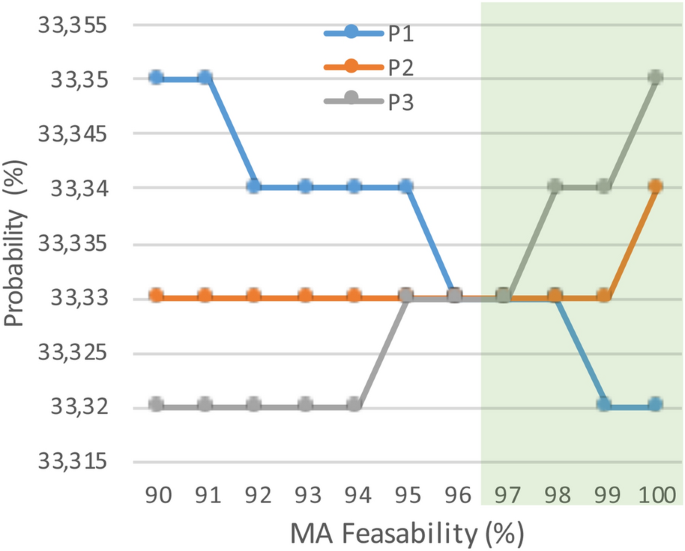
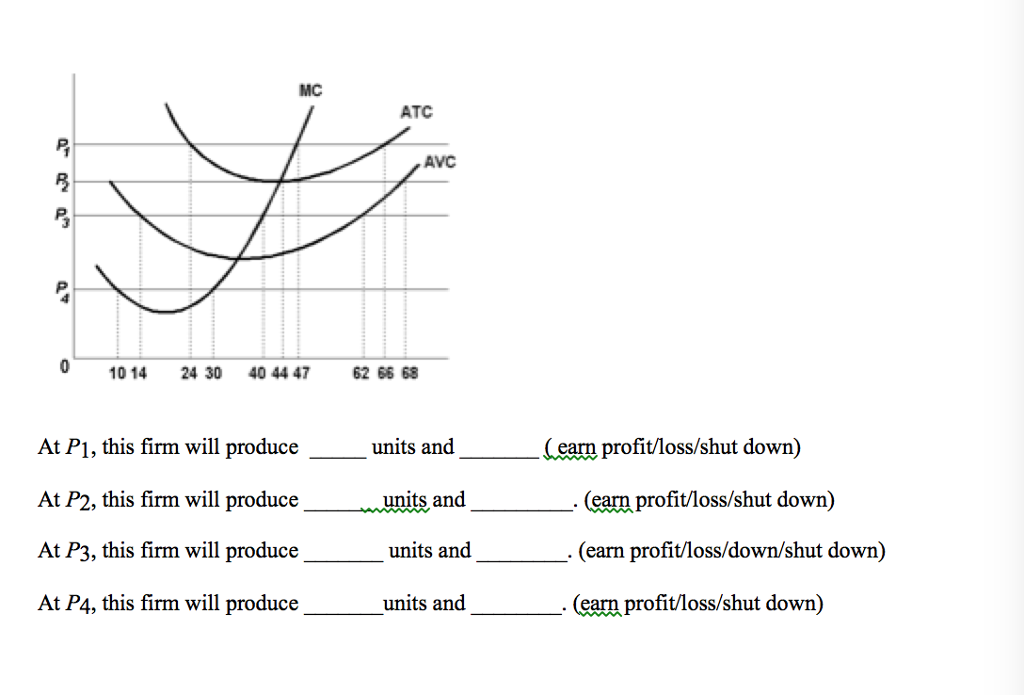
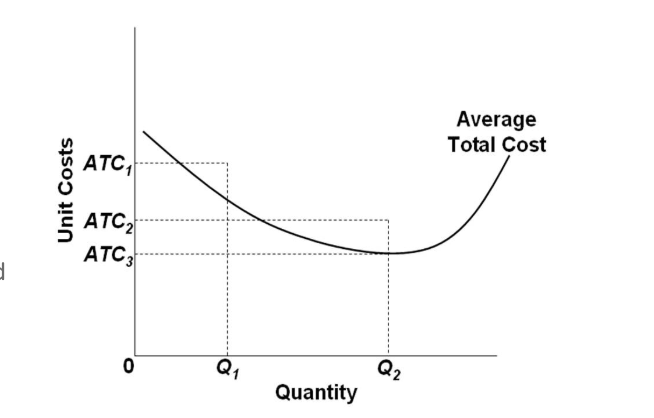
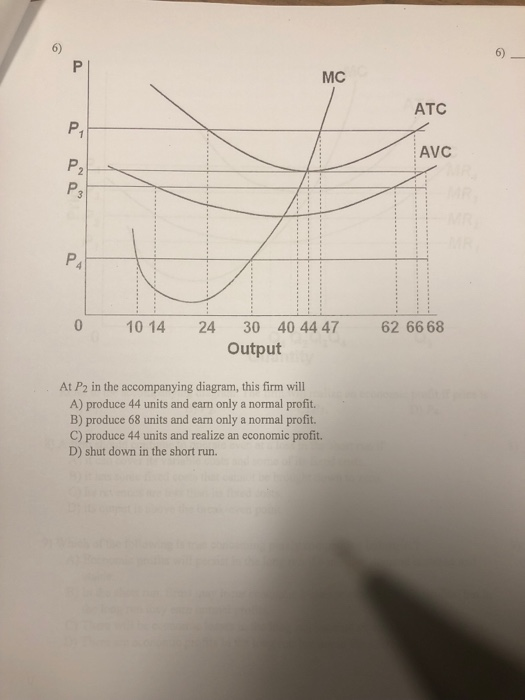
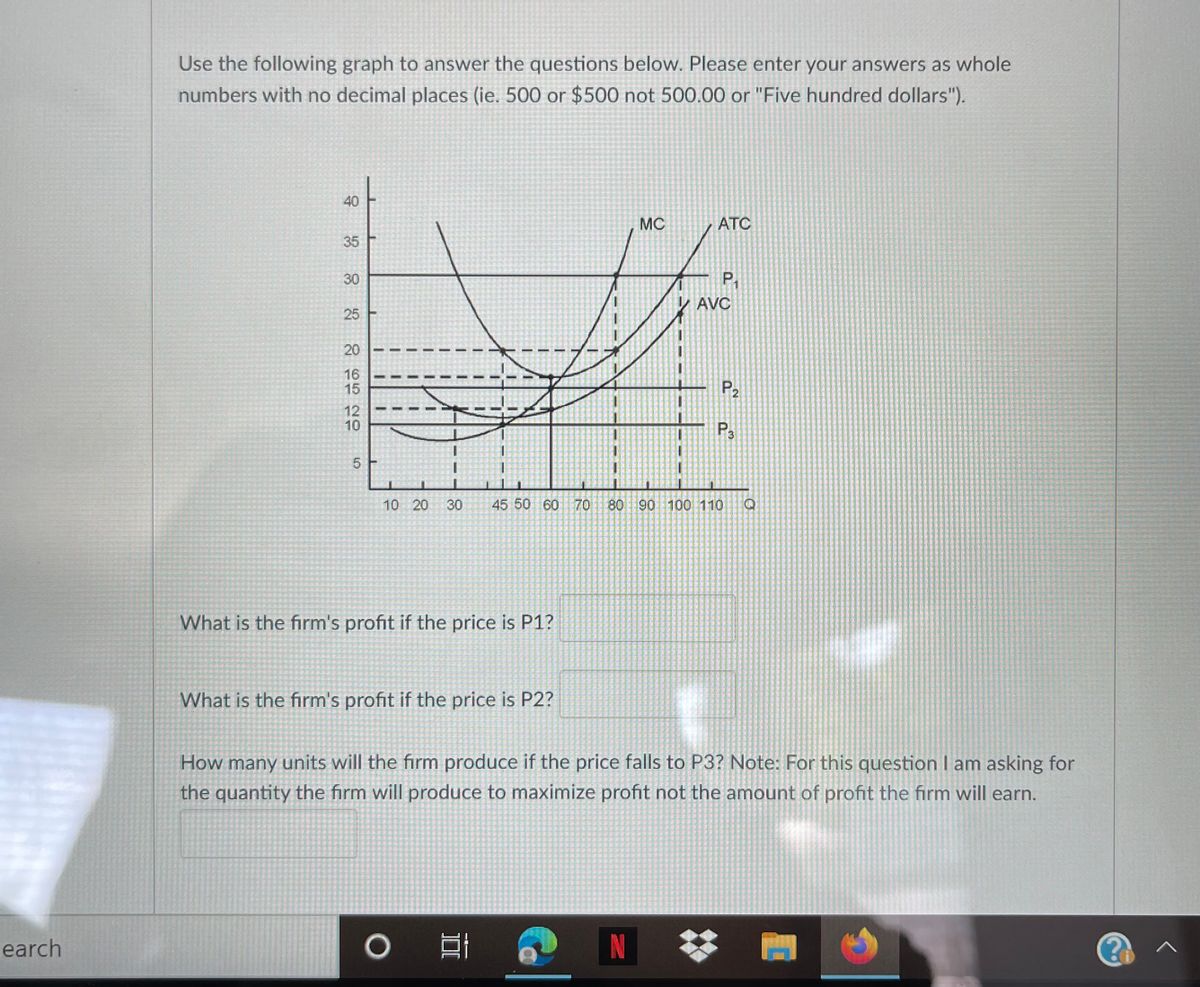
42 at p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce
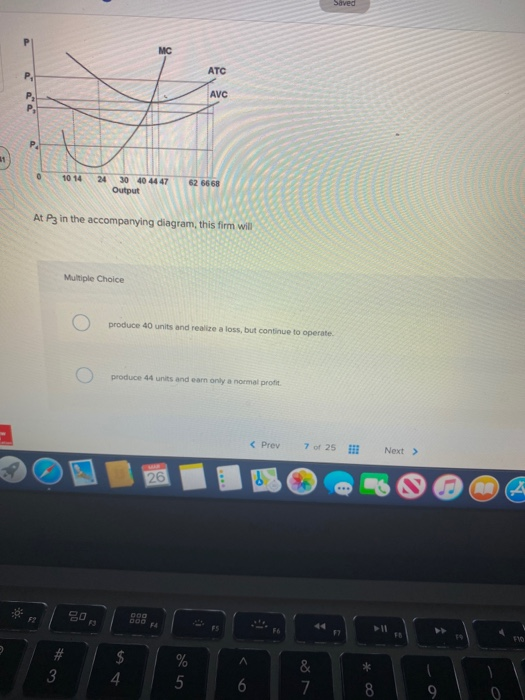
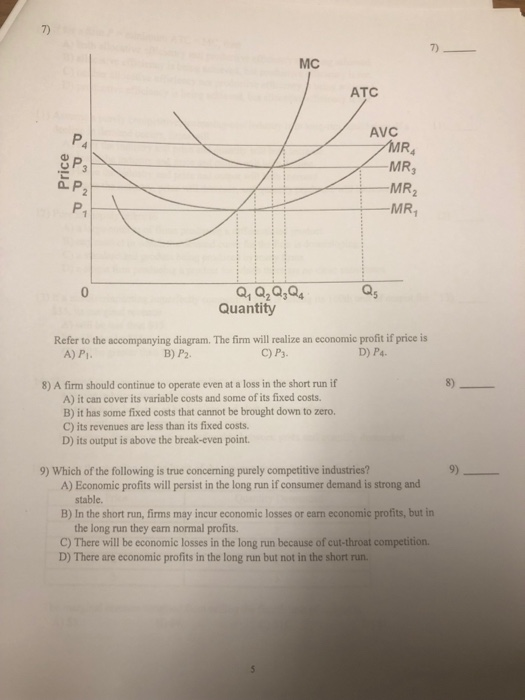
97. At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will A. produce 14 units and realize an economic profit. B. produce 62 units and earn only a normal profit. C. produce 40 units and incur a loss. D. shut down in the short run. AACSB: Knowledge Application Blooms: Understand Difficulty: 02 Medium Learning Objective: 10-05 Explain how purely competitive firms can use the marginal-revenue ... 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which.
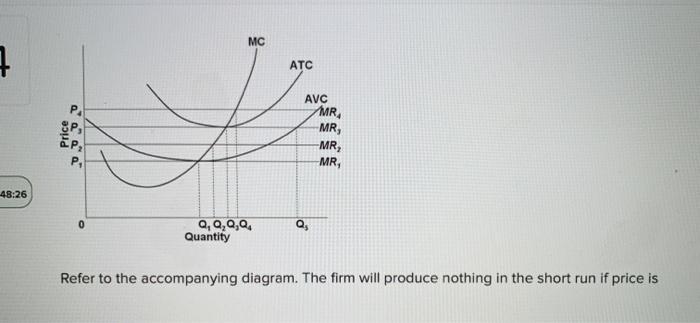
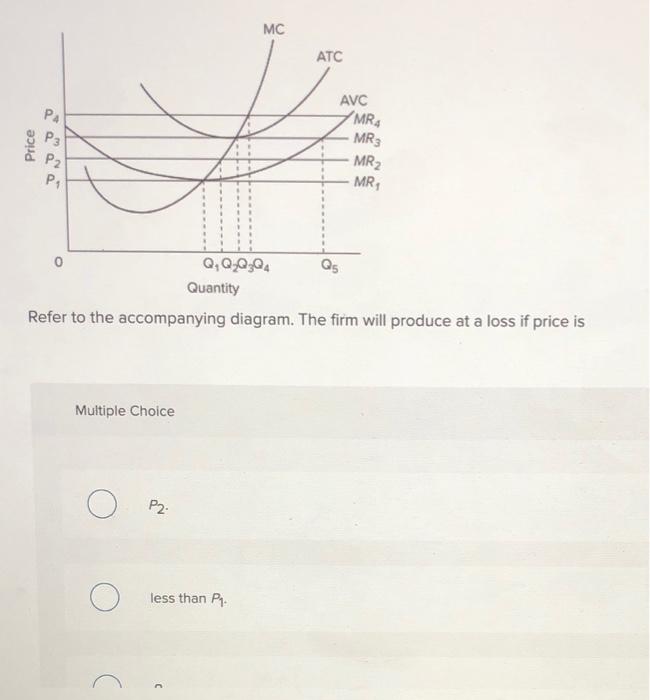
The shut down price is the minimum price a business needs to justify remaining in the market in the short run. A business needs to make at least normal profit in the long run to justify remaining in an industry but in the short run a firm will continue to produce as long as total revenue covers total variable costs or price per unit > or equal to average variable cost (AR = AVC).
At p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce
A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams Advice on drawing diagrams in the exam • The right size for a diagram is ½ of a side of A4 - don't make them too small - if needed, move onto a new side of paper rather than squeezing a diagram in at the bottom of a page 120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. At 3 units of output, total ...
At p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P2 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will A. produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. B. produce 44 units and earn only a normal profit. C. produce 68 units and earn only a normal profit. D. shut down in the short run. View Macroeconomics Quiz 13.pdf from ECO 3320 at University Of Dallas. 106. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the accompanying diagram. The firm will produce at a loss if price is less than P1. See Page 1. 72. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be zero. B) the firm will earn an economic profit. D) new firms will enter this industry. Answer: C. 73. 97. Award: 1.00 point At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce 14 units and realize an economic profit. produce 62 units and earn only a normal profit. produce 40 units and incur a loss. shut down in the short run. References Multiple Choice Difficulty: 02 Medium Learning Objective: 10-05 Explain how purely competitive firms can use the marginal-revenue-marginal-cost ...
If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm will produce: 1. 4 units at a loss of $109. 2. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 3. 8 units at a loss of $48.80. 4. zero units at a loss of $100. 2. Refer to the above data. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce: The firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least as much as the price indicated by the distance: a. F. b. E. c. N. d. P. e. G. ... In the accompanying diagram, this is optimal for prices in the range from 0 to P1. b. The firm operates in the short run despite sustaining 25. Refer to the above diagram. The firm will produce at a loss if price is: A. less than P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4. 26. Refer to the above diagram. The firm's supply curve is the segment of the: A. MC curve above its intersection with the AVC curve. B. MC curve above its intersection with the ATC curve. 70. Refer to the above diagram. At P1, this firm will produce: A. 47 units and break even. B. 47 units and realize an economic profit. C. 66 units and earn only a normal profit. D. 24 units and earn only a normal profit.
If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A) lose P1P 2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B) lose P1P 2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. 105. Refer to the above diagram. At P2, this firm will: A) produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. B) produce 44 units and earn only a normal profit. C) produce 66 units and earn only a normal profit. D) shut down in the short run. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 106. Refer to the above diagram. At P1, this firm will produce: Cambridge International AS and A Level Economics Answers to Coursebook activities Chapter 3 Government microeconomic intervention 30. Forces F1 and F2 act concurrently on point P, as shown in the diagram. The equilibrant of F1 and F2 is A. 14N southwest B. 14N southeast C. 20N southwest D. 20N southeast 31. The accompanying diagram shows a projectile moving with
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: A. Above P1. B. Above P3. C. Above P4. D. Between P2 and P3. 21. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3: A.
At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce 66 units and earn only a normal profit. 24 units and earn only a normal profit. 47 units and break even. 47 units and realize an economic profit.
Quick Quizzes. 1. When a competitive firm doubles the amount it sells, the price remains the same, so its total revenue doubles. 2. The price faced by a profit-maximizing firm is equal to its marginal cost because if price were above marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by increasing output, while if price were below marginal cost, the firm could increase profits by decreasing output.
That's because that when firm produce the output level where MR=MC (output level Q), price is greater than average variable cost. The loss from continuing the business is lower than the loss from totally shutting down. 2. (3.6 page 406) According to a report in the Wall Street Journal, during the fourth quarter of 2003,
If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce... 8 units at an economic profit of $16. ... At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce... 47 units and realize an economic profit. At P4 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will...
The accompanying graph (top of next page) summarizes the demand and costs for a firm that operates in a perfectly competitive market. a. What level of output should this firm produce in the short run? b. What price should this firm charge in the short run? c. What is the firm's total cost at this level of output? d.
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If product price is $60, the firm will A) produce 3 units and incur a $40 loss. B) shut down. C) produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. D) produce 4 units and realize a $120 economic profit.
View Additional Exercise - answer (1).pptx from ECO 2103 at INTI International College Penang. Additional Exercises Perfect Competition Graph Answer Which of the following industries most
2. an inefficient allocation to producers (some with higher costs produce while others with lower costs do not produce), 3. wasted resources from producers competing to sell, 4. inefficiently high quality. Compute the deadweight loss of a quota. Compute the quota rent, as the value of the right to sell under the quota. Question:
Therefore, if Firm 1 can move first, it does best to select "aggressive" in which case Firm 2 will select its best response "passive" earning Firm 1 a payoff of 33 and Firm 2 a payoff of 10. The Subgame perfect equilibrium: In period 2 Firm 2 will choose "passive" if Firm 1 chooses "aggressive" in period 1.
At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. At 3 units of output, total ...
120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams Advice on drawing diagrams in the exam • The right size for a diagram is ½ of a side of A4 - don't make them too small - if needed, move onto a new side of paper rather than squeezing a diagram in at the bottom of a page






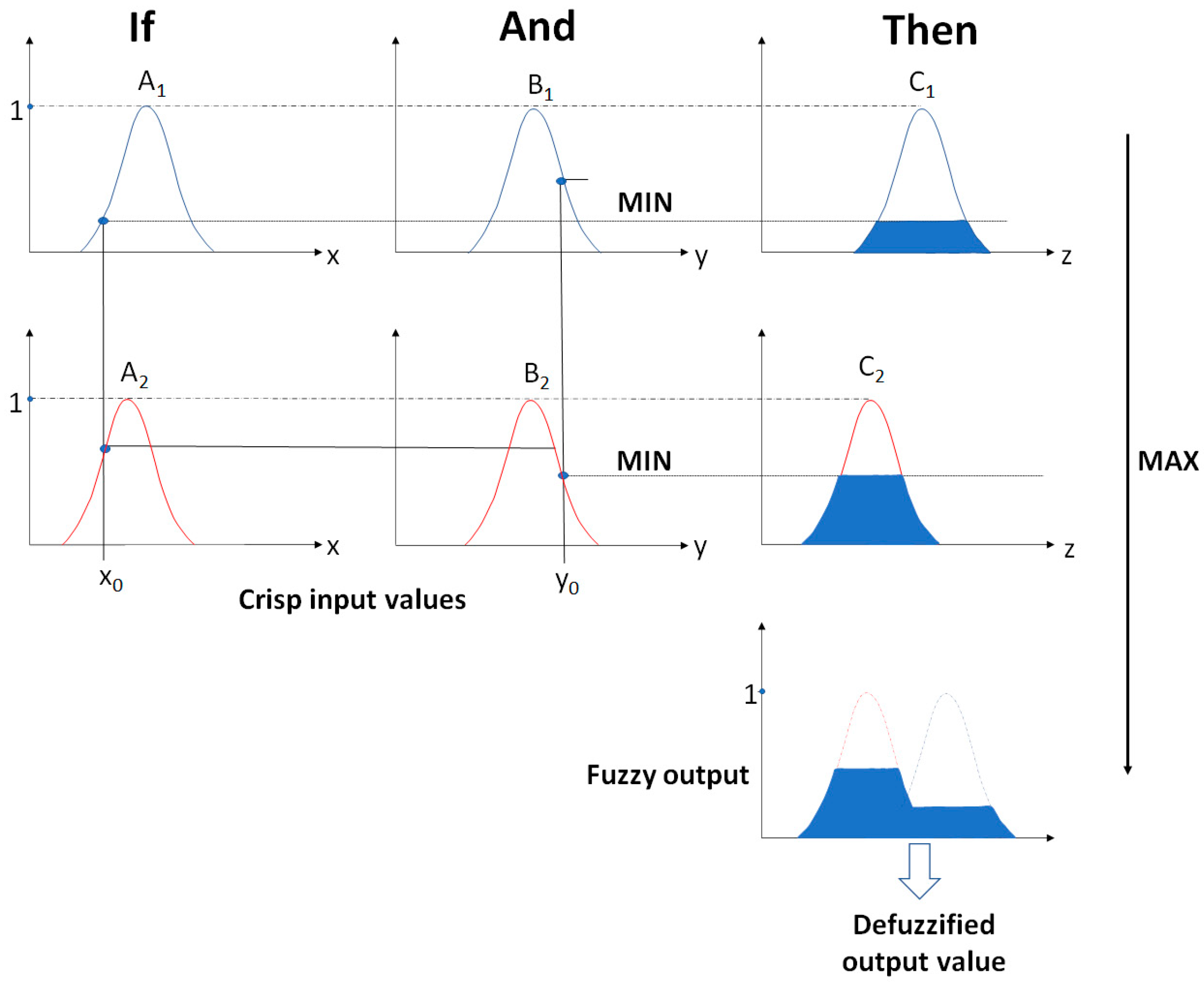






0 Response to "42 at p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce"
Post a Comment