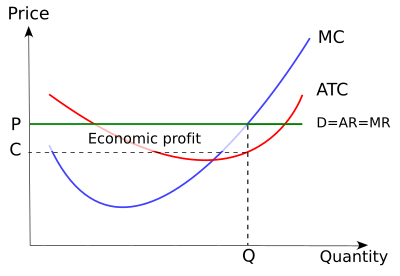
38 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which.
The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price= MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of approximately 85, which is labeled as E' in (a). Remember that the area of a rectangle is equal to its base multiplied by its height.

If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
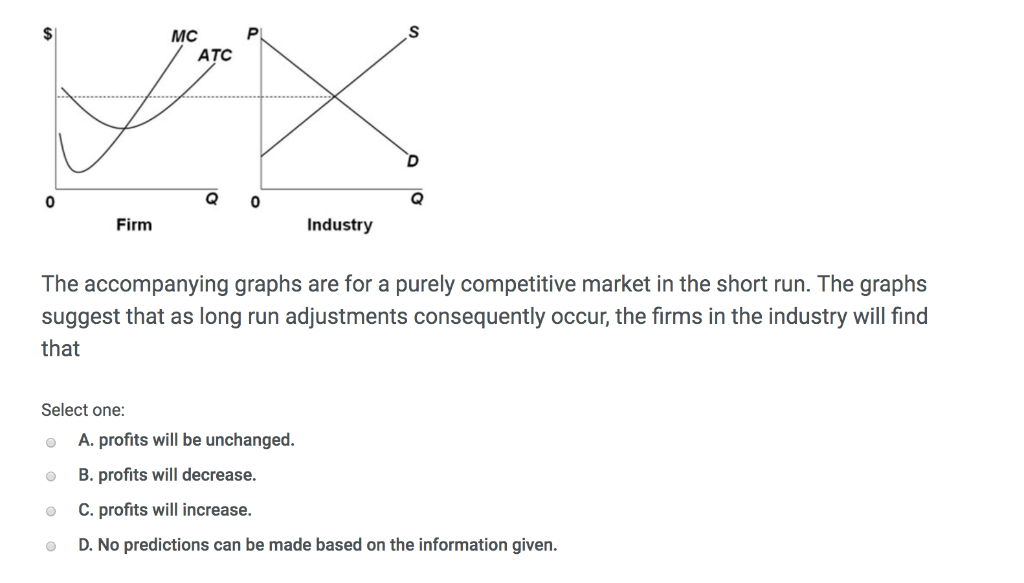
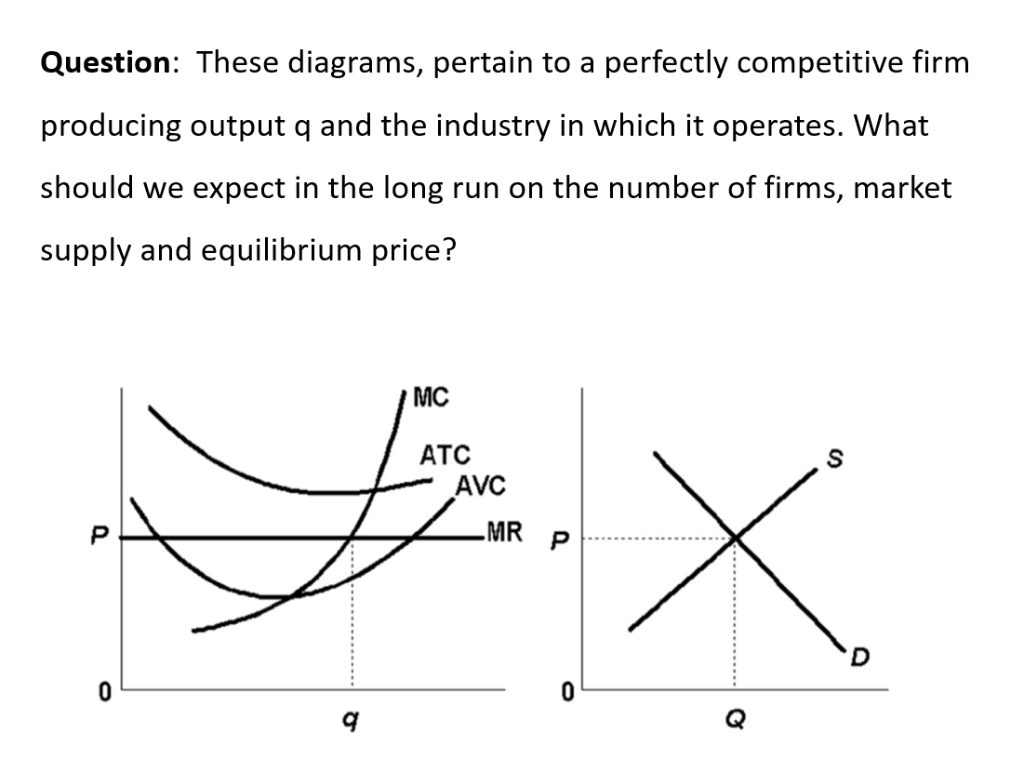
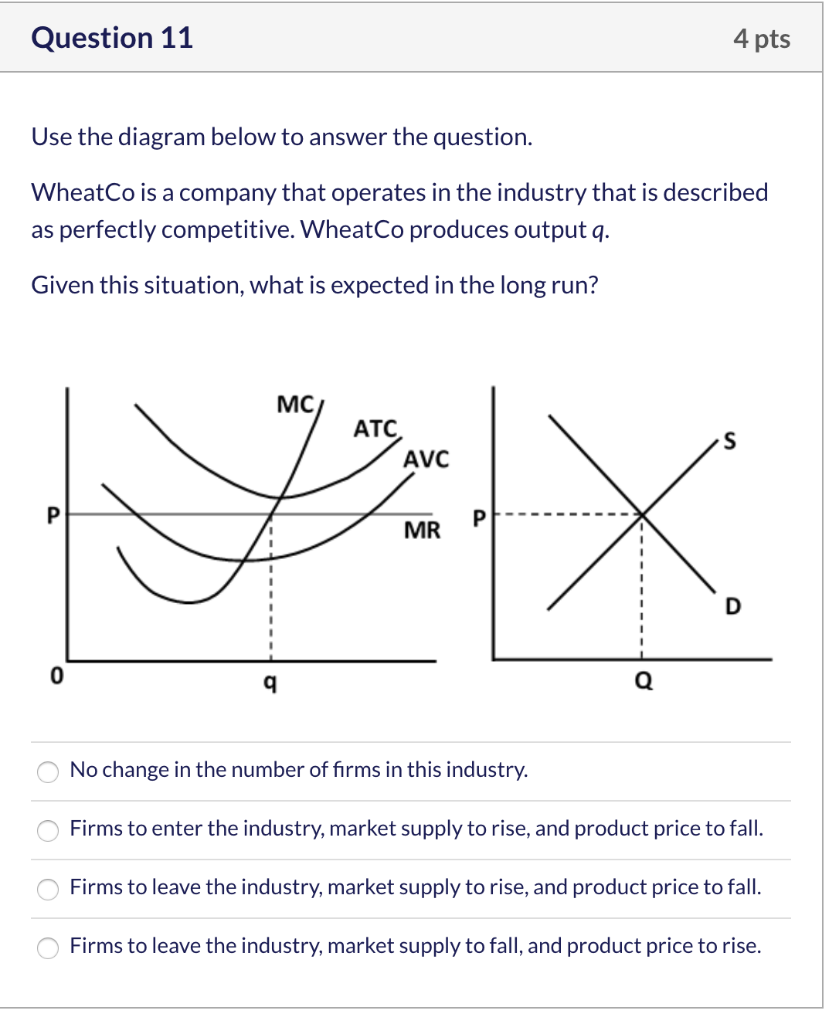
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is ...
Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency.
A perfectly competitive manufacturing industry is in long-run equilibrium. ... will be much stronger, so that ultimately output of a single firm will go up ...
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will.
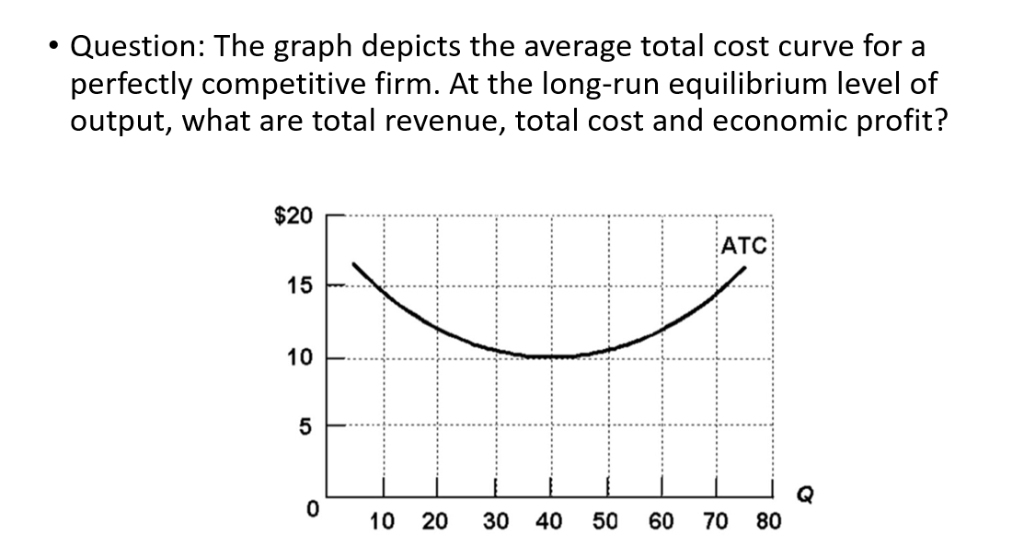
(4.4 Page 407) The graph represents the situation of a perfectly competitive firm. Indicate on the graph the areas that represent the following: a. Total cost=ATC*Q b. Total revenue=P*Q c. Variable cost=AVC*Q d. Profit or loss=(P-ATC)*Q Briefly explain whether the firm will continue to produce in the short run.
B)total revenue is unchanged when the firm lowers its price. C)total revenue increases when the firm lowers its price. D)marginal revenue is equal to zero. 24) 25)A monopoly firm expands its output and lowers its price. The firm finds that its total revenue falls. Hence, the firm is producing in the A)inelastic range of its supply curve.
If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a rate of output for which MC exceeds price, then the firm: A). Must have an economic loss.
Question 1. SURVEY. 120 seconds. Q. The primary force encouraging the entry of new firms into a purely competitive industry is. answer choices. normal profits earned by firms already in the industry. economic profits earned by firms already in the industry. government subsidies for start-up firms.
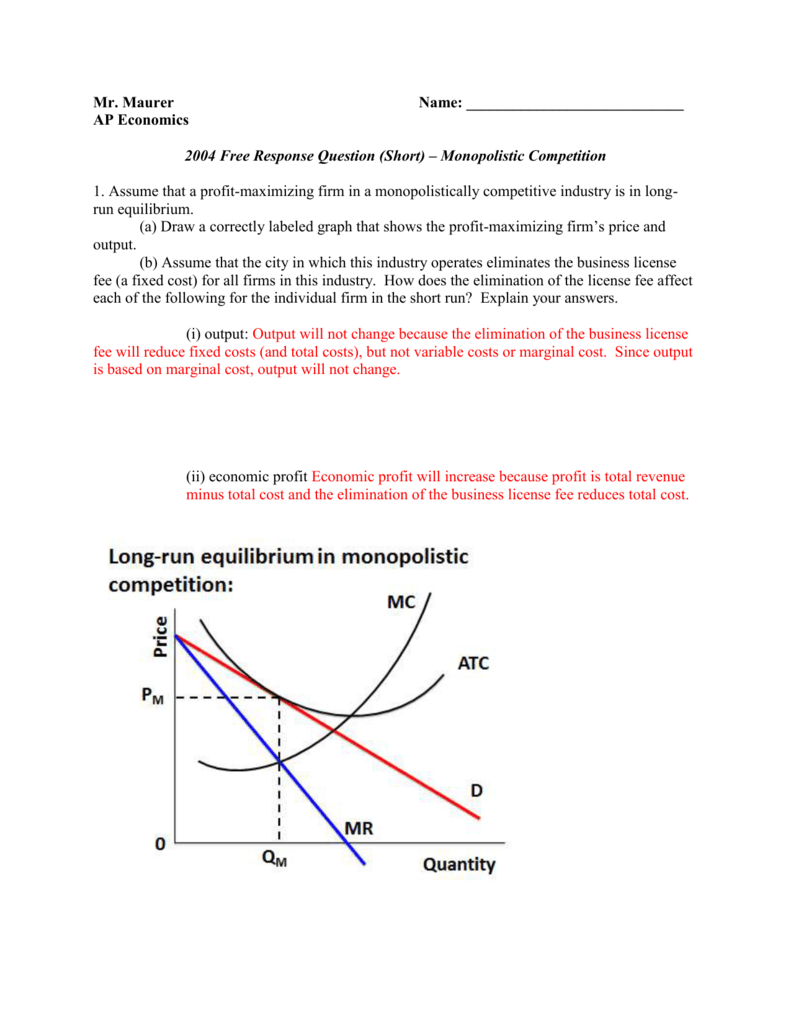
Figure 13 - 14 illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm. 7) Refer to Figure 13 -14. Which of the following statements describes the firm depicted in the diagram? 7) A) The firm is making no economic profit and will exit the industry. B) The firm is in long - run equilibrium and is breaking even.
Similarly at OP 1 price, all the firms of industry are producing 100 xM 1 =100M 1 quantity of output. These quantities will be called supply or output of industry. SS is the supply curve of industry. Point E shows that at OP price firm's supply is OM and an industry's total supply is 100 × M = 100M.
Of these goods, bottled water is probably the closest to a competitive market. Tap water is a natural ... At this point the typical firm produces output q1.
So, the small output Q 1 is not profit- maximising, even though it allows the monopolist to charge a higher price. By producing Q 1 instead of Q* the monopolist would reduce his total profit.. The larger quantity Q 2 is, likewise, not profit-maximising. At this point MC > MR, thus, if the monopolist produces a little less than Q 2, he would increase his total profit.
Because of symmetry, in equilibrium both firms will choose the same level of output. Thus, we can set QQ12= and solve 22 2 33.33 0.5 22.22 QQ Q = − = Since both firms will choose the same level of output, both firms will produce 22.22 units. Price can be found by substituting the quantity for each firm into market demand.
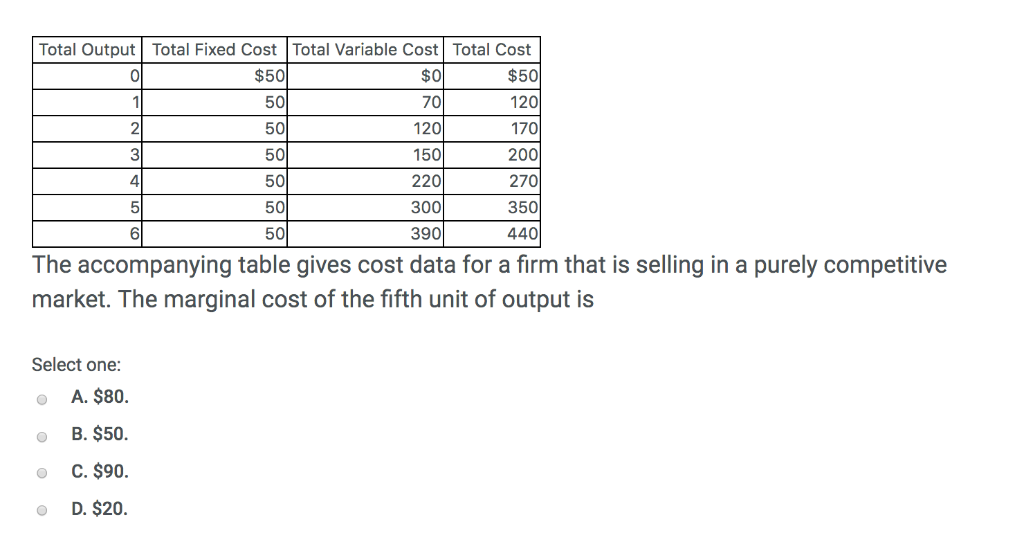
a. Assuming it is appropriate for the firm to produce in the short run, what is the firm's profit-maximizing level of output? 6 (where MR=MC) b. Calculate the firm's total revenue. $20 X 6 = $120 c. Calculate the firm's total cost. $29.50 X 6 = $177 d. Calculate the firm's profit or loss. $120 - $177 = -$57 (or a loss of $57) e.
market price P for all levels of output. These points imply that a perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing output where P = MC.18 pages
Perfect Competition Questions Question 1 Suppose there is a perfectly competitive industry where all the firms are identical with identical cost curves. Furthermore, suppose that a representative firm's total cost is given by the equation TC = 100 + q2 + q where q is the quantity of output produced by the firm.
The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price= MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of 90, which is labeled as e in Figure 4 (a). Remember that the area of a rectangle is equal to its base multiplied by its height.
In the competitive firm, the firm sets… View the full answer Transcribed image text : 6 MC ATC Price MR 00:45:49 Q, Q Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will Multiple Choice suffer an economic loss. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn an economic profit.
Q1 Answer Option B A perfectly competitive firm produces at MC=P where the P>ATC in the graph, so the firm is making a profit in the short run. ... 2 Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will Select one: A. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. B. suffer an economic loss.
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. b. earn a normal profit. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. ... If a purely competitive firm is producing at the MR = MC output level and earning an economic profit, then. new firms will enter this market. If the long-run supply curve is upward sloping, it indicates that resource prices fall when.
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect. firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. ... If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. earn a normal profit.
where Q is total output, i.e. Q = Q 1 + Q 2. a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue curves, and the total marginal cost curve (i.e., the marginal cost of producing Q = Q 1 + Q 2). Indicate the profit-maximizing output for each factory, total output, and price.
A supply curve, tells us how much output it will produce at every possible price. We have seen that competitive firms will increase output to the point at which P = MC, but they will shut down if P < AVC. Thus, for positive output the firm's supply curve is the portion of the MC curve that lies above the AVC curve.
Then the firm decides what price to charge for that quantity. Step 1. The monopolistic competitor determines its profit-maximizing level of output. In this case, the Authentic Chinese Pizza company will determine the profit-maximizing quantity to produce by considering its marginal revenues and marginal costs.
In Panel (b), at price P 1 a single firm produces a quantity q 1, assuming it is at least covering its average variable cost. The firm's losses are shown by the shaded rectangle bounded by its average total cost C 1 and price P 1 and by output q 1. Because firms in the industry are losing money, some will exit.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. earn a normal profit. Marginal cost is _____. (TVC+TFC)/Q. The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue ... Refer to the provided graph for a purely competitive firm ...
15) Crazy Horse is one of many identical competitive firms producing horse shoes. Its cost function is given by C(Q) = Q2 + 4, where Q is the number of horse shoes produced. i) Give an equation for and graph the horse shoe industry long run supply curve.
The analytical nature of Economics as a subject often gives the students sleepless nights. Economics is social science that studies the production, distribution and consumption of the goods and services. There are various different topics and dynamics of sale and purchase that are covered in economics and this subject finds its applications in the field of business, finance, governance, education, health, law, politics, religion, science, crime and personal decision making. If you are stuck wit...
Key: The firm will produce a positive quantity as long as the price is larger than where MC intersects AVC. Since we know the firm produces where P = MC, this means the firm will product as long as MC > AVC: 100 + 20q > 100 + 10q 10q > 0, which means q > 0 So, MC = P > 100 + 20*(0) = 100. The firm will produce for P > 100. e.
The following diagram shows a typical firm's short-run output in a competitive market. In the long run the industry's output will decrease and the typical firm's output will: Able Pads, Inc., sells plain white printer paper in a perfectly competitive market.
Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A. suffer an economic loss. B. earn a normal profit. C. earn an economic profit. D. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency.
Short Run and Long Run Equilibrium under Perfect Competition (with diagram)! Under perfect competition, price determination takes place at the level of industry while firm behaves as a price taker. It produces a quantity depending upon its cost structure. The industry under perfect competition is defined as all the firms taken together.



















0 Response to "38 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will"
Post a Comment