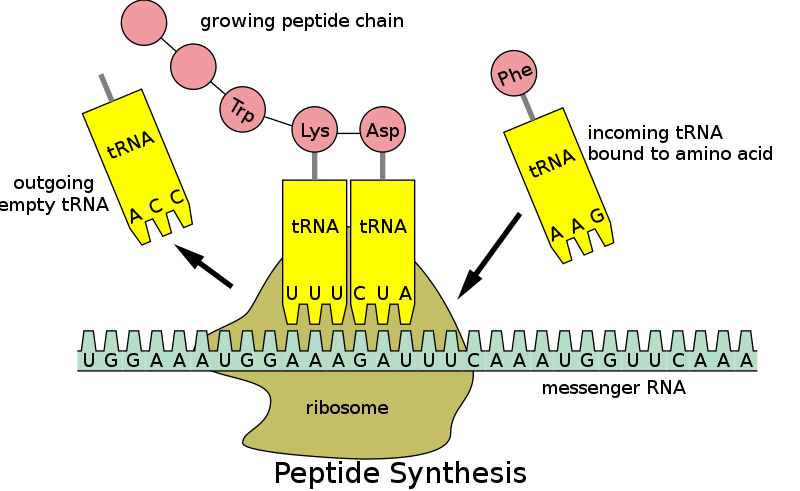
38 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
The most common shape found at the secondary level of protein structure is the alpha-helix. Alpha helices (α-helices) are characterized by tight, right-handed coils. These structures are ...
For example, little is known about the structure of the first ~30 amino acids of the intracellular JM region (Fig. 1A), which may play an important regulatory role (31, 48). Moreover, the most C-terminal ~190 amino acids of EGFR that contains multiple tyrosine phosphorylation sites is poorly characterized, but is clearly implicated in ...
5.09 Quiz: RNA Makes Protein. Refer to the diagram to answer the question. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? Refer to the diagram to answer the question. Which two structures are first to combine in translation?

Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids
Aug 08, 2016 · Find an answer to your question Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? (Points : 1) 1 2 3 4 Which two structures are first to …
tRNA is made of nucleotides, many of which is modified for structural and functional reasons. At the 3' end of the tRNA, the amino acid is attached to the 3'OH via an ester linkage. tRNA structure: clover leaf structure with anticodon at the tip, and the amino acid at the 3' tail.
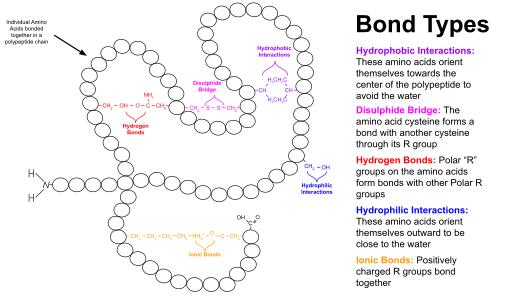
ADVERTISEMENTS: By convention, four levels of protein organization may be identified; these are called the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of the protein. 1. Primary Protein Structure: Successive amino acids forming the backbone of a polypeptide chain are linked together through peptide bonds and it is believed that these are the only covalent associations […]
Which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids.
Mar 11, 2019 · profile. JoiePatel. Answer: The correct answer would be tRNA . tRNA ( transfer ribonucleic acid) is a type of RNA which brings amino acid to a ribosomal site which is then added to the growing polypeptide chain. The charged tRNA which has a complementary anti-codon site to the codon of mRNA brings the specific amino acid to the A site of the ribosomal complex.
Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? 2. Which two structures are first to combine in translation? 1 and 4. Which structure holds the original code from the DNA gene? 4. Which structure will become the product of translation? 3.
The tRNA is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome. The tRNA contains an anti-codon that matches up with a codon, when it does this it will release an amino acid. How does the structure of a ribosome enable its function?
4 Answers. okay so it's really simple okay.<3. So the first one is which structure brings in the amino acid think about it about it tRNA look at it like this tRNA is the Transfering so you have T for transfer so it's tRNA its' an easy way to remember it. The second one is mRNA and tRNA. the third one is mRNA. and the last one is like amino acid.
Functions of the different cellular organelles. Eukaryotic cells are a type of cells that contain membrane-bound organelles. The organelles play specific functions that aid in the integrity of cells.
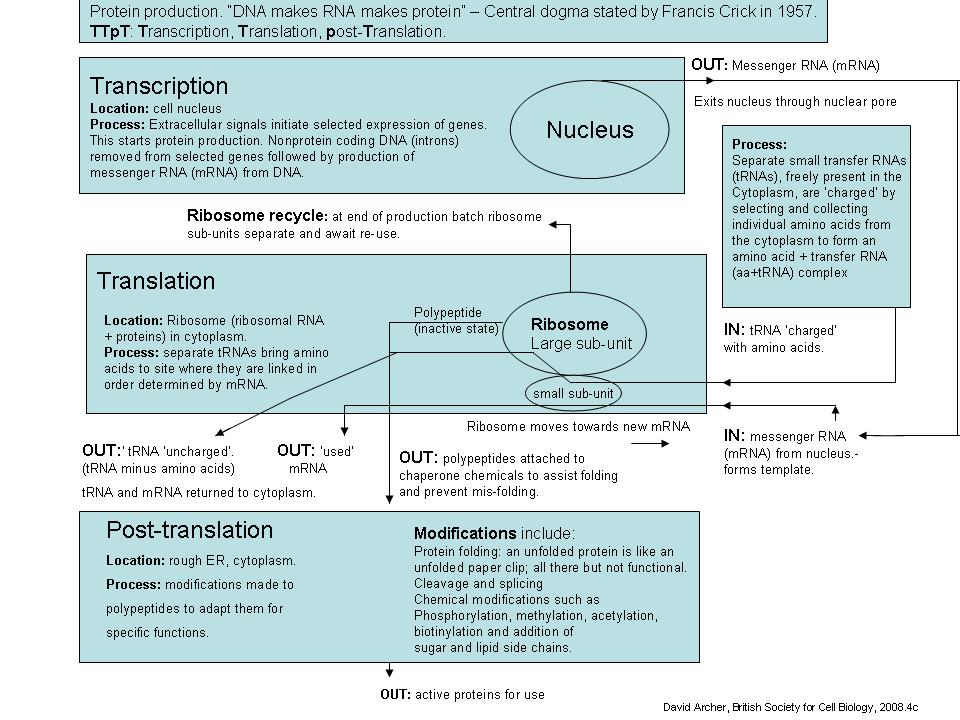
Therefore, a gene, which is composed of multiple triplets in a unique sequence, provides the code to build an entire protein, with multiple amino acids in the proper sequence (Figure 3.4.1). The mechanism by which cells turn the DNA code into a protein product is a two-step process, with an RNA molecule as the intermediate.
However, there are other aspects to a tRNA's structure such as the D-arm and T-arm, which contribute to its high level of specificity and efficiency. Only 1 in 10,000 amino acids are incorrectly attached to a tRNA, which is a remarkable number given the chemical similarities between many amino acids.
Role and structure of ribosomes. mRNA is translated into a polypeptide chain (and therefore a protein) at ribosomes, complex macromolecules composed of rRNAs and many distinct polypeptides. Ribosomes are the sites of mRNA translation into a polypeptide. Ribosomes may consist of different numbers of rRNAs and polypeptides, depending on the organism.
Match. Gravity. Look at the diagram. Which structure is responsible for bringing in the amino acids? Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 2.
Each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins has at least one corresponding kind of tRNA, and most amino acids have more than one. Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Transfer RNA. (a) In the two-dimensional structure of a yeast tRNA molecule for phenylalanine, the amino acid binds to the acceptor stem located at the 3′ end of the tRNA primary sequence.
answer choices. the shape (structure) of the nitrogen bases. the order (sequence) of the nitrogen bases. the color of the nitrogen bases. the frequency (number) of nitrogen bases. Tags: Question 5. SURVEY. 45 seconds.
Thus tRNA transfers specific amino acids from the cytoplasm to a growing polypeptide. The tRNA molecules must be able to recognize the codons on mRNA and match them with the correct amino acid. The tRNA is modified for this function. On one end of its structure is a binding site for a specific amino acid.
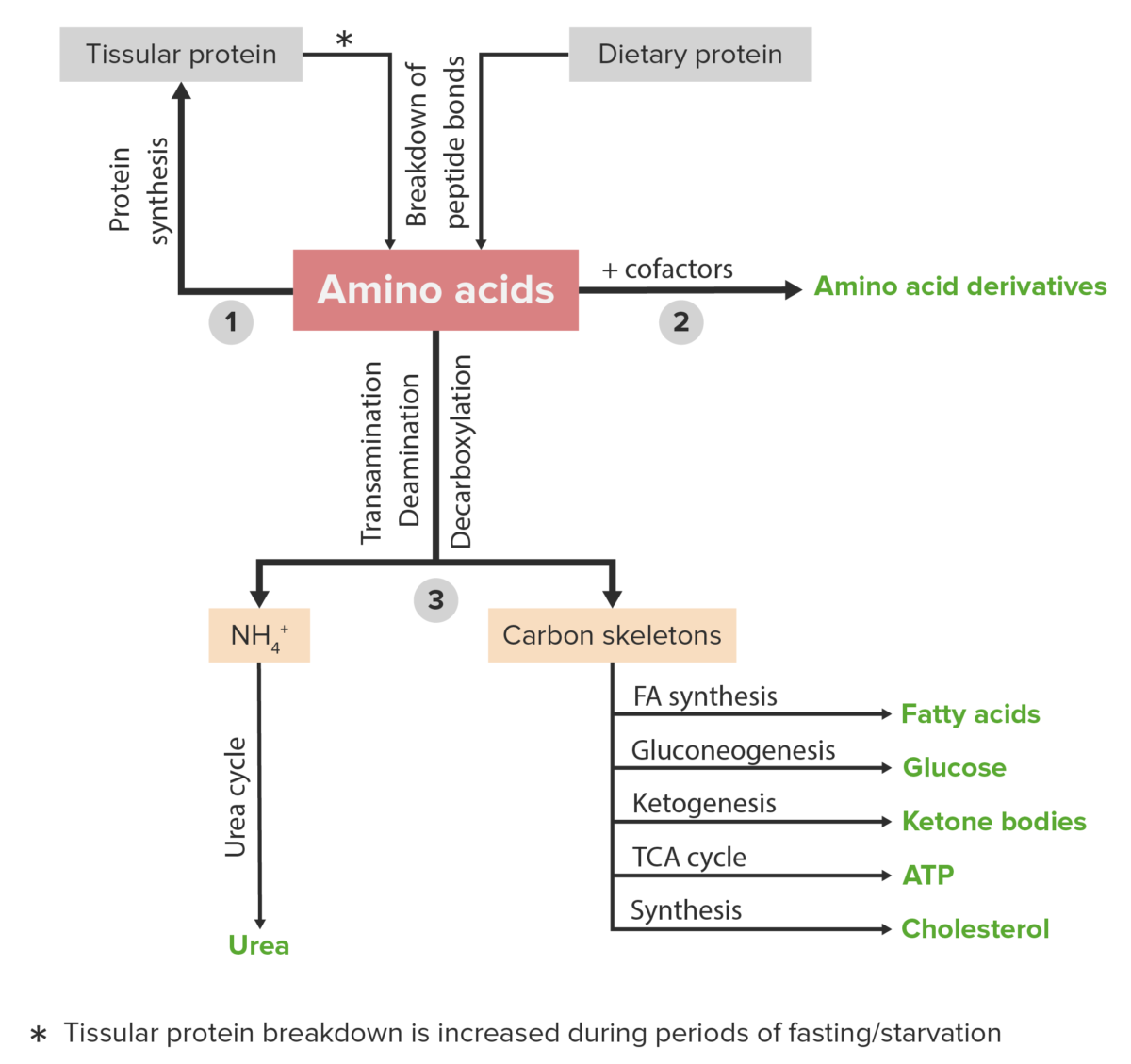
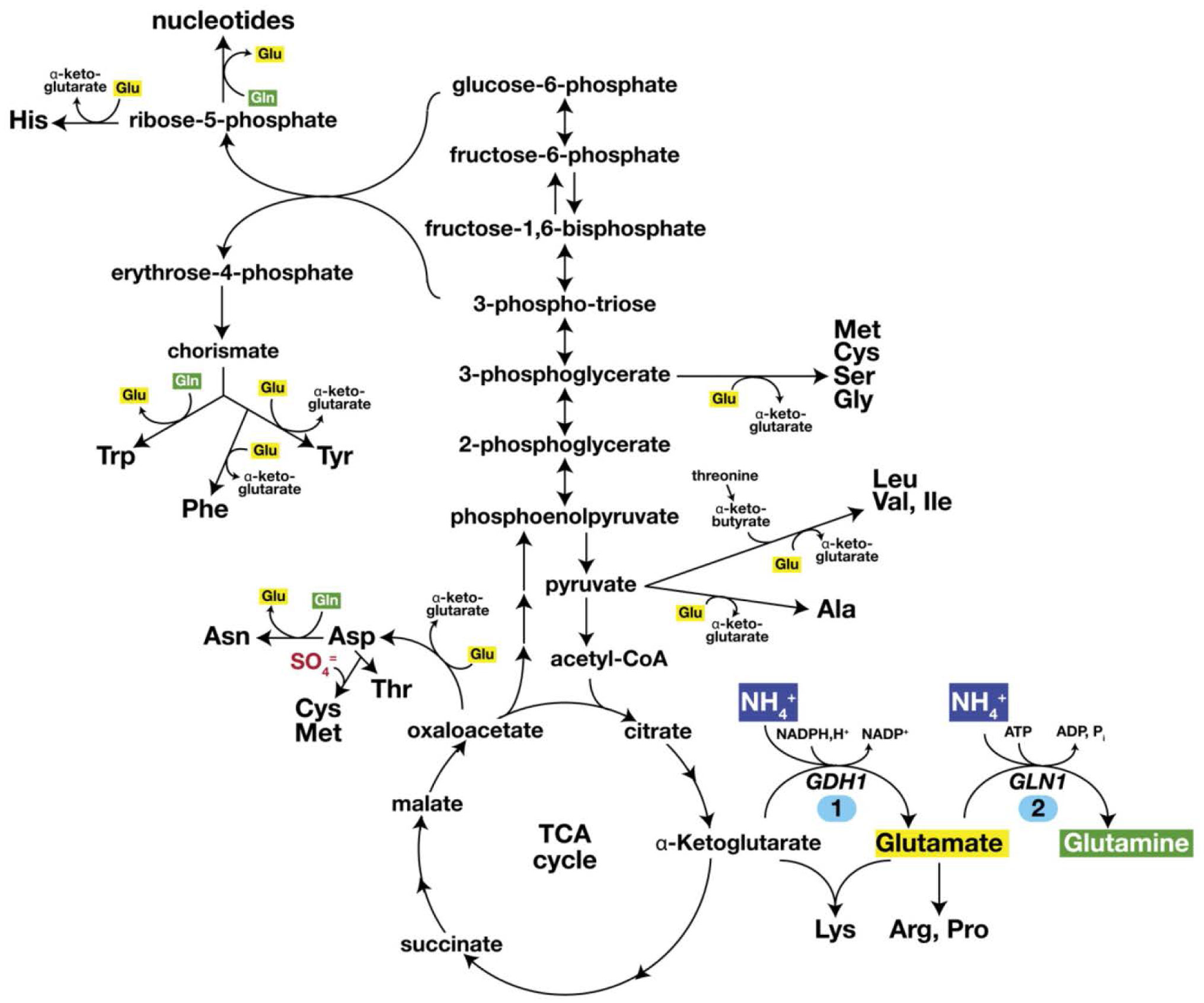
These amino acids are called glucogenic amino acids. Amino acids that are converted to acetoacetyl-CoA or acetyl-CoA, which can be used for the synthesis of ketone bodies but not glucose, are called ketogenic amino acids. Some amino acids fall into both categories. Leucine and lysine are the only amino acids that are exclusively ketogenic.
The human calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a class C G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) responsible for maintaining Ca 2+ homeostasis in the blood. The general consensus is that extracellular Ca 2+ is the principal agonist of CaSR. Aliphatic and aromatic L-amino acids, such as L-Phe and L-Trp, increase the sensitivity of CaSR towards Ca 2+ and are considered allosteric activators.
Which Structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids. tRNA. Which two structures contain codons and anticodons. mRNA and tRNA. Which structure carries the genetic "blueprints" for building a specific kind of protein? mRNA. ... which structure is missing from the diagram but help mRNA and tRNA bind together. ribosome.
In order for amino acids to be linked, the _____ on the mRNA will match with the _____ on the tRNA. 2. What molecule is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis? 3. What are the steps for protein synthesis? 4. How many amino acids are affected by a change in one nitrogen base? 5.
The synthetase enzymes use the energy of ATP to covalently attach the amino acid to the tRNA molecule. A diagram of this process is shown in Figure 7.14. For each of the 20 amino acids, there is a specific tRNA molecule and a specific synthetase enzyme that will ensure the correct attachment of the correct amino acid with its tRNA molecule.
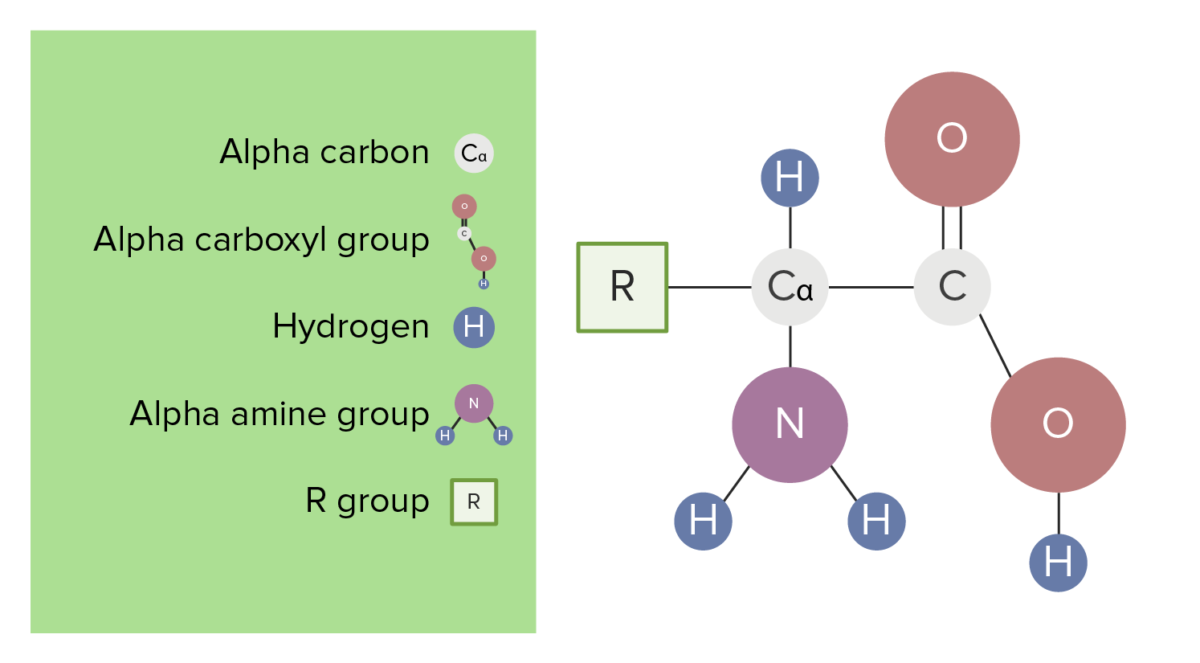
The first of these is the primary structure, which is the number and sequence of amino acids in a protein's polypeptide chain or chains, beginning with the free amino group and maintained by the peptide bonds connecting each amino acid to the next.
Structure and Function. It is a small RNA chain of about 80 nucleotides. During translation, tRNA transfers specific amino acids corresponding to the mRNA sequence to the growing polypeptide chain in the ribosome. tRNA pairs with mRNA complementarity in a parallel manner with each of its base pairs having three nucleotides paired to mRNA.
Chapter 14 - Translation. All of the following are involved in the process of tRNA charging EXCEPT __________. Ribosomal RNA and ribosomes form the site of protein translation. Transfer RNAs work to bring amino acids to the ribosome.
machine responsible for synthesizing proteins • Transfer RNA, tRNA , is used to bring correct amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis • Micro RNAs (mRNAs) are important in regulating gene expression • others Transcription involves the synthesis of rRNA from DNA using RNA polymerase
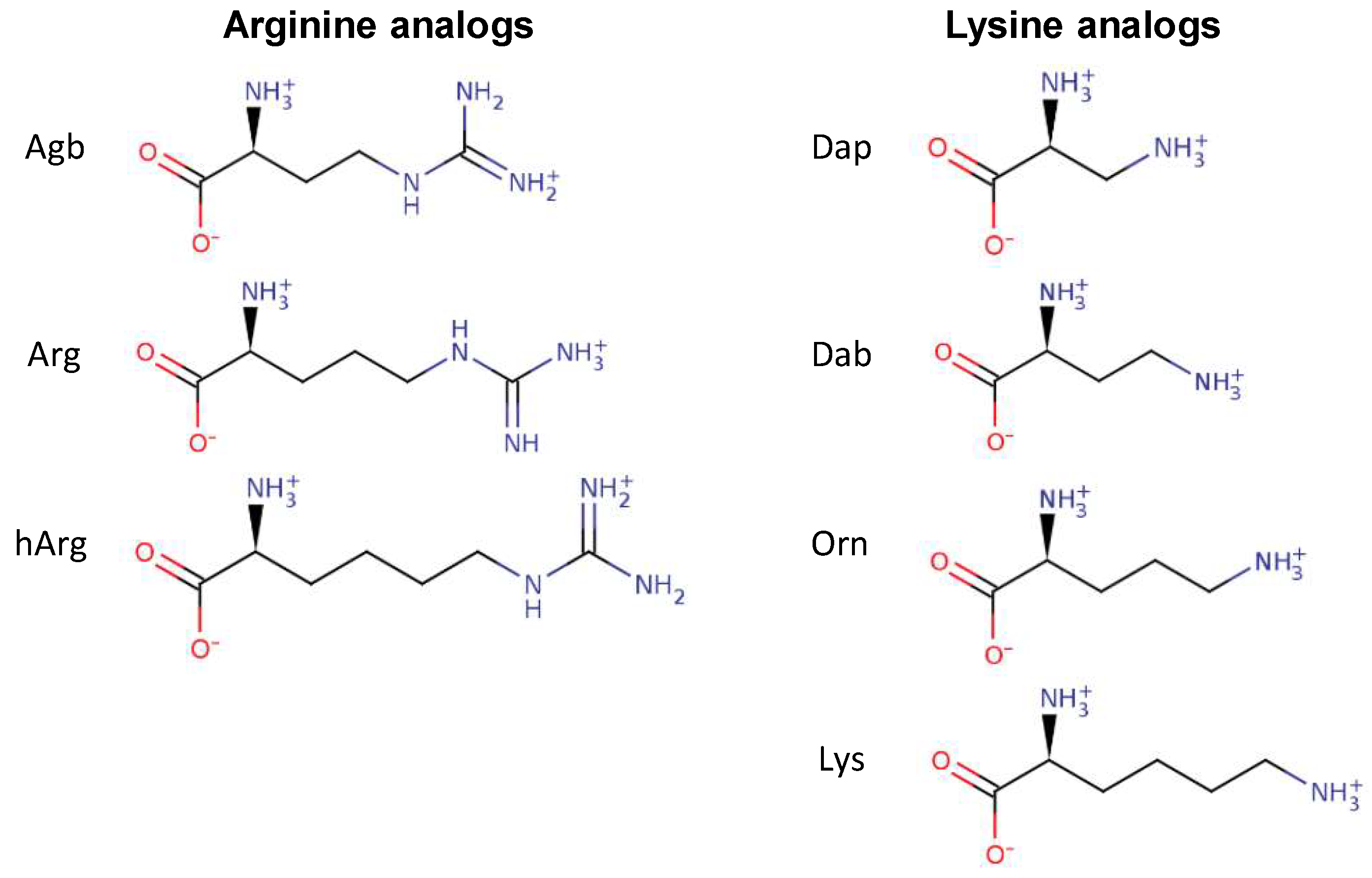
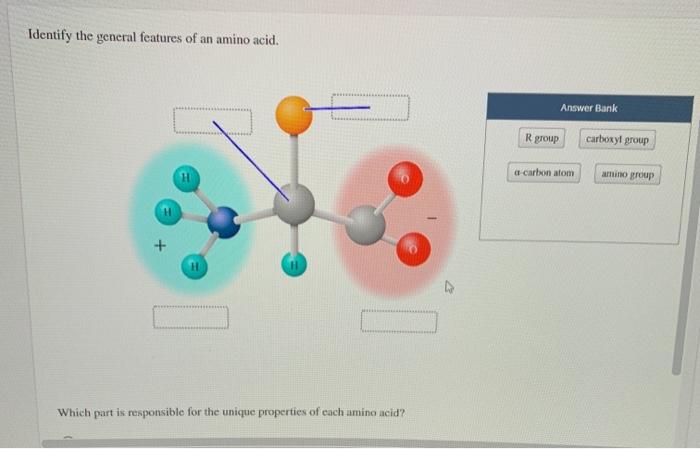
Amino acids are compounds that contain an amino group and carboxyl, as shown in the diagram. Proteins are formed from long chains of amino acids, brought together by a particular bond known as a ...
Although the basic structure of biological membranes is provided by the lipid bilayer, membrane proteins perform most of the specific functions of membranes. It is the proteins, therefore, that give each type of membrane in the cell its characteristic functional properties. Accordingly, the amounts and types of proteins in a membrane are highly variable.
structure dna diagram science trends, bio lab exam 4 flashcards quizlet, mrna ... structure of nucleic acids like rna and dna the chemical structure of nucleotides is almost the same ... responsible for bringing amino acids basic protein building blocks to these protein factories in.
A fourth weak force also has a central role in determining the shape of a protein.As described in Chapter 2, hydrophobic molecules, including the nonpolar side chains of particular amino acids, tend to be forced together in an aqueous environment in order to minimize their disruptive effect on the hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules (see p. 58 and Panel 2-2, pp. 112-113).
Translation is the process by which the genetic code contained within a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.It occurs in the cytoplasm following DNA transcription and, like transcription, has three stages: initiation, elongation and termination. In this article we will discuss the components and stages of DNA translation.



















0 Response to "38 which structure in the diagram is responsible for bringing in amino acids"
Post a Comment