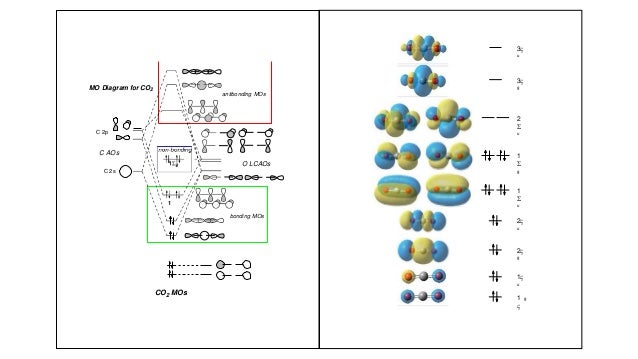
40 mo diagram for co2
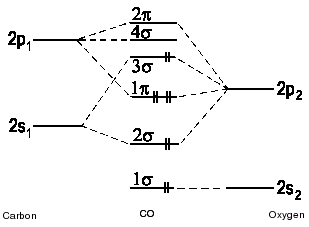
Carbon Dioxide by Reducible Representations Γ2s= Ag+ B1u Γ2pz= Ag+ B1u Γ2px= B2g+ B3u Γ2py= B3g+ B2u B3u B2u Ag Ag 2p x 2p y 2p z 2s B2g B3g B1u B1u These are the same group orbital symmetries that we got using inspection. We can (re)draw them. 5. Find matching orbitals on central atom Ag B1u B3u B2u 6. Build MO diagram… The Molecule. CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN] - and with N 2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than CO. The formal bond order of CO is 3, from about one σ- bond and two π- bonds. Its most important property is burning in air to give CO 2 , in the combustion of fossil fuels.
6.2.2: Carbon dioxide. Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for CO 2. Step 1. Find the point group of the molecule and assign Cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. Step 2. Identify and count the pendant atoms' valence orbitals. Step 3. Generate the Γ 's. Step 4.

Mo diagram for co2
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Introduction: Methane, CH 4. Using the carbon and hydrogen atomic orbitals, methane, CH 4, is constructed by overlapping the carbon's one 2s and three 2p AOs with the four hydrogen 1s AOs.. Methane's MOs have a topology similar to the AOs of carbon, but the structure can be very difficult to visualise, so the methane MO construction diagrams A, B and C (below) are shown with the AOs and MOs ... MO-Diagram for the first 10 elements: Works great for O 2-> explains O 2's paramagnetism But predicts B 2 to be diamagnetic-> Orbital Mixing! 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic ... 5.4.2 Carbon Dioxide's Molecular Orbital Diagram
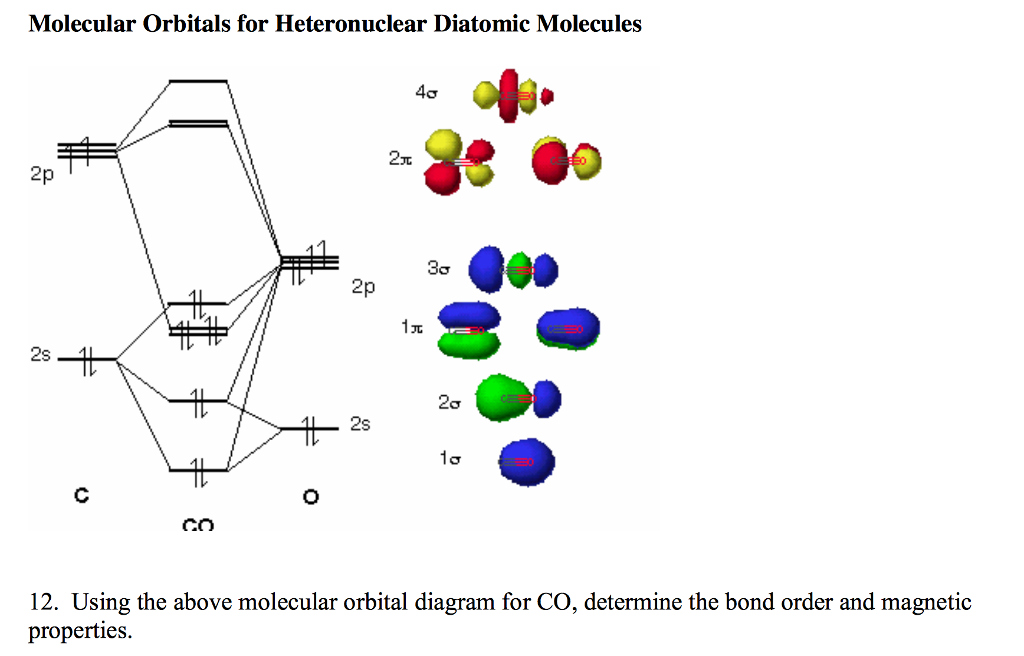
Mo diagram for co2. Apr 06, 2019 · Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions – Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc. . σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... CO Lewis Structure, Geometry, and Hybridization. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a tasteless and odorless flammable gas that is quite toxic in nature to the fauna. It is so because, carbon monoxide uses hemoglobin, an oxygen carrier, to reach throughout the body when in a concentration of more than 35ppm. The carbon monoxide is produced from the ... "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram.
1. The Lewis. Molecular Orbital theory (MO) is the most important quantum mechanical theory This particular diagram shows the orbitals for both the hydrogen atom and the. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. The valence electron configuration of "O" is ["He"] 2s^2 2p^4. Jmol Molecular Models Showing Orbitals for CO2. ... To view a model, click on an orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown ... Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram In a Molecular Orbital Diagram, the 2s orbital of oxygen is nonbonding because of the high energy difference between carbon and oxygen atoms. Based on the rules of the Lewis Structure, all 16 electrons are filled upon bond formation, but the nonbonding orbitals remain vacant, as in the case of CO2.
Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory May 09, 2018 · A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. Q-ton is a heat pump with natural R744 (CO2) refrigerant to be used for high temperature domestic hot water production in residential, commercial, tourist and industrial applications. Q-ton can heat and produce hot water up to 90°C in the presence of an outdoor temperature of -25°C. CO2 MOs MO Diagram for CO2 C 2p C 2s bonding MOs antibonding MOs C AOs O LCAOs 1 3 u 3 g 2 u 1 g 1 u 2 u 2 g 1 u 1 g 15. Molecular orbital theory for SF6 molecule- • Electronic configuration of sulphur: • Electronic configuration of Fluorine: • Total number of valence electron: • Hybridization: • Structure of SF6-
Use the following MO diagram for Be2, Be2+, and Be2-. Based on this diagram, Be2+ and Be2- are both more stable than Be2. The paramagnetism of O2 is explained by ... Which of the following best describes CO2? It has a molecular geometry that is non-linear molecular shape with no lone pairs on the I atom.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2) However, unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2, there are oxyge...
I am fairly sure the first diagram I drew for carbon dioxide is wrong in terms of showing π bonding. This is because we use a π orbital twice, which isn't possible. The second diagram corrects this by realizing there are two unused p orbitals on the carbon.
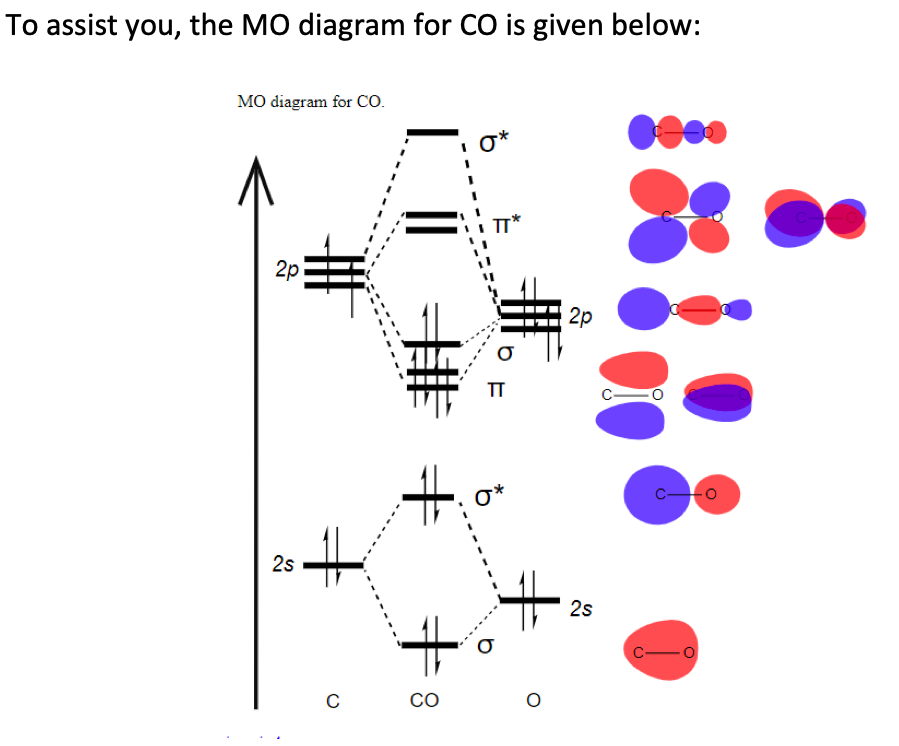
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Now carbon monoxide's MO diagram is:
Oct 05, 2020 · File:MO Diagram CO2.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 406 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 162 × 240 pixels | 325 × 480 pixels | 406 × 600 pixels | 520 × 768 pixels | 694 × 1,024 pixels | 1,387 × 2,048 pixels | 420 × 620 pixels.
Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 17, 2020 by Maisa (45.7k points) selected Dec 18, 2020 by Panna01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic configuration of C atom: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. ...
MO diagram for dihydrogen. Here electrons are shown by dots. ... This MO is called the bonding orbital and its energy is lower than that of the original atomic orbitals. A bond involving molecular orbitals which are symmetric with respect to rotation around the bond axis is called a sigma bond (σ-bond). Hope it helps you,
MO Calculation These orbitals were calculated at a low ab initio level (rhf/3–21g*) which can, however, show bond polarisation and fully delocalised molecular orbitals At the much higher level df/6-311g(2df) the calculated molecular orbital models look very similar, but the weakly antibonding MO σC(2 p )O(2 p ) appears below the bonding π ...
Apr 25, 2020 · 1 answerQuestion #112252. Draw molecular orbital diagram for CO2. 1. Expert's answer. 2020-04-27T01:53:22-0400. Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO2.
The lewis structure of CO2 can be with some simple steps, but before that, it is important to understand lewis structure properly. So lewis structure generally gives us an idea about the nature of bonding and octet fulfillment of the atoms. According to the octet rule, an atom attains stability by fulfilling its octet. For example, in CO2, carbon needs 6 electrons to fulfill the octet, whereas oxygen needs only 2 electrons. Now, let us quickly go through the steps for creating a lewis structure of any compound. Step 1– First and foremost we need to calculate the total valence electrons present in the molecule. Care should be taken regarding +, – signs. A ‘+’ sign means losing electrons and ‘-‘ means gaining. Step 2– Next we need to figure out the central atom of the molecule. Mostly the atom with the highest bonding sites is the central atom. Step 3– Next step will be, creating a skeleton containing only single bonds. Step 4– Then we need to complete the octet of the atoms with the...
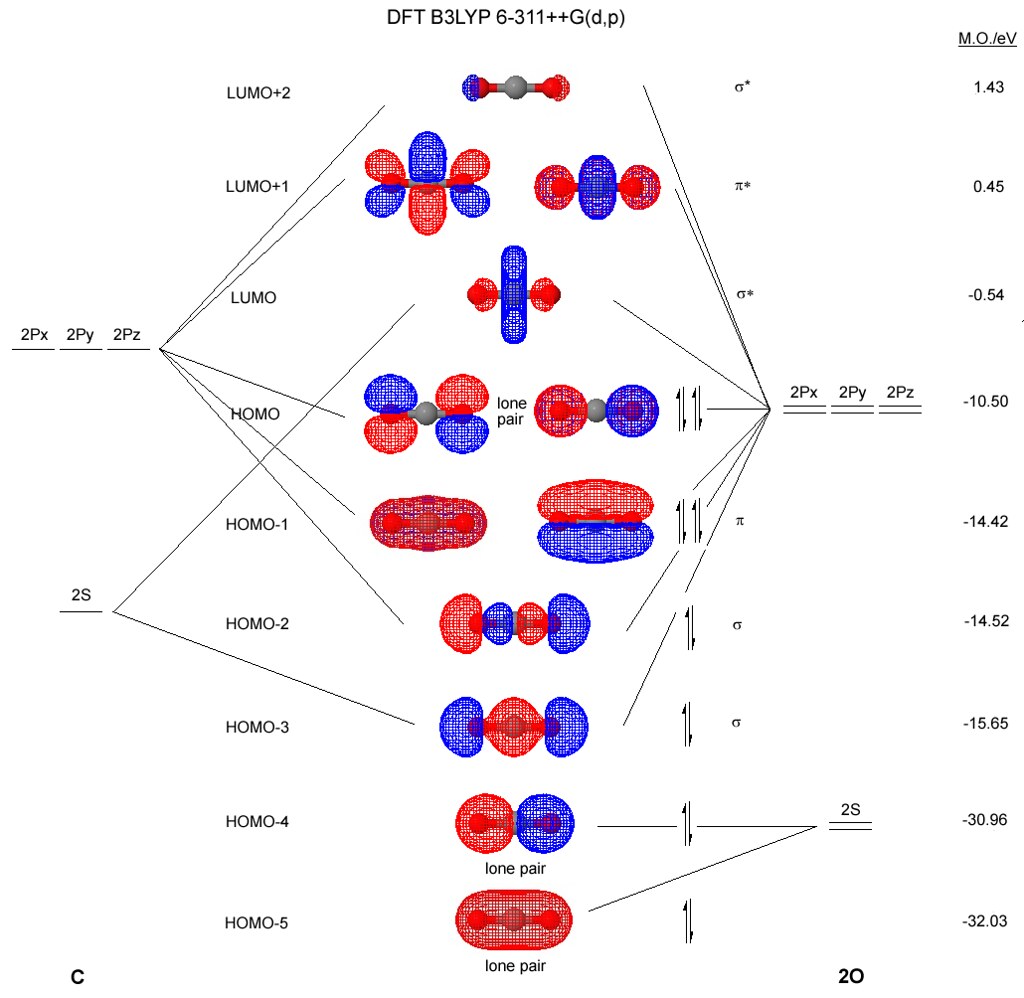
Question 1 To build the MO diagram for CO2, we will consider the s and p orbitals on C and the two O's. How many oxygen SALCs are there? Question 2 12 pts Part A. Draw the oxygen SALCs. (2 pts) Part B. Placing the atomic orbitals of carbon on the left side and the SALCs of oxygen on the right side, draw a MO diagram for CO2. Although this is a
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
In a homework we are asked to compare the bond orders of I3- and I3+ after creating their MO diagrams. After much searching and trying to figure out the MO diagram for I3-, I found out that it's very easy and only involves the three 5pz orbitals in a "4 electron 3 center bond." But I don't know if I3+ is similar.
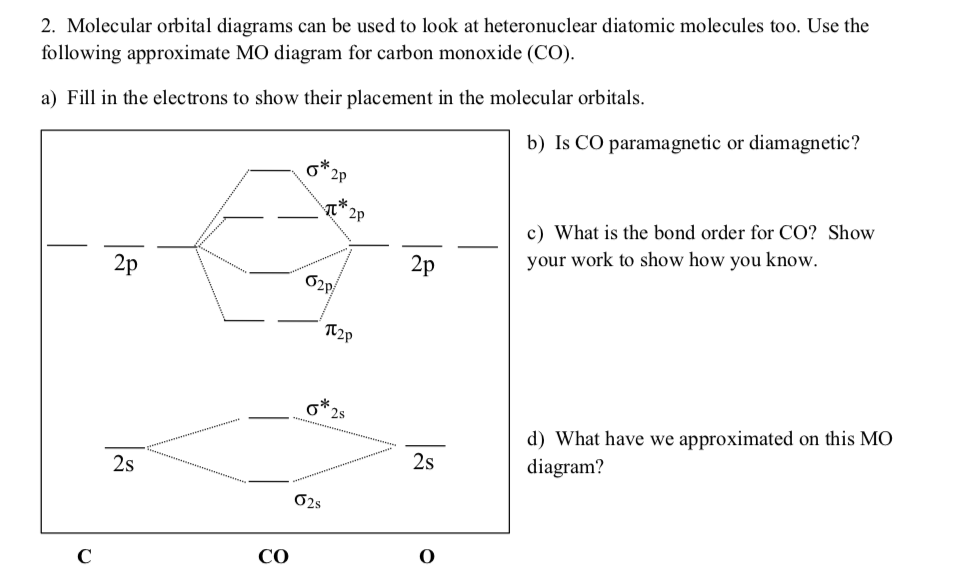
Below is the MO diagram for CO2. a. Complete the MO diagram by adding the electrons. b. When two electrons are added to the CO2 does the bond order increase or decrease; explain. c. What effect does removing an electron have on the bond order of CO2; explain.
Feb 3, 2021 — The carbon dioxide MO diagram is based on a C atom and an O--O ligand fragment. Carbon has 2S and 2Px,y,z orbitals and the O--O fragment has 2S ...Introduction · MO Theory · Carbon Dioxide MO diagram
MO-Diagram for the first 10 elements: Works great for O 2-> explains O 2's paramagnetism But predicts B 2 to be diamagnetic-> Orbital Mixing! 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules 5.2 Homonuclear Diatomic ... 5.4.2 Carbon Dioxide's Molecular Orbital Diagram
Introduction: Methane, CH 4. Using the carbon and hydrogen atomic orbitals, methane, CH 4, is constructed by overlapping the carbon's one 2s and three 2p AOs with the four hydrogen 1s AOs.. Methane's MOs have a topology similar to the AOs of carbon, but the structure can be very difficult to visualise, so the methane MO construction diagrams A, B and C (below) are shown with the AOs and MOs ...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine

.png)





















0 Response to "40 mo diagram for co2"
Post a Comment