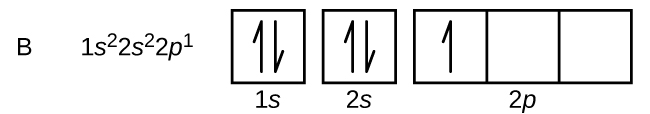
40 orbital diagram of boron
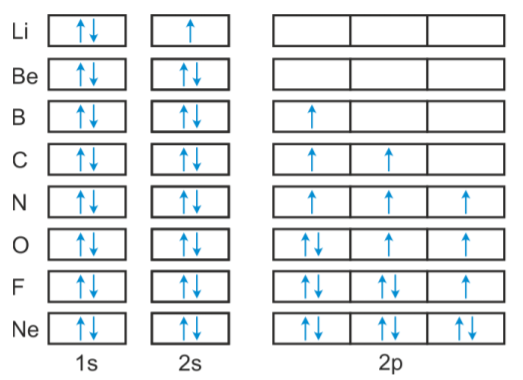
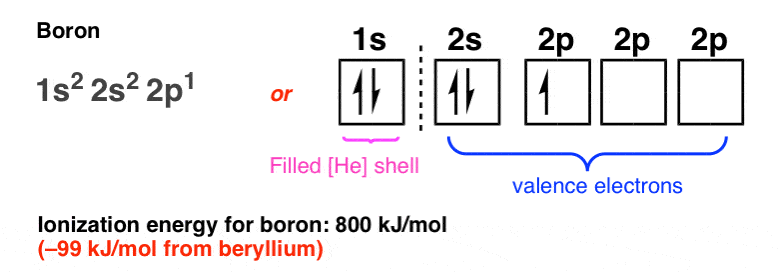
Figure 6.8. 1: One electron in. From the orbital diagram, we can write the electron configuration in an abbreviated form in which the occupied orbitals are identified by their principal quantum number n and their value of l ( s, p, d, or f ), with the number of electrons in the subshell indicated by a superscript. The Figure below shows how a set of three p orbitals is filled with one, two, three, and four electrons. Diagram of Hund's rule in boron, carbon, nitrogen, ...
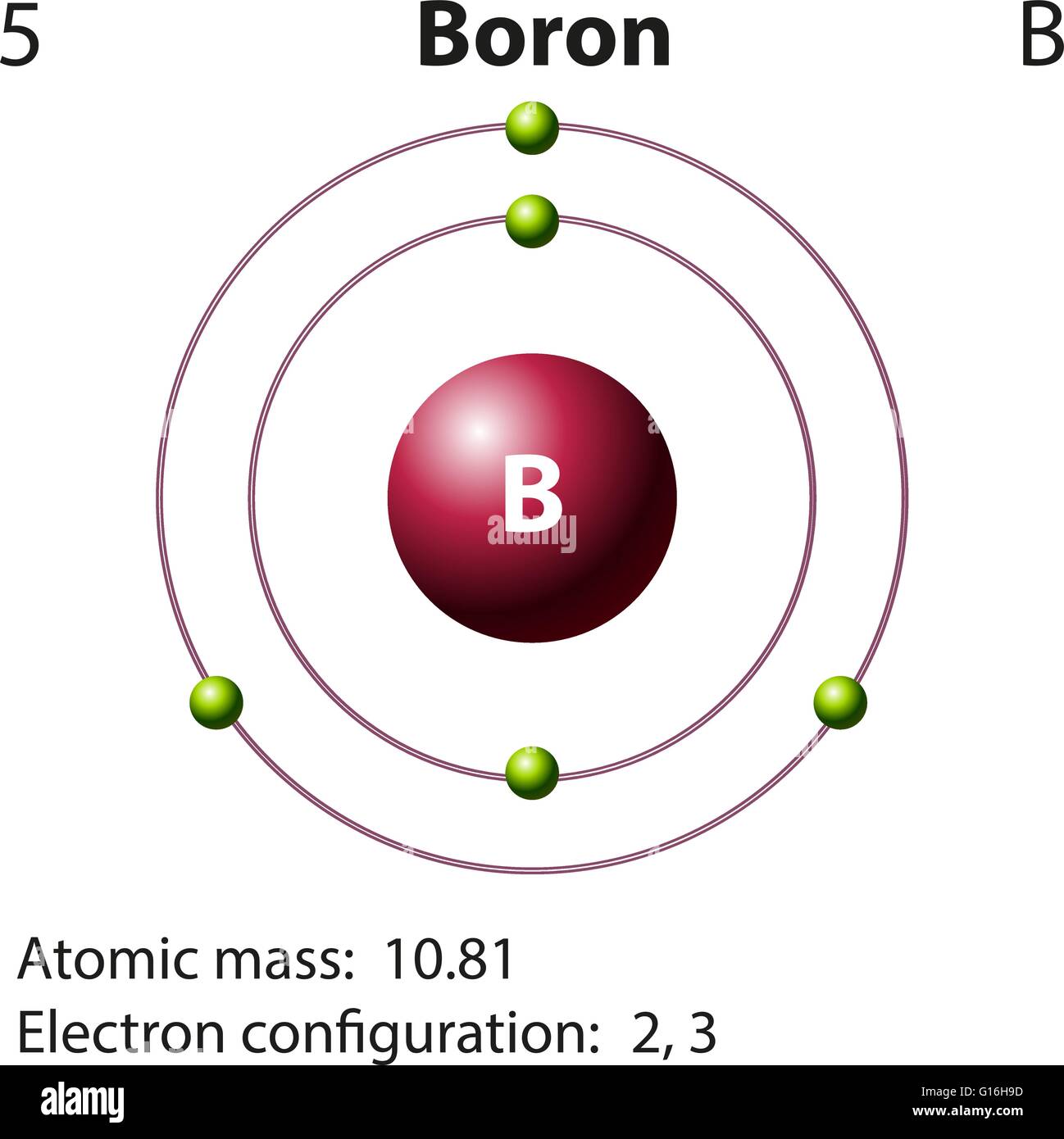
The Bohr Model of Boron(B) has a nucleus that contains 6 neutrons and 5 protons. This nucleus is surrounded by two-electron shells named K-shell and L-shell. The outermost shell in the Bohr diagram of Boron contains 3 electrons that also called valence electrons.

Orbital diagram of boron
Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Oxygen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The eighth element in the periodic table is oxygen. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
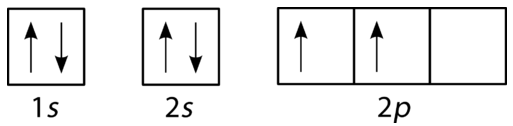
Orbital diagram of boron. Problem: Part A. Complete an orbital diagram for boron.Draw orbital diagrams, and use them to derive electron configurationsTo understand how to draw orbital diagrams, and how they are used to write electron configurations.The electron configuration of an element is the arrangment of its electrons in their atomic orbitals. Electron configurations can be used to predict most of the chemical ... The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of: Molecular Orbital Diagram of Boron Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.Wa... Boron Through Neon - The 2p Orbitals Draw orbital diagrams and then the electron configurations for the following atoms. The number of electrons in an atom of an element is equal to the at number. the packing of the shell is: 1st (s2) 2nd (s2p6) 3rd (s2p6d10).
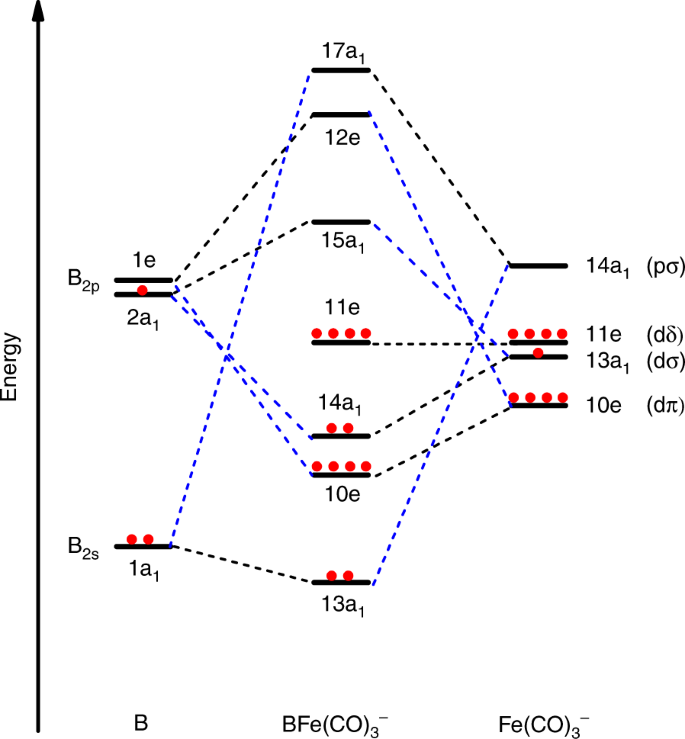
The diagram on the right of side of Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows how energy levels are affected by orbital mixing. Starting from the simplified MO diagram and mixing molecular orbitals of like symmetry : If we start with the simplified diagram shown on the right, we can pick out the orbitals with like symmetry and consider what will happen if ... Molecular orbital diagrams give us an idea about the mixing of orbitals in molecules. Let's look into the MO diagram of boron trichloride. The blue color refers to the atomic orbitals of boron, the red color refers to the atomic orbitals of chlorine and the molecular orbital of the molecule is indicated by the purple color. • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down. 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 Boron 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d1. Scandium. Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Draw an orbital diagram for ...
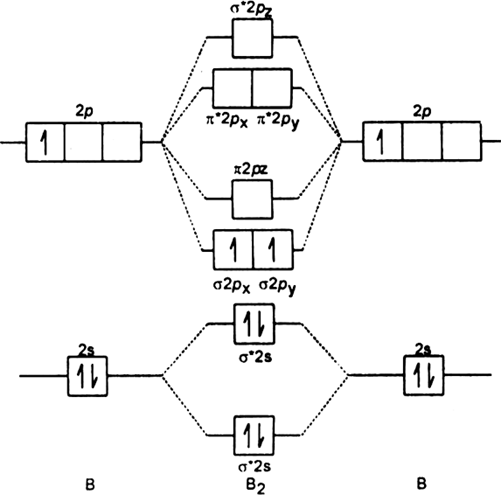
You can complete the orbital diagrams of Boron (B) and Scandium (Sc) by referring to the periodic table, locating the position of each element in it, and ...Sep 16, 2020 Draw an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. How many orbitals are there in the third shell (n = 3)? Express your answer numerically as an integer. Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of. Question: Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13: Orbital diagram of Aluminum (Al) 14: This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p .
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for Boron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for B goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital.
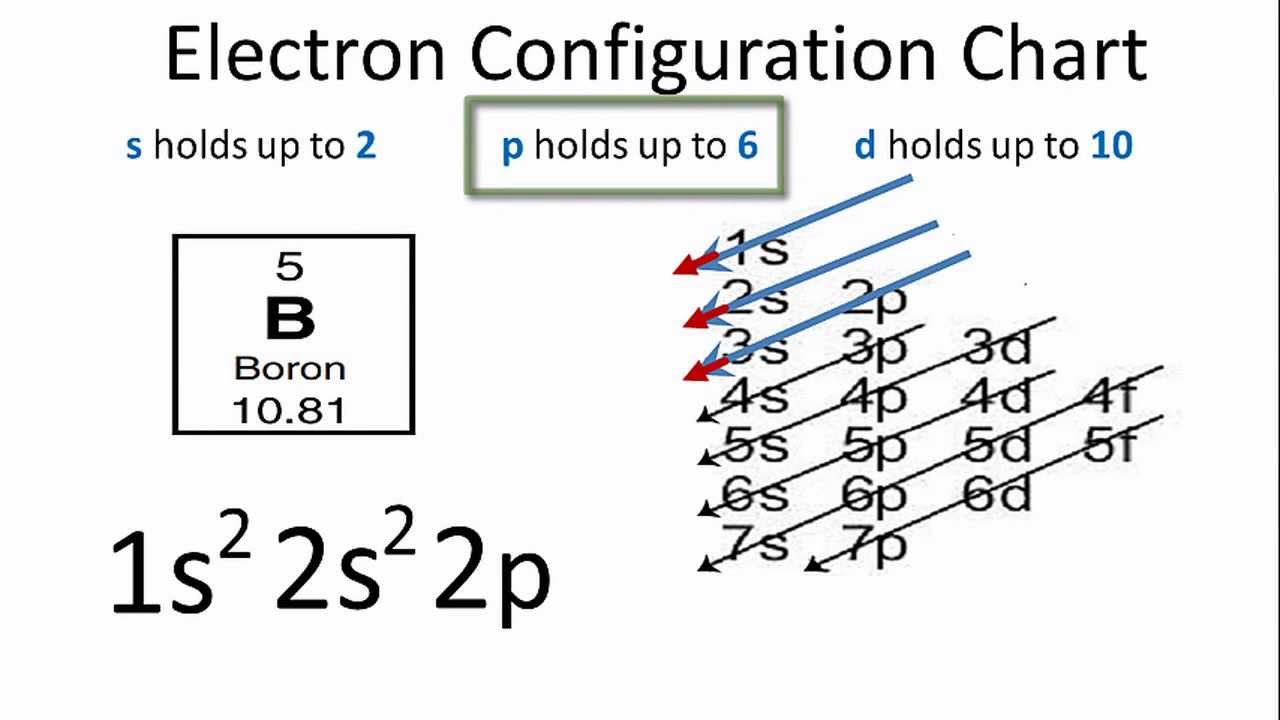
Boron electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1.The period of boron is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of boron(B) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of boron, application of different principles.. The fifth element in the periodic table is the boron(B).
In this video we will draw the molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic nitrogen, carbon and boron. We will also calculate their bond order and determine if t...
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of.
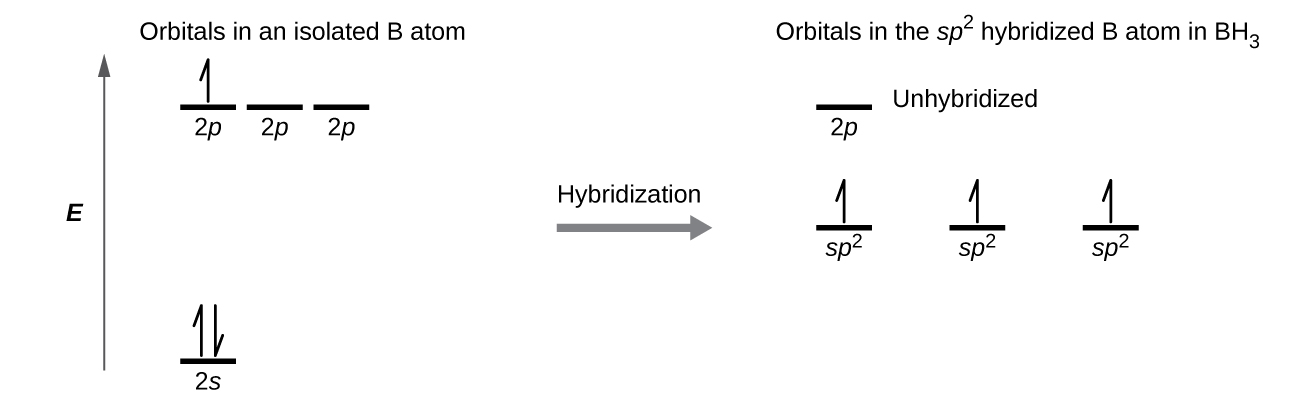
(a) Starting with the orbital diagram of a boron atom, describe the steps needed to construct hybrid orbitals appropriate to describe the bonding in BF3. (b) What is the name given to the hybrid orbitals constructed in (a)? (c) On one origin, sketch the large lobes of the hy- brid orbitals constructed in part (a). (d) Are there any
Boron has:- 1s2 2s2 2p1. Why are the outermost electrons the only ones included in the orbital filling diagram and the electron dot diagram?
B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the formation of B 2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. MO electronic configuration:
Boron (atomic number 5) has five electrons. Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s22s22p1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18.
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹ which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital two electrons in the 2s orbital and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital.
Bf3 Molecular orbital Diagram - Bf3 Molecular orbital Diagram , D3h Boron Trifluoride is Loaded
For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Question: Part C Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron.
An atom of boron (atomic number 5) contains five electrons. The n = 1 shell is filled with two electrons and three electrons will occupy the n = 2 shell. Because any s subshell can contain only two electrons, the fifth electron must occupy the next energy level, which will be a 2p orbital.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Oxygen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The eighth element in the periodic table is oxygen.
Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).














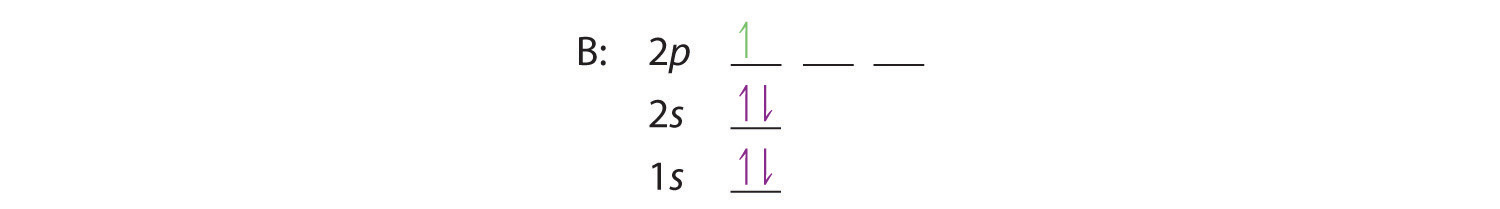





0 Response to "40 orbital diagram of boron"
Post a Comment