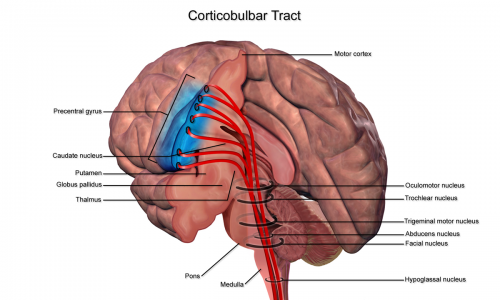
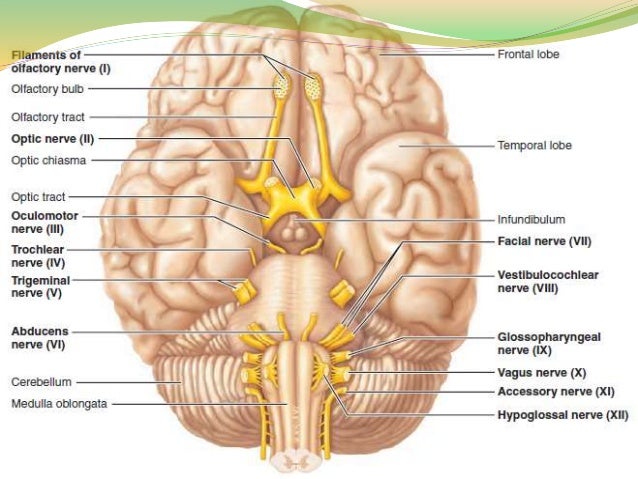
42 which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing?
Circulation. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) Both 1 and 2 e) All of these choices. e. The cerebellar cortex consists of folia, which are a) parallel folds of white matter. b) found in the vermis only. c) portions of the pyramids. d) parallel folds of gray matter. e) used in the RAS system.
The structure labeled 3 in the diagram is a a somatic motor neuron. D parasympathetic postganglionic neuron. The majority of these cranial nerves have both sensory and motor neurons though some of them only have motor neurons. Cranial nerve has a somatic motor function primarily involved in movement of the eyeball.
The cranial nerve functions are broken up into managing different aspects of your bodys daily tasks from chewing and biting to motor function hearing sense of smell and vision. 60 which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing?
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? asked Sep 25, 2015 in Anatomy & Physiology by VanDerLand. anatomy-and-physiology; A dentist identified the source of the college student's pain while chewing food or gum. Which cranial nerve was inflamed?
CN Names. 13 terms. wellz896 PLUS. Exam 4. 49 terms. wellz896 PLUS. Quiz Chapter 13 - Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves. 36 terms. wellz896 PLUS.
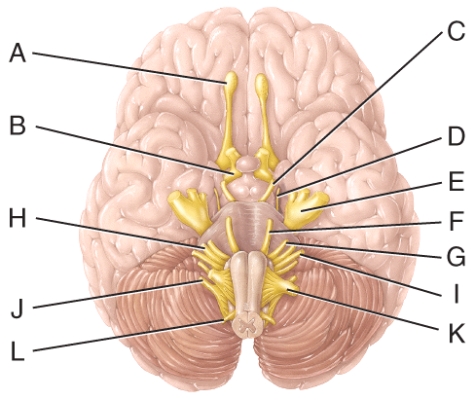
А 00 B ס ס ח וד D E F ОА B OC What is the cranial nerve labeled J and it's function? с A- B -Ε I F ס ח ד פ - x G J K O (CN 1) Olfactory; Sensory O (CN XI) Accessory; Motor O (CN V) Vagus; Both Sensory & Motor O (CN XII) Hypoglossal; Motor Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing?.
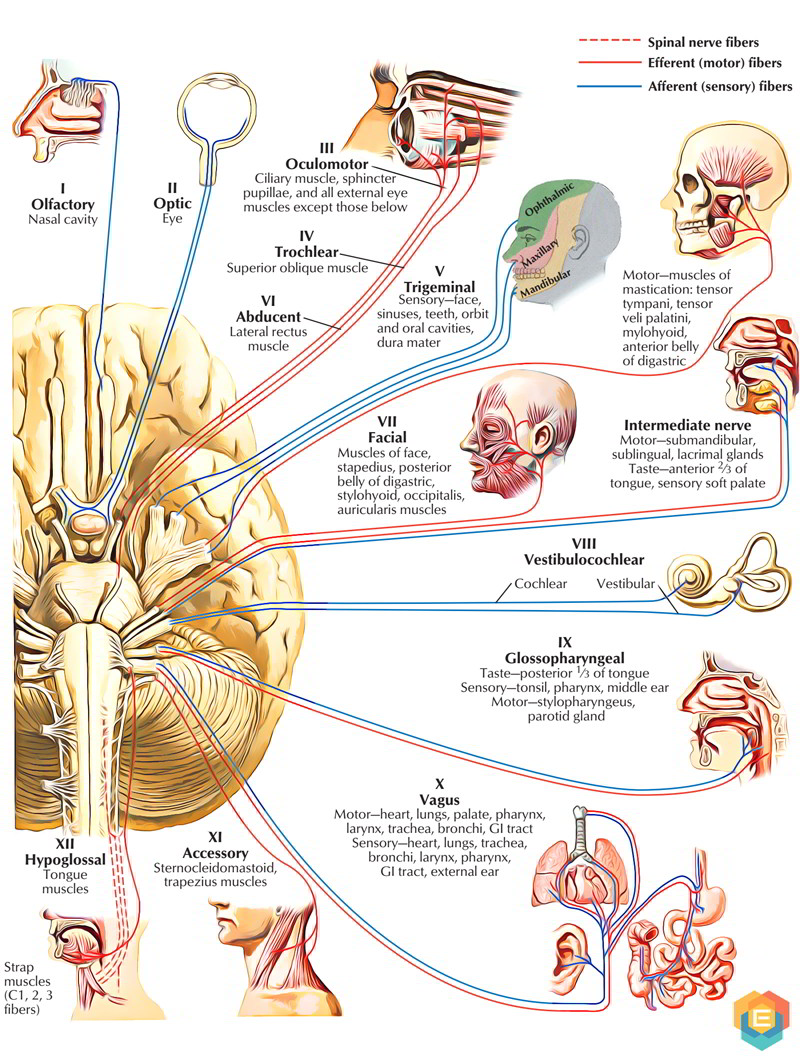
The trigeminal nerve is the largest of your cranial nerves and has both sensory and motor functions.. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions, which are: Ophthalmic. The ophthalmic division sends ...
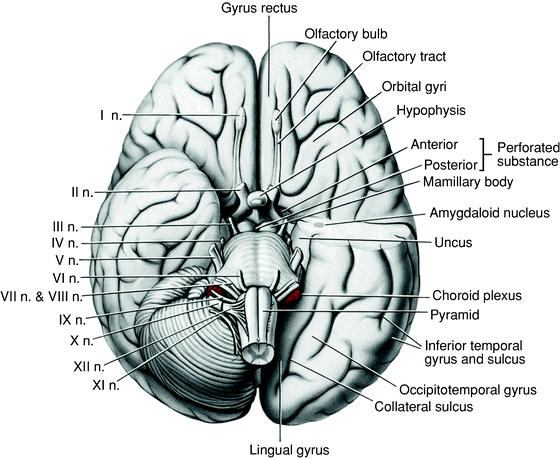
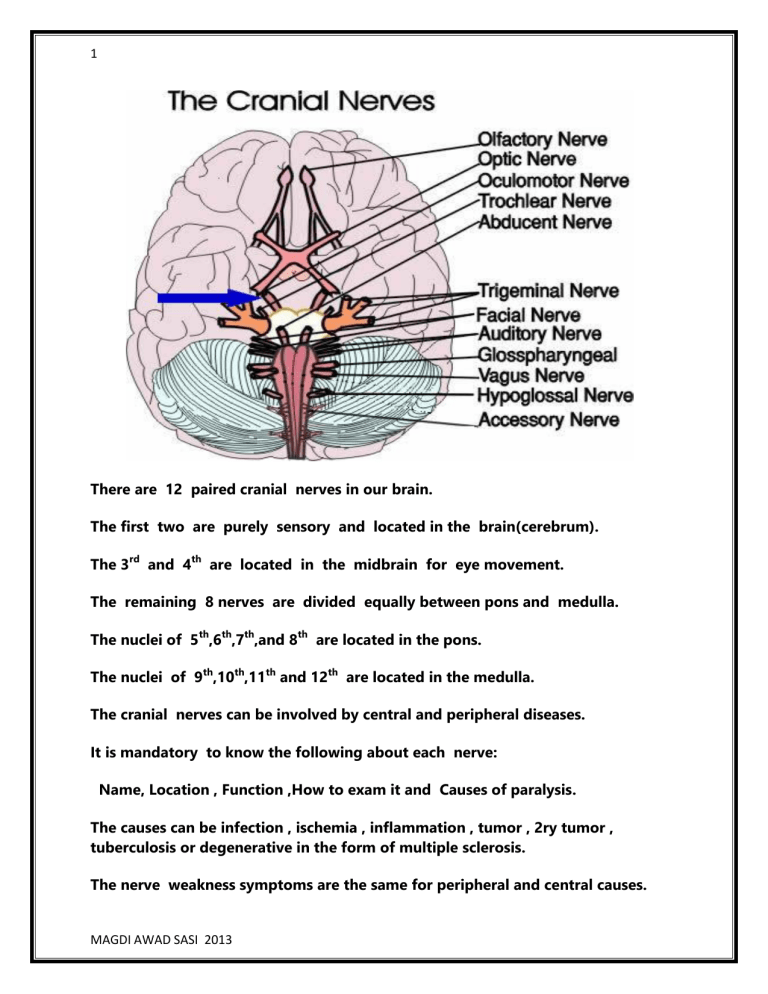
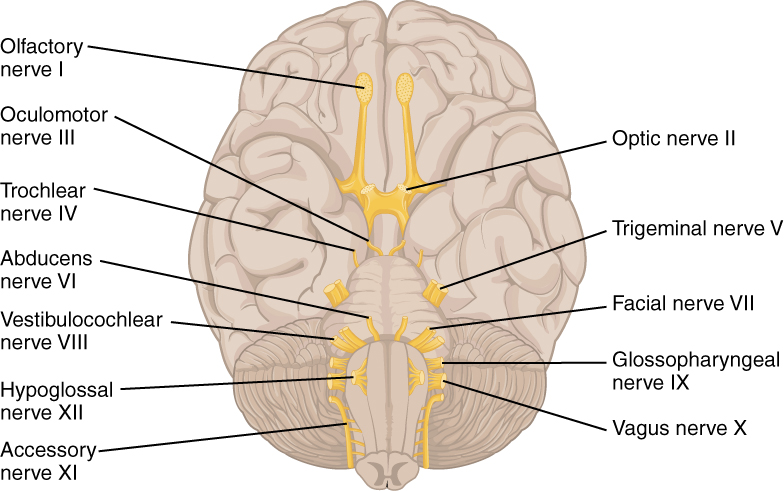
I. Olfactory Nerve. This nerve functions primarily for the sense of smell. Its name is derived from the Latin words 'olfactare', which means to sniff at, and 'olfacere', which means to smell.Among all the cranial nerves, this is the only one capable of self-renewal since it has the property to regenerate continually through adulthood.
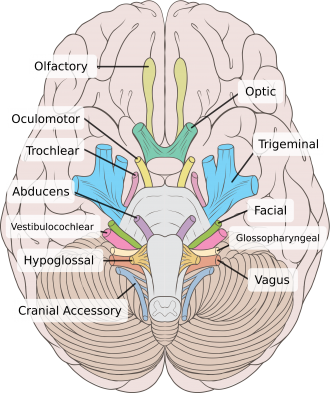
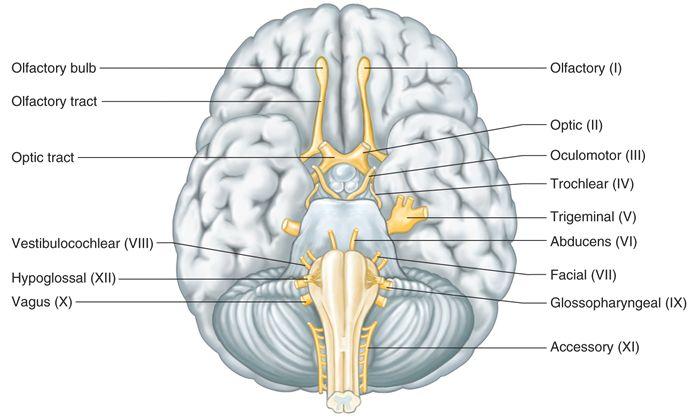
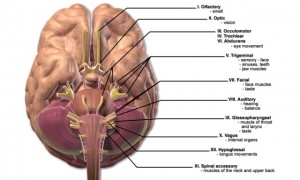
What are the 12 cranial nerves and their function? The 12 cranial nerves and their functions are - - Olfactory nerve (I) - Smell - Optic nerve (II) - Vision - Oculomotor nerve (III) - Eye movement,...
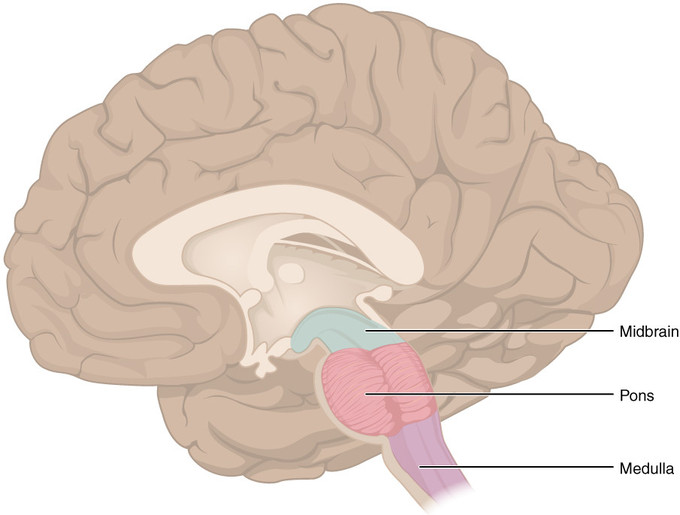
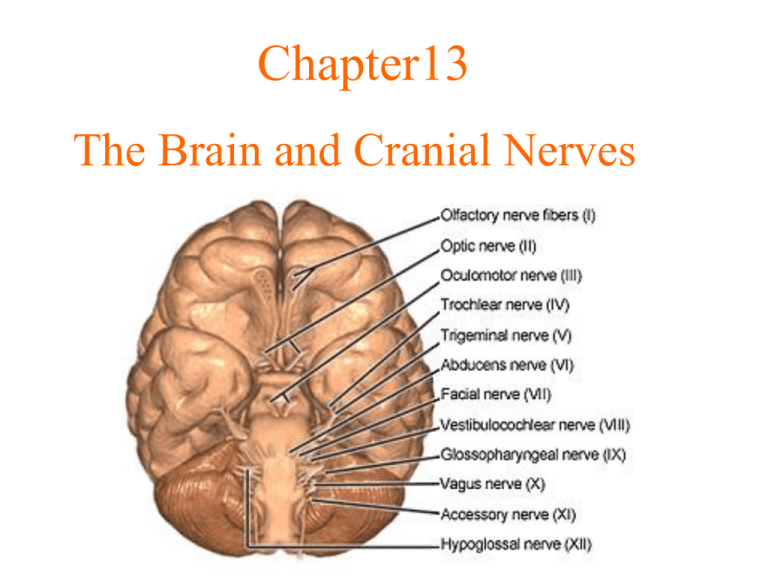
Quiz 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. The brain and spinal cord develop from the ______ neural tube. A)mesodermal B)endodermal C)ectodermal D)cranial E)caudal. This brain vesicle gives rise to the midbrain and cerebral aqueduct. A)Prosencephalon B)Mesencephalon C)Rhombencephalon D)Telencephalon E)Myelencephalon.
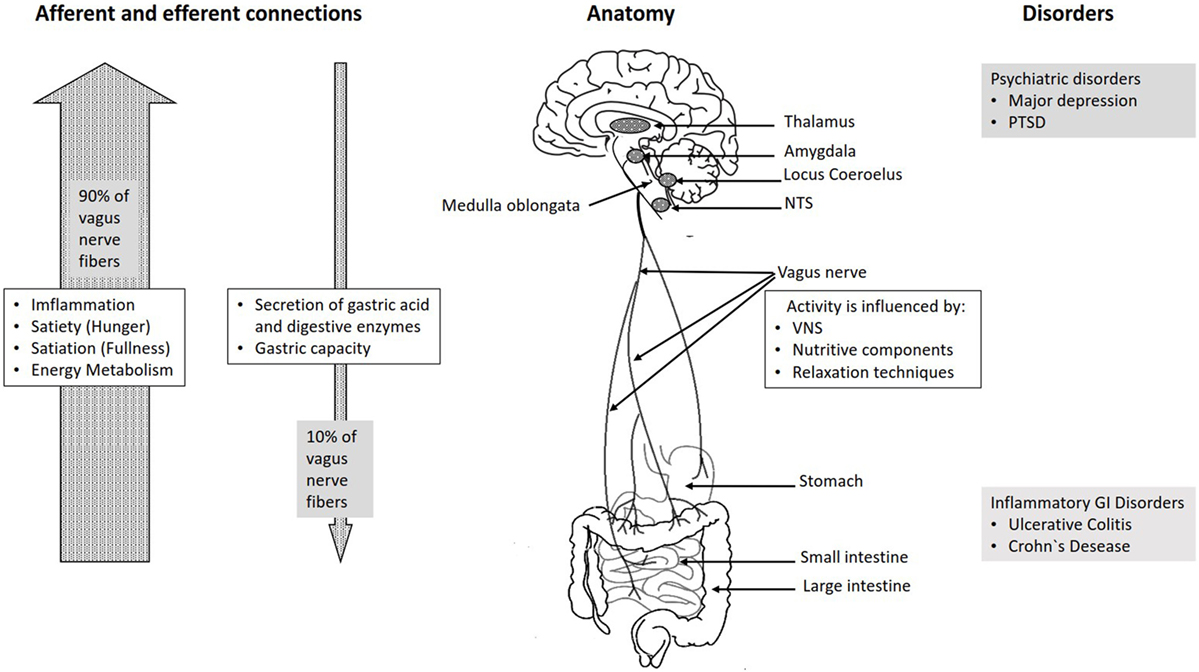
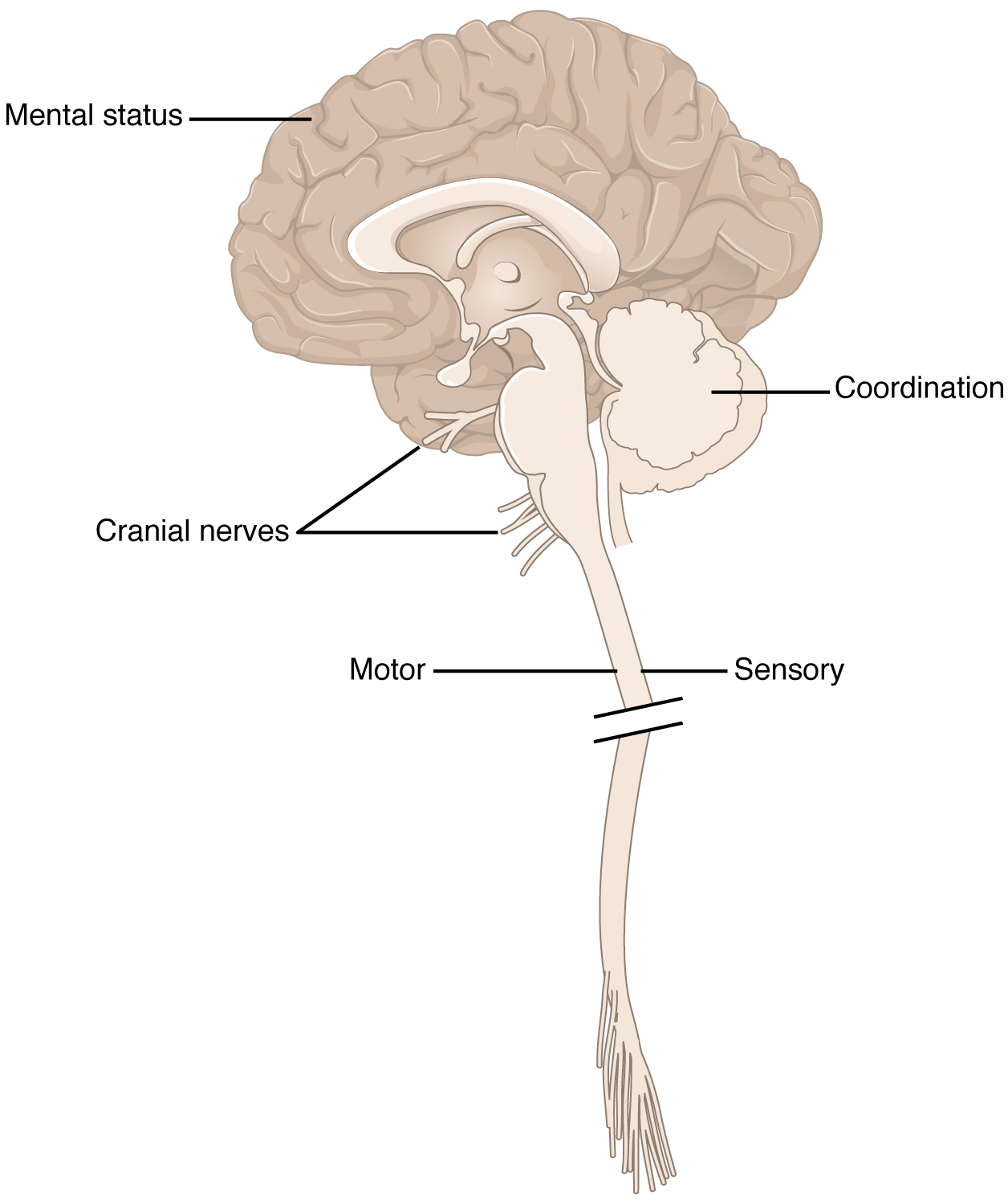
The CNS has two neural outputs: the somatic motor system, which innervates and commands skeletal muscles through motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates the functions of the body's internal organs through the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous systems.
24) This major portion of the brain is used to monitor movements initiated by the motor areas of the cerebrum. _____ Use the second diagram to the right to answer the next 6 questions. 25) Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball?
Cranial nerve has a somatic motor function primarily involved in movement of the eyeball. Bell S Palsy Facial nerve viig which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in stimulating secretion of saliva. Damage to which cranial nerve in the diagram by shingles or lyme disease produces bells palsy.
Cranial nerve has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? trigeminal (5) nerve Patients with damage in the left hemisphere often exhibit aphasia (inability to use or comprehend words).
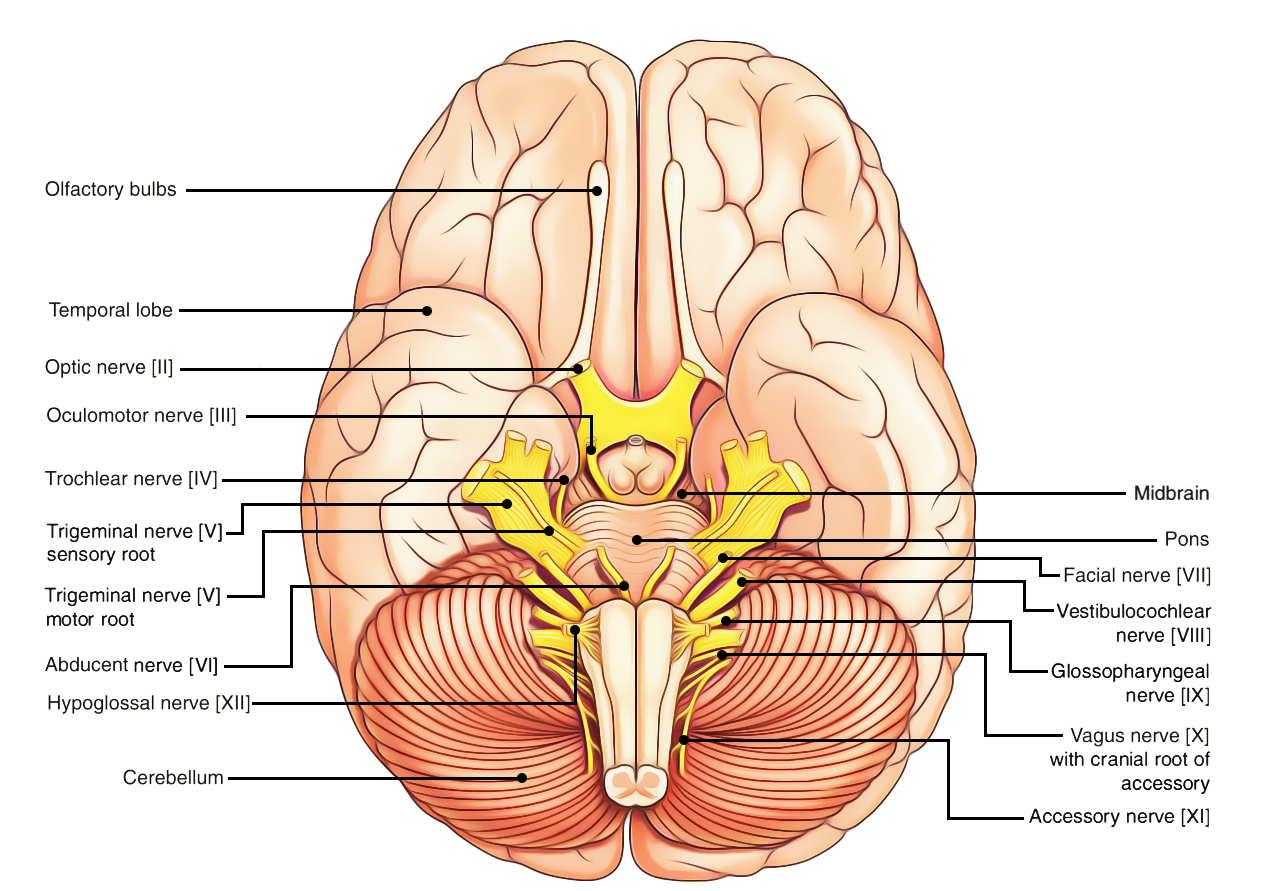
Motor cranial nerves Author: Nadia Solomon • Reviewer: Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD, PhD Last reviewed: October 28, 2021 Reading time: 21 minutes In this article we describe in detail the motor cranial nerves.. Anatomy is a tough subject for many students, especially when it comes to learning about the nervous system.Trying to learn about innervations of the head and neck takes this challenge to ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? E) trigeminal nerve. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? pyramids; it contains nuclei for equilibrium and movements of the eyeball ...
60) Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? E 61) The maxillary branch of this labeled cranial nerve is found in the area where dentists apply anesthetic drugs for numbing the upper jaw.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing. 1410 identify the termination of the optic nerve in the brain the foramen through which it exits the skull and its function. Damage to which cranial nerve in the diagram by shingles or lyme disease produces bells palsy.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball? ... Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? a. E. b. G. c. H. d. I. ... Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball and an autonomic function involved in iris muscle contraction? C The right hemisphere exhibits greater activity for which functions?
Motor: Somatic Motor to muscles of mastication (chewing muscles) Lesion: Loss of sensation in face and forehead or increased sensitivity to pain known as Trigeminal neuralgia. (Described Later). Also, muscle weakness of the muscles of mastication. Cranial Nerve 6 (CN VI): Abducens. Major Function: Somatic Motor to lateral rectus eye muscle
The trochlear nerve provides somatic motor innervation to the superior oblique eye muscle. This cranial nerve originates at the trochlear nucleus located in the tegmentum of the midbrain at the inferior colliculus level and exits the posterior side of the brainstem. It is also a pure motor nerve fiber.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball? C . Damage to which cranial nerve in the diagram will cause the inability of an eyeball to move laterally beyond the midpoint? F . Patients with damage in the left hemisphere often exhibit aphasia (inability to use or ...
Cranial Nerve IV. trochlear, motor, movement of the eyeball. Cranial Nerve V. trigeminal, mixed, sensory function- conveys impulse for touch, pain and temperature sensations and proprioception, somatic motor function- chewing. Cranial Nerve VI. abducens, motor, movement of the eyeball. Cranial Nerve VII.
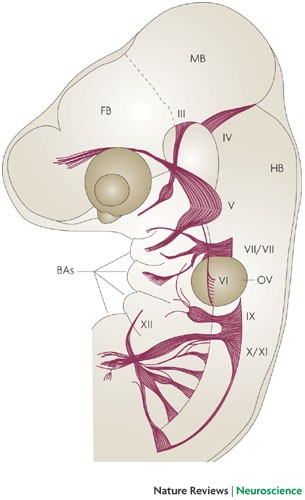
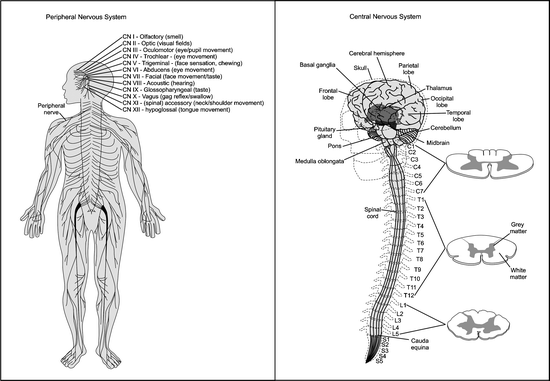
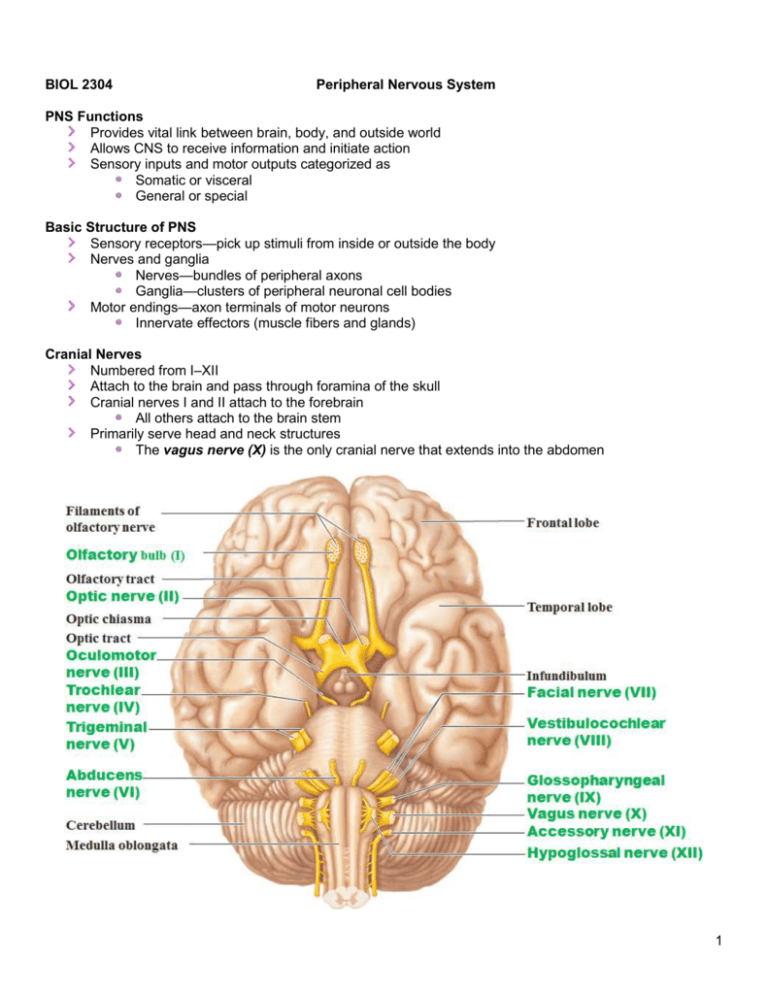
Cranial Nerves. The cranial nerves are composed of twelve pairs of nerves that emanate from the nervous tissue of the brain.In order to reach their targets they must ultimately exit/enter the cranium through openings in the skull.Hence, their name is derived from their association with the cranium. The following are the list of cranial nerves, their functions, and tumor examples:
Which of the following cranial nerves is primarily responsible for changing facial expressions? Facial. 56. Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? B. 57. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing? E. 58.
Cranial nerves. The cranial nerves contain the sensory and motor nerve fibers that innervate the head. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons lie either in receptor organs (e.g., the nose for smell, or the eye for vision) or within cranial sensory ganglia, which lie along some cranial nerves (V, VII-X) just external to the brain.
Each cranial nerve has a specific set of functions. Some of the cranial nerves control sensation, some control muscle movement, and some have both sensory and motor effects. Several of the cranial nerves run through bones in the skull.
A e b g c h d i e j. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing. The average person is exposed to commercials a year.
















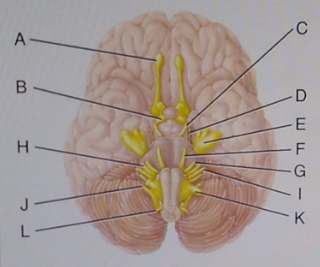


0 Response to "42 which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing?"
Post a Comment