40 draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens
Two situations involving objects and diverging lenses are shown below. Draw three principal rays for these two situations. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge and then describe the image in the space provided (i.e. relative location, magnification, orientation, etc.). Problem: A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) where the three principle waves converge.B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. 1.
We derived the lens equation above by using a specific case involving a convex lens. The equation can be applied to all situations involving a convex lens or a concave lens if we use the following sign conventions. The focal length is positive for a converging lens, and negative for a diverging lens.

Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens
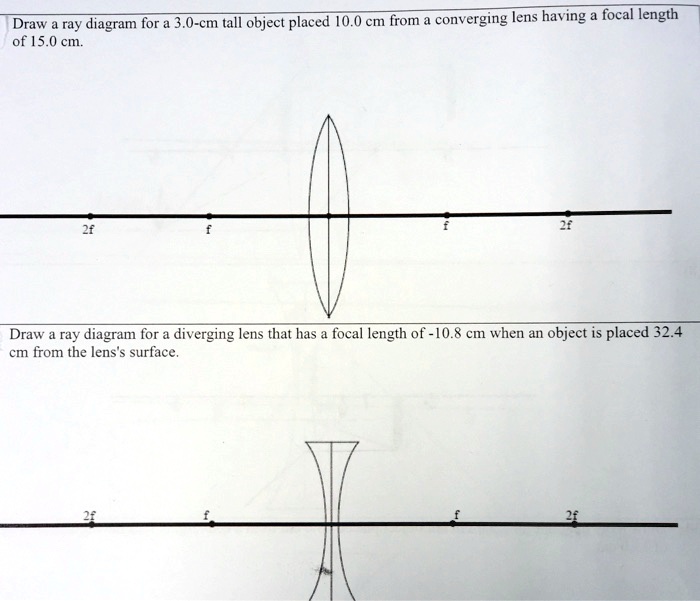
Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis. A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens. Jared Loggins, visiting assistant professor at Amherst College of Black Studies and Political Science, is the author of a new book on King: Prophet of Discontent Martin Luther King Jr. and the Critique of Racial Capitalism · Find information about the College’s response to the evolving situation ... A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three... Solved • Jul 10, 2020 6:30 PM - 7:30 PM Current 6th and 7th Grade Parent Night/Next Year 7th and 8th Grade · 5:30 PM - 8:00 PM 7th Grade BBB vs WMS @ CMS The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further ... A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens.The ray tacing needs to have the three principal rays.Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principle waves converge.. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further ... A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.
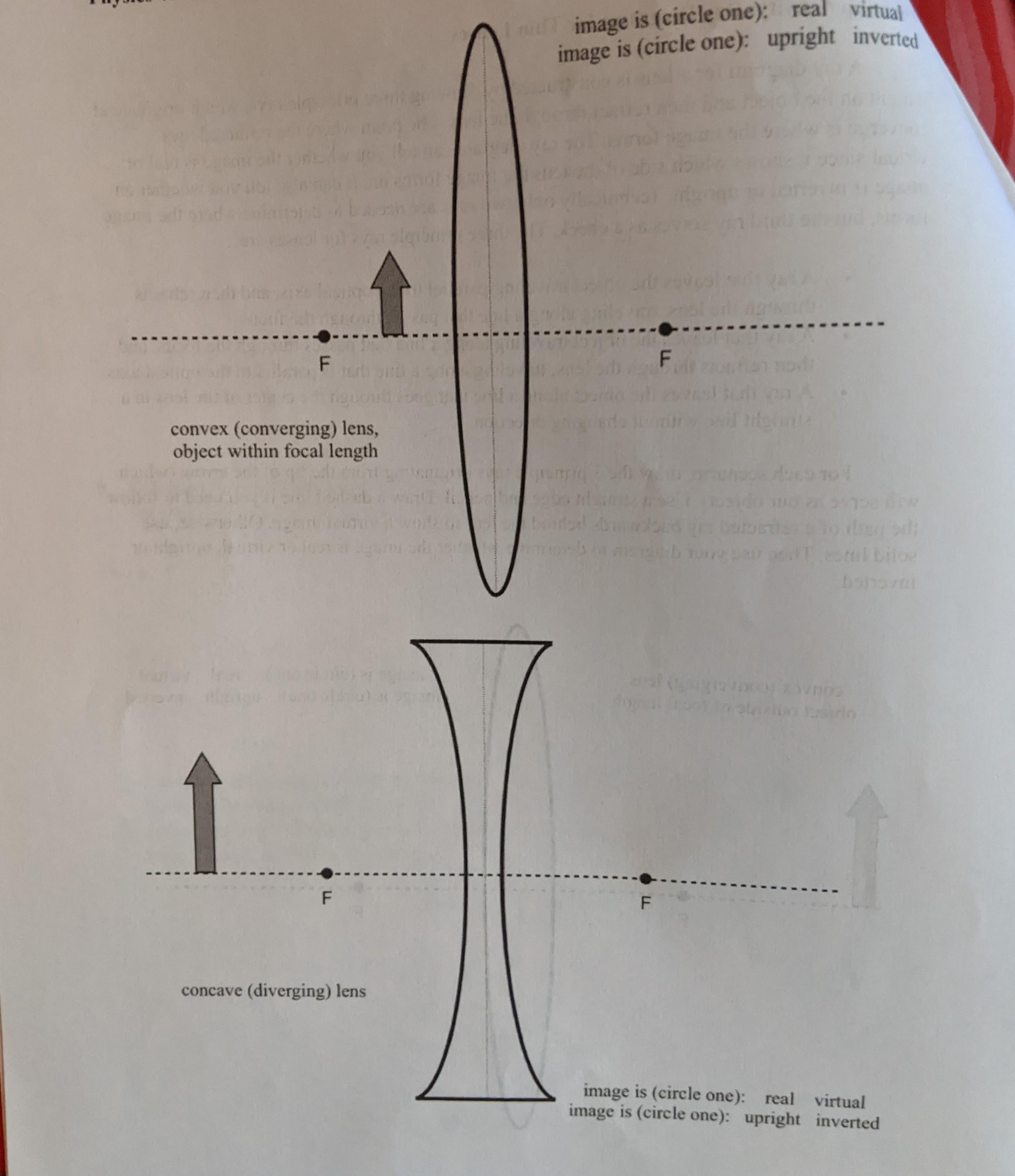
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will ... a) draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tacing needs to have the three principal ... A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tacing needs to have the three principal ... (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its center. (f) Light rays from a point source (object) passing through a lens emerge convergent to a point or divergent from a point.
Method for drawing ray diagrams – Concave lens. How to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens that shows the principal focal point and image size and location.
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then, verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
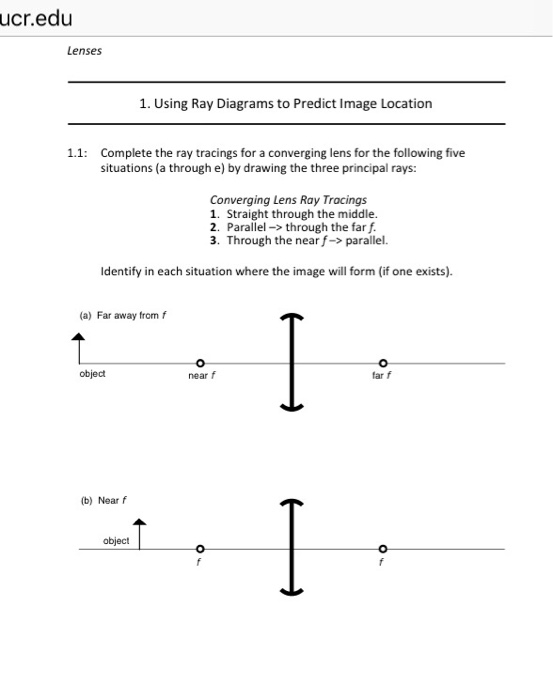
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
Drawing ray Diagrams for lenses: Since the light refracts through the lens, and doesn't bounce off, like a mirror, when drawing ray diagrams, there is ONE difference. Instead of drawing the 3rd ray through the center of curvature, draw the third ray through the CENTER of the lens, it will pass straight through, no refraction (this is the ...
For aconvex lens, we draw the ray diagram as follows: Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the middle of the lens. Its direction is not changed. Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis. It is refracted by the lens to pass through the focal point. F From the diagram we see that the image in this example is inverted.
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science.
Draw a ray diagram because that the following case involving a diverging lens. Likewise draw the image on the beam diagram whereby the three primary rays converge. Because the 3 refracted rays space diverging they have to be prolonged behind the lens in order to intersect. Diverging lenses beam diagrams.
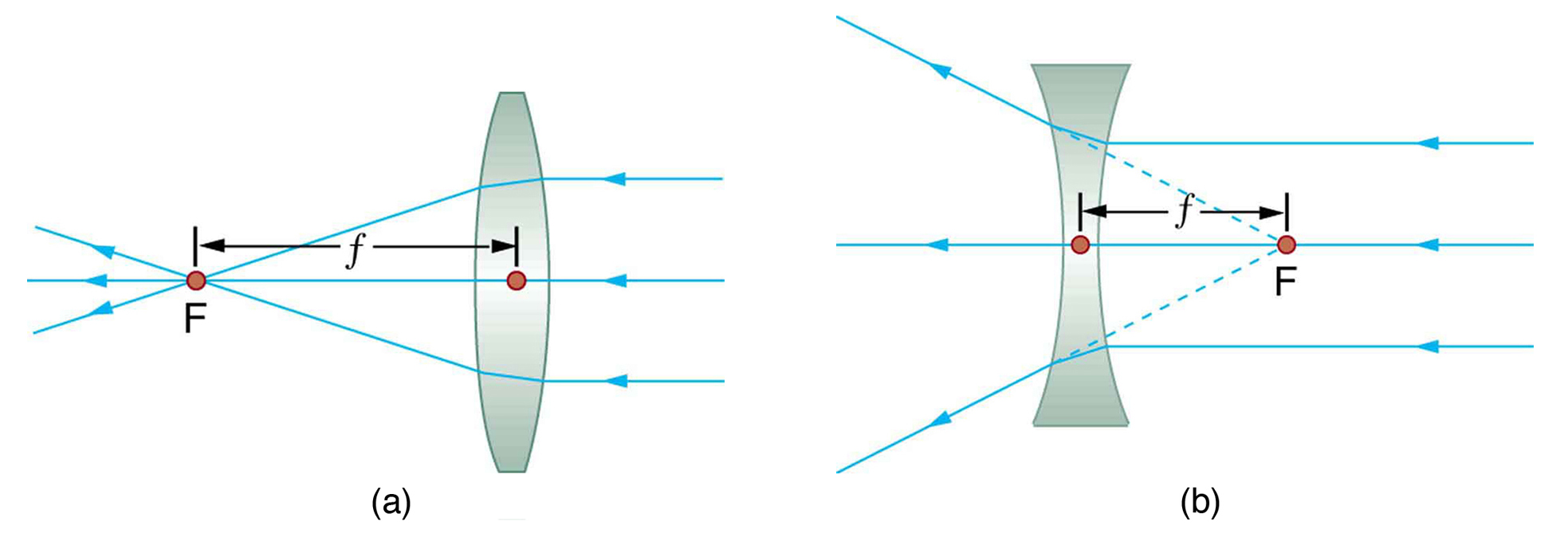
Figure 16.26 Rays of light enter a concave, or diverging, lens parallel to its axis diverge and thus appear to originate from its focal point, F. The dashed lines are not rays; they indicate the directions from which the rays appear to come. The focal length, ƒ, of a diverging lens is negative.An expanded view of the path taken by ray 1 shows the perpendiculars and the angles of incidence and ...
November 18, 2021 - For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
When drawing ray diagrams for lenses, there are a few more important things to note. Firstly, lenses can either be drawn as lens shapes or as lines with arrows on them. The convention is that a diverging lens has inwards pointing arrows and a converging lens has outwards pointing arrows, mimicking the shapes of the lenses.
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. b) Use a ruler to measure the …
Earlier in Lesson 5, we learned how light is refracted by double concave lens in a manner that a virtual image is formed.We also learned about three simple rules of refraction for double concave lenses: . Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such that its ...
The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length · The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image ...
Ray diagrams for mirrors. You must be able to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors, and be able to calculate image and object heights, Spherical Mirrors: concave and convex mirrors. For situations involving multiple lenses or mirrors, the image formed from one of these components can act as the object for another one.
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The a) ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays r Use a ruler to measure the ...
Transcribed image text: Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.
The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens.
(b). In this case, the index of refraction of the lens material is less than that of the surrounding medium. Under these conditions, a biconvex lens will be divergent. 5. Although a ray diagram only uses 2 or 3 rays (those whose direction is easily determined using
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis.

























0 Response to "40 draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens"
Post a Comment