37 orbital diagram of f-
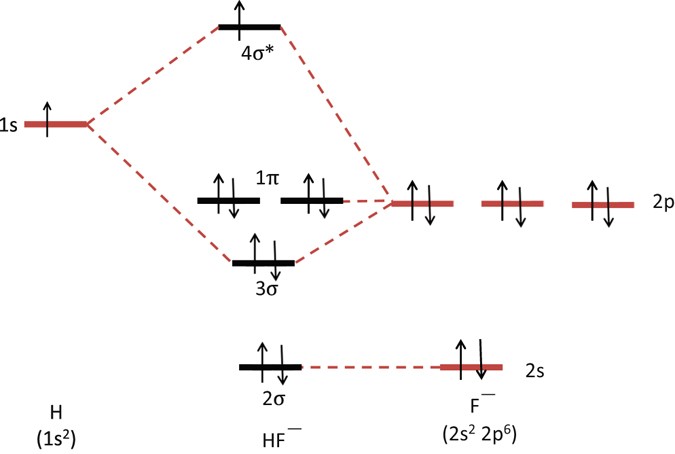
Molecular orbital (MO) level diagram for H 2 TBP and MTBP complexes. The values of higher occupied molecular orbital-lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) gaps are given in eV. Table 1. Molecular parameters 1 of H 2-tetrabenzoporphyrin and its metal complexes optimized at PBE0/def2-TZVP level. The magnetization measurement was performed in the Bi0.3Sb1.7Te3 single crystal. The magnetic susceptibility revealed a paramagnetic peak independent of the experimental temperature variation. It is speculated to be originated from the free-aligned spin texture at the Dirac point. The ARPES reveals that the Fermi level lies below the Dirac point.
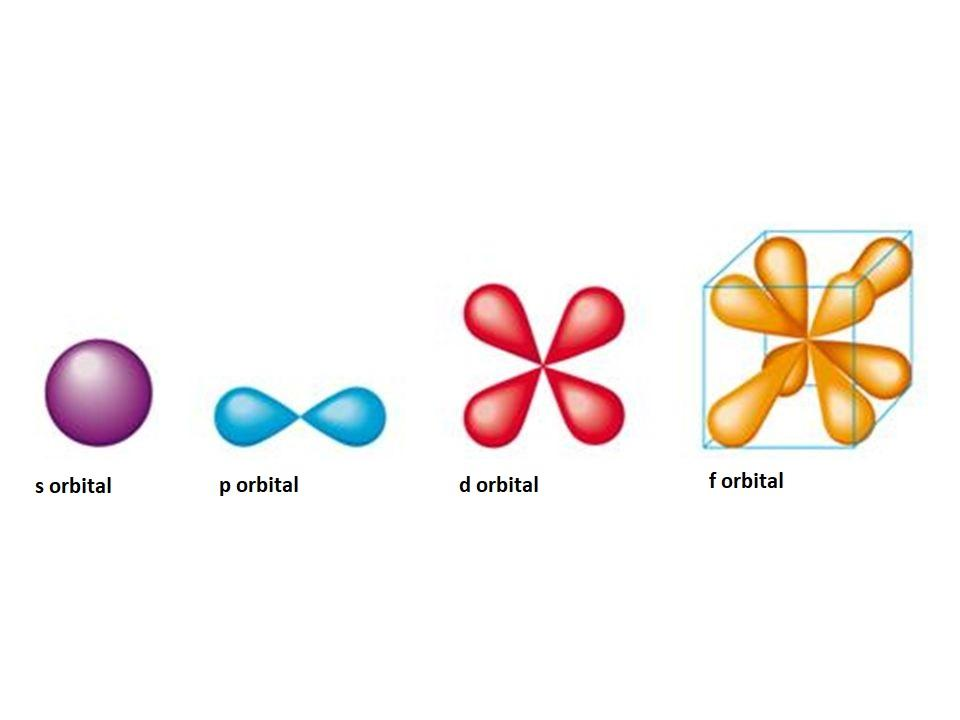
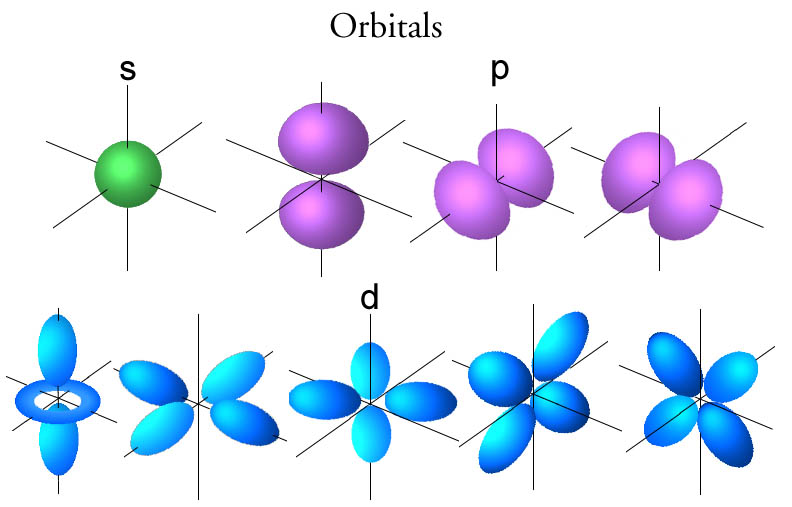
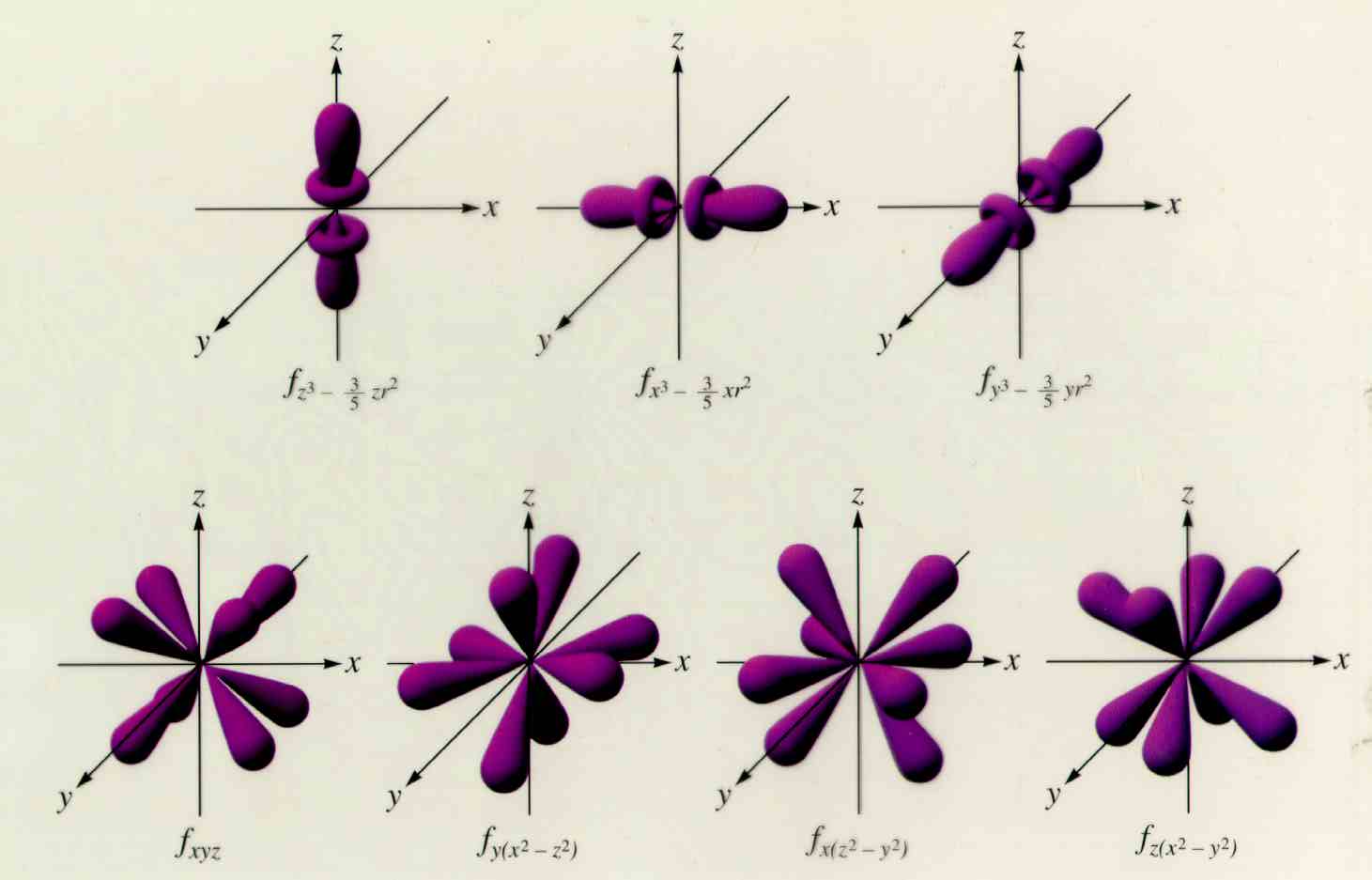
Dec 27, 2021 · The f orbitals are given the designations and f z 3. Each f orbital has a multi-lobed and complex shape with several nodal points. The 4f y 3 - 3x 2 y orbital corresponds to l = 3, ml = -3, and n = 4; The 4f xyz orbital corresponds to l = 3, ml = -2, and n = 4. The 4f 5yz 2 - yr 2 orbital corresponds to l = 3, ml = -1, and n = 4.
Orbital diagram of f-
Stellar dynamics is the branch of astrophysics which describes in a statistical way the collective motions of stars subject to their mutual gravity.The essential difference from celestial mechanics is that the number of body >>; typical galaxies have upwards of millions of macroscopic gravitating bodies and countless number of neutrinos and perhaps other dark microscopic bodies. View this answer. Orbital diagram of F − F −. The atomic number of F is 9. After removing one electron, fluorine becomes F − F − and in this case... See full answer below. 4. Which of the four quantum numbers (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) determine (a) the energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom and in a many-electron atom, (b) the size of an orbital, (c) the shape of an orbital, (d) the orientation of an orbital in space. (4 points) 5.
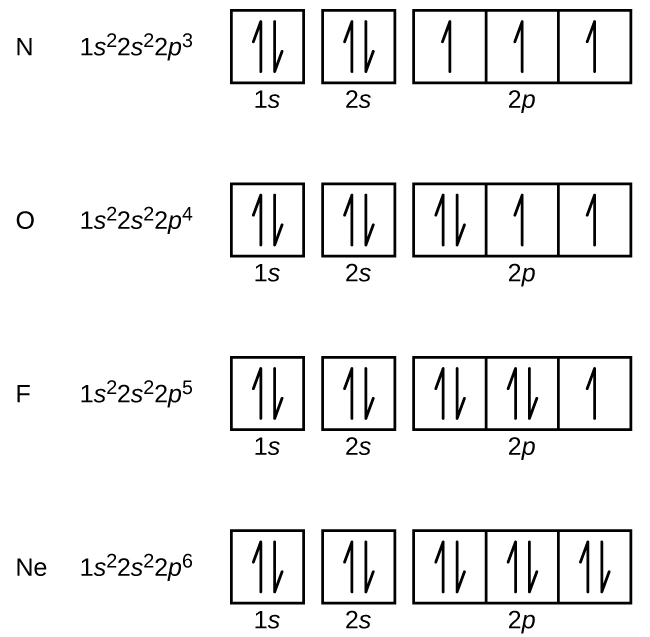
Orbital diagram of f-. Start studying Cisco Chapter 4. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Free DIY garden tool shed plans, 6ftx4ft, slanted roof. Learn how to make your own shed with step by step instructions. 👍 Correct answer to the question Careers in psychology that are expected to grow in the future include - ehomework-helper.com Fluorine (F) electron configuration with full orbital diagram. Fluorine (F) is the 9th element in the periodic table and the first element in group-17. The standard atomic mass of fluorine is 18.998403 and its symbol is ‘F’. The period of fluorine is 2 and it is a p-block element.
Jan 01, 2022 · Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ... Postby Vincent Nguyen 3G » Sat Jan 15, 2022 1:17 am. Protonation refers to giving a proton to another molecule, so percent protonation typically refers to what percent of the original acid was able to give away a proton. We can typically find this by dividing the concentration of the conjugate base by the original concentration of the acid. Jan 03, 2022 · The electronic configuration of Fluoride ion is 1s^2 3s^2 2p^6. As the energy of the atomic orbital is 1s^2 < 2p^6 (2p^2_x = 2p^2_y = 2p^2_z), the orbital energy diagram is represented as shown below: Hottest videos. Widget. ★★★ Correct answer to the question: Name each angle in four ways. Please help - edu-answer.com
Ground State Electron Configuration Calcium - 9 images - fluorine electron configuration f with orbital diagram, e configs2, This 3d orbit diagram is a feature of our 3D Solar System Simulator and shows the orbit of Comet C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) with respect of the Sun and the orbits of the major planets. The position of Comet C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) and the planets along their orbits in this diagram accurately represents the current configuration of the objects in the Solar ... Schematic representation energy level diagram of FTO/TiO \(_2\) with P3HT films with different thickness: (a) 80 nm, (b) 70 nm, (c) 60 nm, (d) 46 nm, (e) 41 nm and (f) 32 nm. The HOMO and LUMO energy level position of P3HT at different thickness and CB and VB level energy of TiO \(_2\) are shown for comparison Jun 23, 2016 · #"F: " 1s^2 2s^2 2p^5# Now, the #"F"^(-)# anion is formed when #1# electron is added to a neutral fluorine atom. Notice that the 2p-subshell of the neutral atom contains #5# electrons. Its maximum capacity is actually #6# electrons, two electrons for each p-orbital.
4. Which of the four quantum numbers (n, ℓ, mℓ, ms) determine (a) the energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom and in a many-electron atom, (b) the size of an orbital, (c) the shape of an orbital, (d) the orientation of an orbital in space. (4 points) 5.
View this answer. Orbital diagram of F − F −. The atomic number of F is 9. After removing one electron, fluorine becomes F − F − and in this case... See full answer below.
Stellar dynamics is the branch of astrophysics which describes in a statistical way the collective motions of stars subject to their mutual gravity.The essential difference from celestial mechanics is that the number of body >>; typical galaxies have upwards of millions of macroscopic gravitating bodies and countless number of neutrinos and perhaps other dark microscopic bodies.
























0 Response to "37 orbital diagram of f-"
Post a Comment