilyn ...
The implementation of Data Science to any problem requires a set of skills. Machine Learning is an integral part of this skill set.. For doing Data Science, you must know the various Machine Learning algorithms used for solving different types of problems, as a single algorithm cannot be the best for all types of use cases.
The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ...
Bayes' theorem; Boole's inequality; Venn diagram; Tree diagram; In probability theory, the sample space (also called sample description space or possibility space) of an experiment or random trial is the set of all possible outcomes or results of that experiment.
Bayes' theorem; Boole's inequality; Venn diagram; Tree diagram; v; t; e; A diagram representing a two-state Markov process, with the states labelled E and A. Each number represents the probability of the Markov process changing from one state to another state, with the direction indicated by the arrow. For example, if the Markov process is in ...








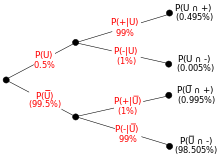






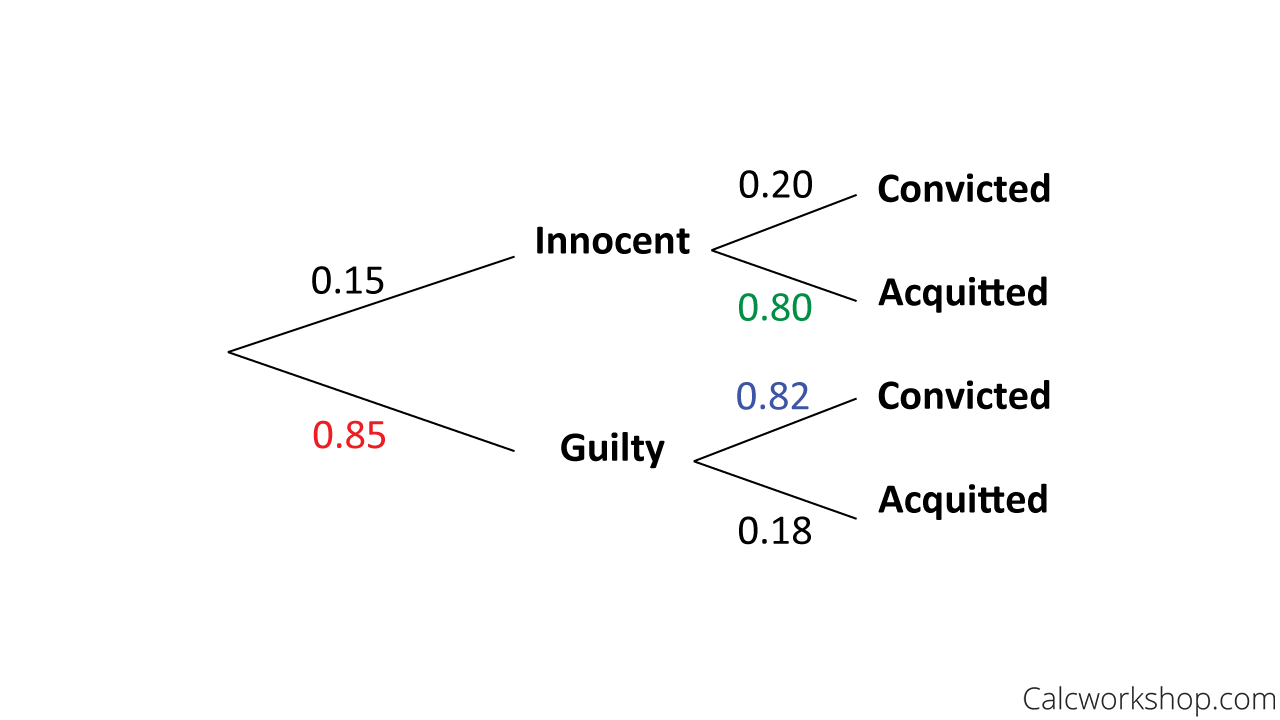
0 Response to "37 bayes theorem tree diagram"
Post a Comment