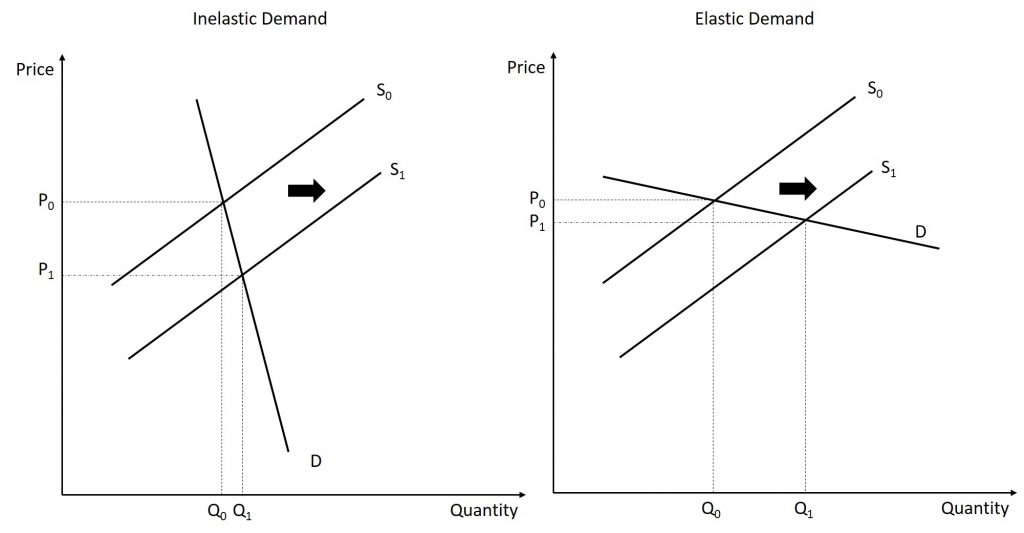
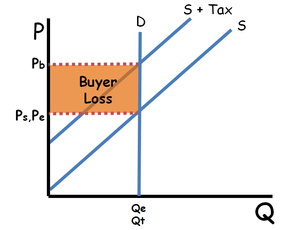
41 refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:
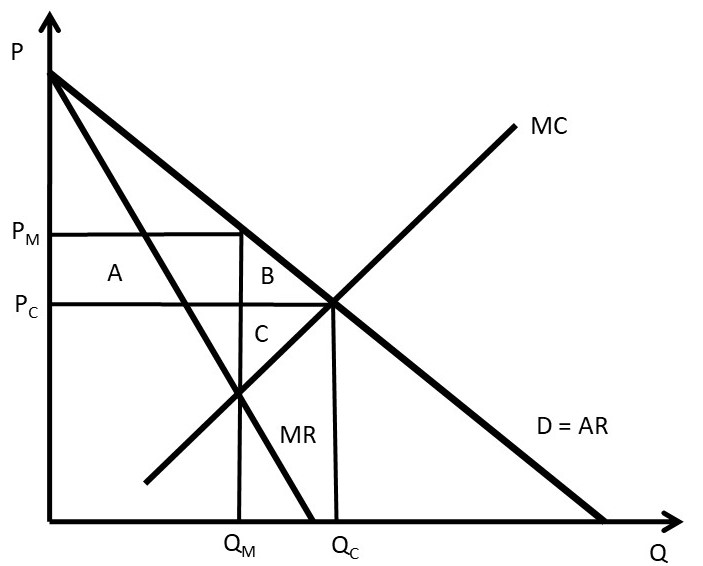
Relative elasticity is the same. In fact, we cannot pass judgement if one is elastic or inelastic unless we are referencing to another. The concept of relative elasticity is not based on the calculations in 4.1 and 4.2, as each demand curve has an inelastic, elastic and unit elastic region. Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If supply is S1 and demand D0, then A) 0F represents a price that would result in a shortage of AC. B) a surplus of GH would occur. C) 0F represents a price that would result in a surplus of AC. D) at any price above 0G a shortage would occur.
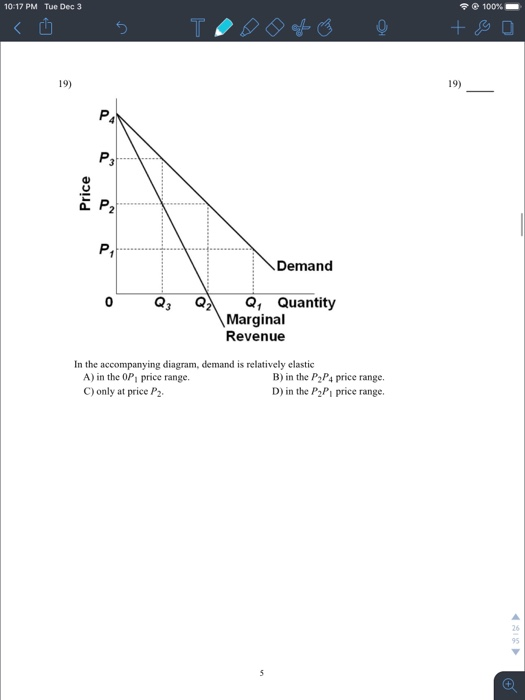
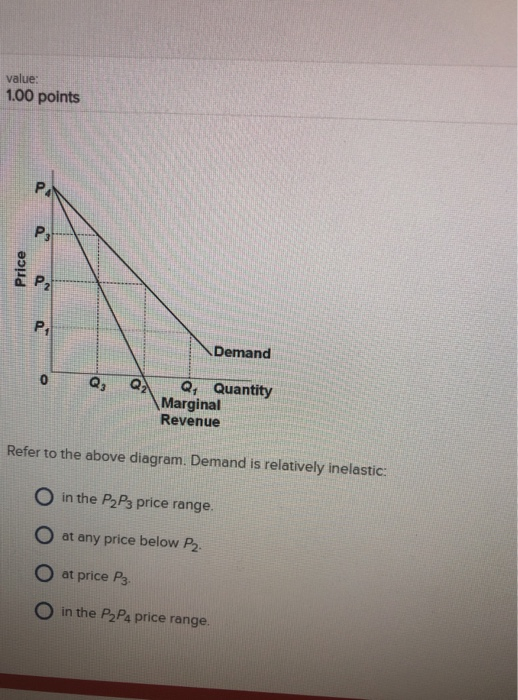
36. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A) at price P3. B) at any price below P2. C) in the P2P4 price range. D) in the P2P3 price range.

Refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:
Perfectly Inelastic Demand and Relatively Inelastic Demand. Answer: Perfectly Inelastic Demand: When a change in price brings no change in quantity demanded then, demand is said to be Perfectly Inelastic demand. The numerical co-efficient is zero (e = 0). The slope of the demand curve is straight line parallel to Y-axis. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 4. In the market for "White Russian" mixed-drinks, you observe price decrease by 50% and quantity demanded increase by 20%. The elasticity of demand in this case is: A. perfectly elastic. B. elastic (relatively) C. unit elastic. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 5. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: in the P2P4 price range. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: at any price below P2. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by:
Refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:. Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. Figure 1 pertains to: a purely competitive firm. ... Refer to the diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic:. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: in the P2P4 price range. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic. at any price below P2. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: ... inelastic demand for business travel. ... (TCO 2) Refer to the diagram. A decrease in demand is depicted by a diagram2 Graph Description (Points : 3) move from Point x to Point y. shift from D1 to D2. ... Goods for which the income-elasticity coefficient is relatively high and positive. 45. The demand for a necessity whose cost is a small portion of one's total income is: A. perfectly price inelastic. B. perfectly price elastic. C. relatively price inelastic. D. relatively price elastic. Use the graph below to answer question 46 46. Refer to the diagram and assume that price increases from $2 to $10.
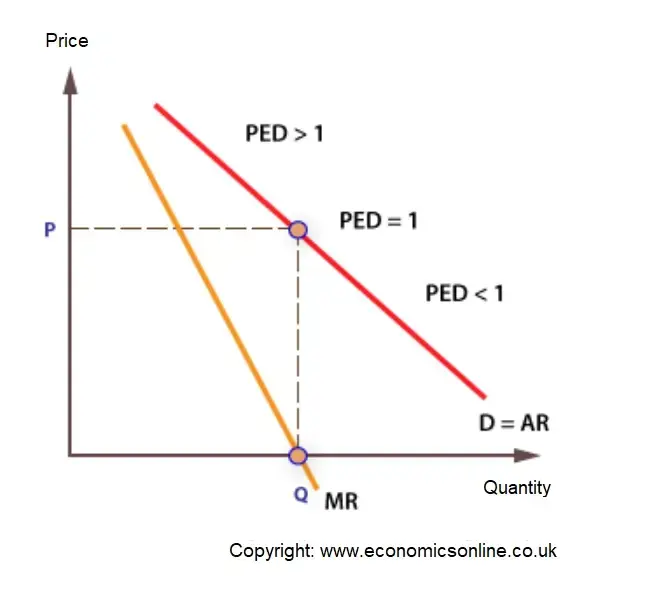
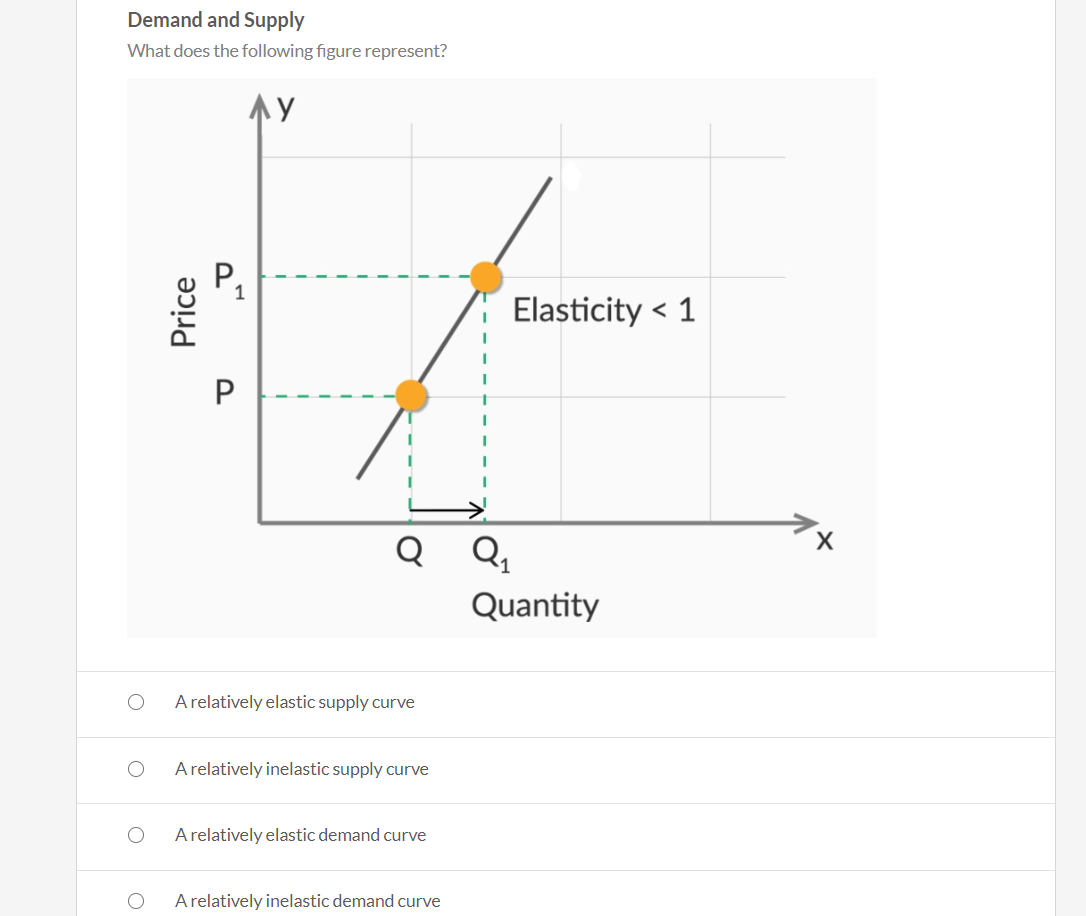
Relatively elastic demand and Relatively inelastic demand. Answer: Relatively Elastic Demand. When percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price then demand is said to be Relatively Elastic demand. The numerical co-efficient is greater than one (e > 1). Demand curve slopes flatter. d) Relatively elastic demand: When a percentage change in price leads to more than proportionate change in quantity demanded, the demand is said to be relatively elastic. 2) In the following diagram AE is the linear demand curve of a commodity. On the basis of the given diagram state whether the following statements are True or False. Economics. Economics questions and answers. Picture Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. March 5, 2020 - Most demand curves are relatively elastic in the upper-left portion because the original price: from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small. The coefficient of price elasticity is 0.2.
Elasticity vs. Inelasticity of Demand: An Overview . Inelasticity and elasticity of demand refer to the degree to which demand responds to a change in another economic factor, such as price ... Transcribed image text: value 1.00 points P. Demand o Q Q Quantity Marginal Revenue Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: O in the P2Ps price range. O at any price below P2 O at price Pa O in the P2P4 price range Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: a) in the P2P1 price range. b) in the 0P1 price range. c) in the P2P4 price range. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 4. In the market for "White Russian" mixed-drinks, you observe price decrease by 50% and quantity demanded increase by 20%. The elasticity of demand in this case is: A. perfectly elastic. B. elastic (relatively) C. unit elastic. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 5.
Relatively inelastic demand occurs when the percentage change in demand is less than the percentage change in the price of a product. For example, if the price of a product increases by 15% and the demand for the product decreases only by 7%, then the demand would be called relatively inelastic.
c. an elastic segment of the demand curve. d. a demand curve with an inelastic segment of the demand curve from $7.50 to $6.50 followed by an elastic segment. Figure 10-3 shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. 17) Refer to Figure 10-3.
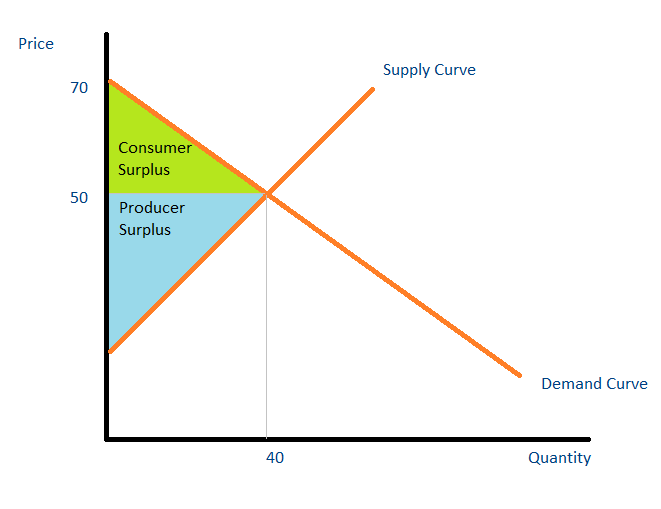
Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s):. A. B+D. Shopping.com is a leading price comparison site that allows you to shop online for the best deals and lowest prices. Our mission is to help consumers use the power of information to easily find, compare and buy products online - in less time and for the best price! Movement along demand curve ...
In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively elastic a. in the P2P1 price range b. in the 0P1 price range ... Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. ... c. start operating at the inelastic portion of its demand curve d. increase production so that MR > MC.
A natural monopoly exists when. a. a monopolist produces a product, the main component of which is a natural resource. b. economies of scale are so large that only one firm can survive and achieve low unit costs. c. a firm is the exclusive owner of a key resource necessary to produce the firm's product. d. there are no close substitutes for a ...
(TCO 2) Refer to the diagram. A decrease in demand is depicted by a Graph Description (Points : 3) move from Point x to Point y. shift from D1 to D2. shift from D2 to D1. move from Point y to Point x. Question 20.20. (TCO 2) Refer to the information and assume the stadium capacity is 5,000.
A perfectly inelastic demand curve ... In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively inelastic ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist.
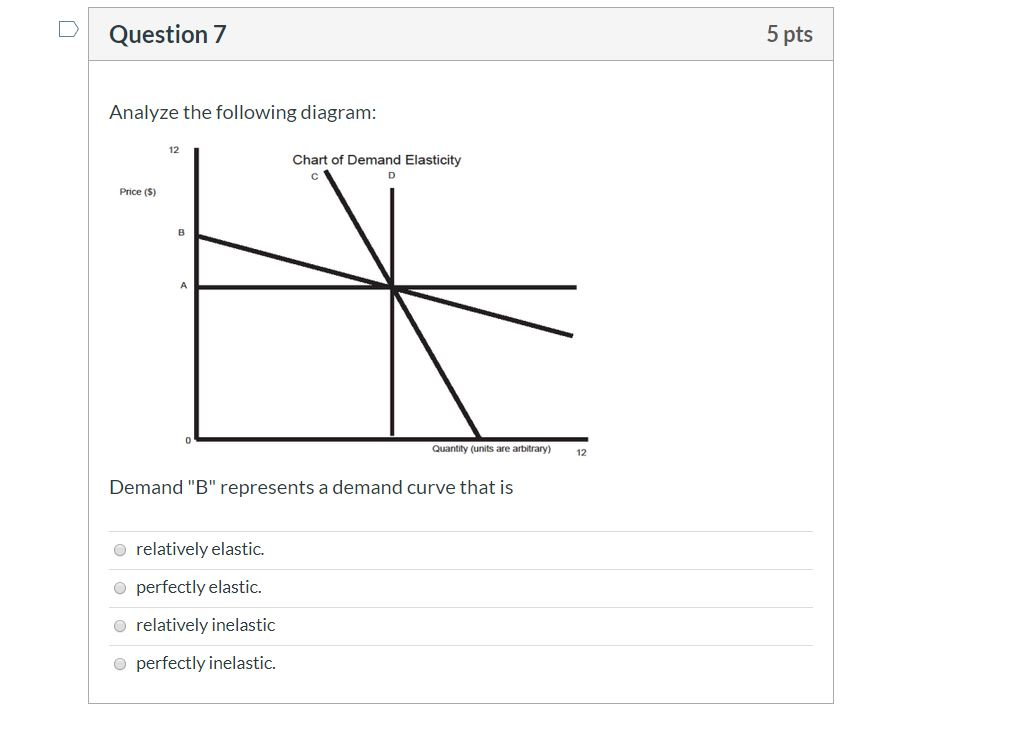
PA A с Price P B D Demand Quantity Refer to the diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes. O b. that demand is elastic with respect to price. Oc. that demand is inelastic with respect to price.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. the firm's profit-maximizing price will be $16 refer to the figure. suppose the graphs represent the demand for use of a local golf course which there is no significant competition (it has a local monopoly); P denotes the price of a round of golf; Q is the ...
February 10, 2017 - Answer (1 of 14): Relatively inelastic demand is one where quantity demanded doesn’t change much with respect to change in price of the good. There are many good which exhibit such inelastic demand pattern, few examples being : * Necessary goods like salt and sugar. It is difficult to give up ...
b) perfectly inelastic over all ranges of output. ... Demand is relatively inelastic: a) at ... Image: Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist.
(Supposed to be a graph) In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively inelastic a.) at price P3. b.) at any price below P2. c.) in the P2P4 price range. d.) in the P2P3 price range.
"Inelastic demand" is a term that economists use to refer to a situation where demand for an item remains the same, no matter how far its price rises or falls. It's important to understand this concept if you're learning about economics.
30. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P 3 B. at any price below P 2 C. in the P 2 P 4 price range. D. in the P 2 P 3 price range. . . 31. Price exceeds marginal revenue for the pure monopolist because the: A. law of diminishing returns is inapplicable.
Picture Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. Refer to the diagram. In the P 3 P 4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic.
Refer to the diagram Between prices of 570 and 630 D 1 is more elastic than D 2 from ECON 202 at Louisiana State University, Shreveport
D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 4. In the market for "White Russian" mixed-drinks, you observe price decrease by 50% and quantity demanded increase by 20%. The elasticity of demand in this case is: A. perfectly elastic. B. elastic (relatively) C. unit elastic. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 5.
Most demand curves are relatively elastic in the upper left portion because the original price. D. from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small. The price elasticity of demand of a straight line demand curve is.
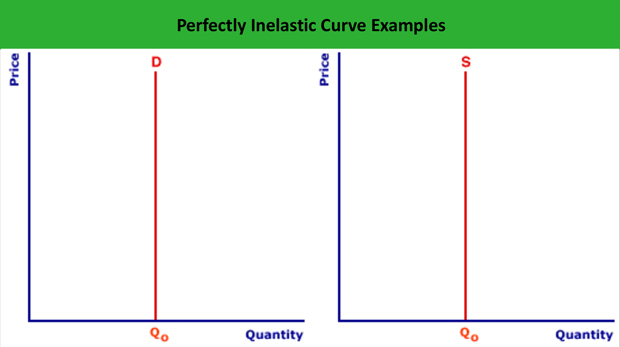
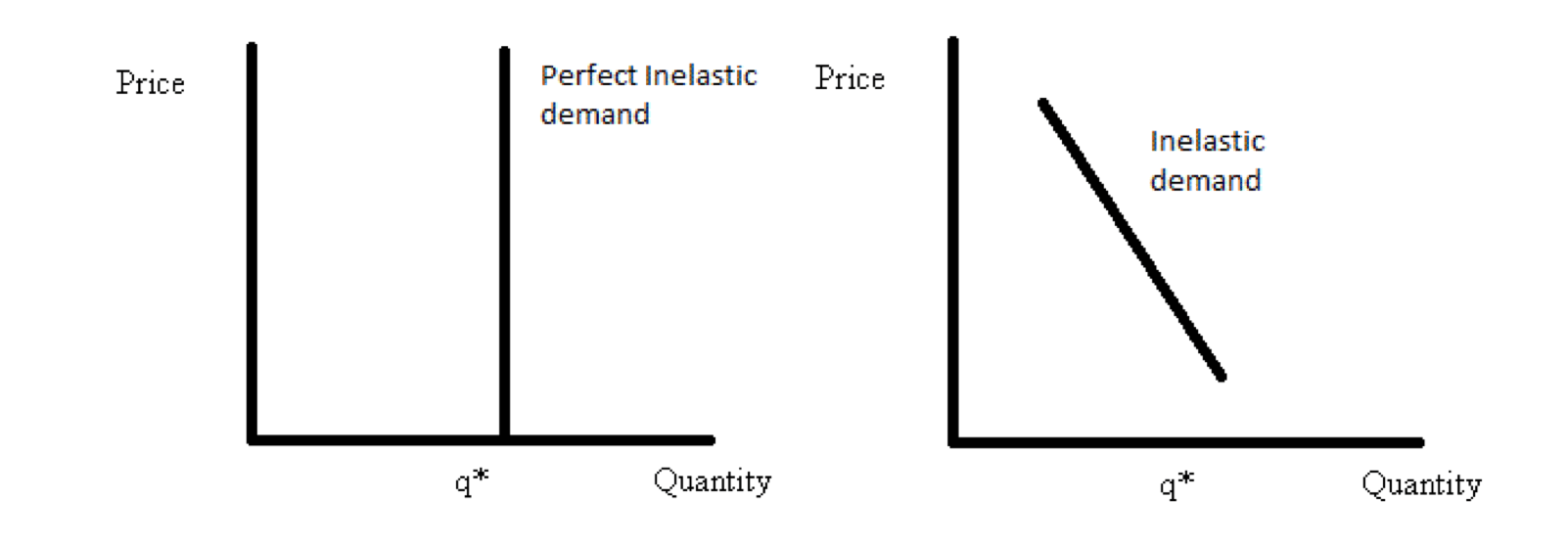
To make easy to understand the concept of perfectly inelastic demand, it is presented in the graphical presentation in the below diagram. See the graph, price of the goods changing or raises from P1 to P2 and P3 but there is no change in demand at Q. In fact the quantity demand should not be changed without change in price according to the law ...
D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic . 4. In the market for "White Russian" mixed-drinks, you observe price decrease by 50% and quantity demanded increase by 20%. The elasticity of demand in this case is: A. perfectly elastic. B. elastic (relatively) C. unit elastic. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic . 5.
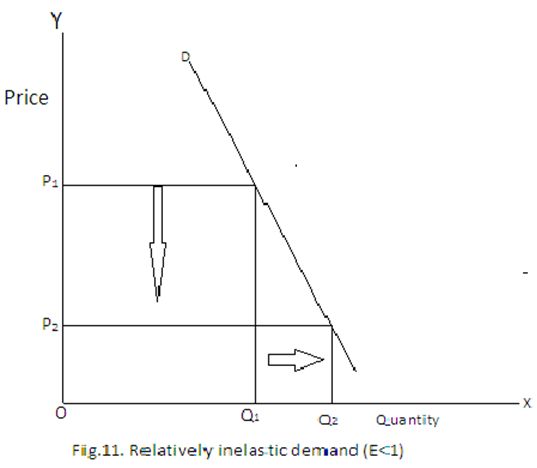
Here the .demand curve (DD) is flatter. Relatively inelastic demand Demand for a commodity is relatively inelastic when a change in price causes a less than proportionate change in the quantity demanded in this Ped < 1. Ex: When a 10, per cent change in price causes a per cent change in demand In this case Ped < 1. Unitary elastic demand
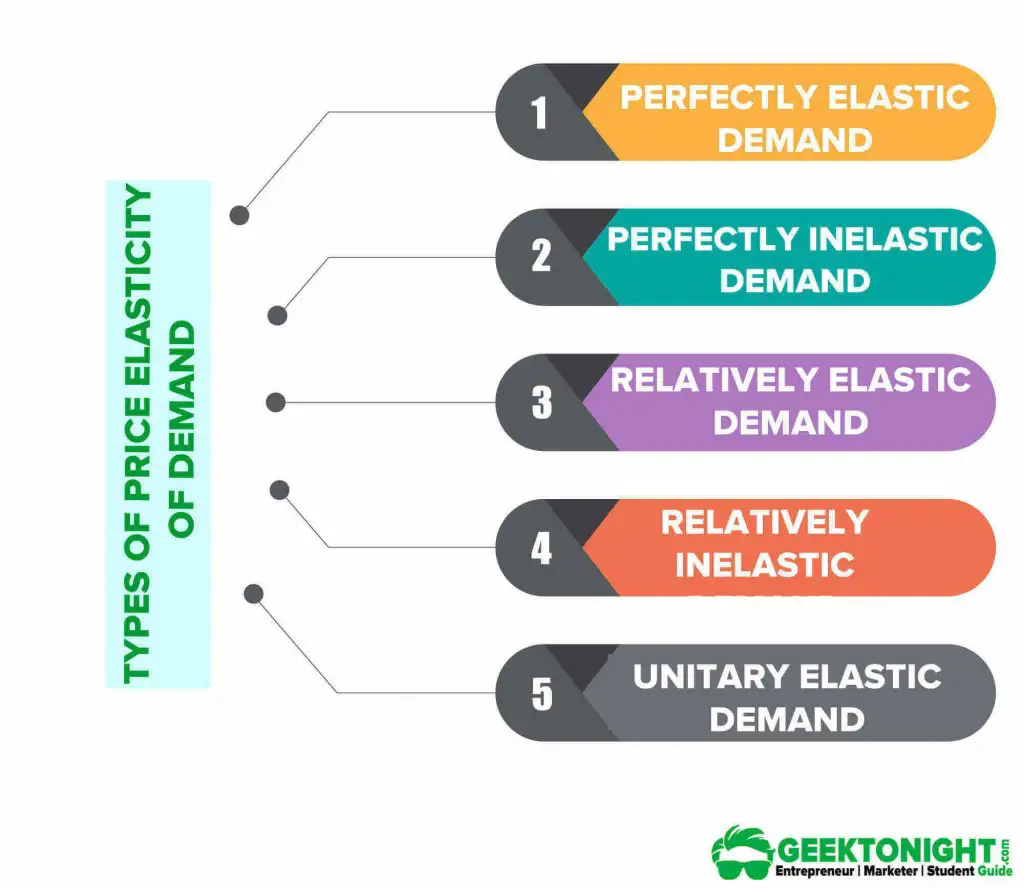
This characterization of elasticity is most important for the price elasticity of demand and the price elasticity of supply. Relatively inelastic is one of five elasticity alternatives. The other four are perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, relatively elastic, and unit elastic.
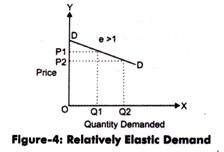
Then Elasticity at point "P" is 1.5 which is e > 1. So demand is Relatively Elastic. On a given linear demand curve elasticity of demand at different point is different as shown in the diagram. Now to find elasticity of demand on a nonlinear demand curve on a given point "P" as shown in the diagram.
perfectly inelastic. b) negatively sloped. c) relatively elastic. d) perfectly elastic. Question 4 (4 points) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: Question 4 options: a) $10. b) $13. c) $16. d) $19. Question 5 (4 points)
If the demand curve is relatively inelastic, lowering prices is the best option for increasing total revenue. That will result in a more significant increase in demand. Thus, the effect of increased demand on revenue is higher than the effect of a price decrease. Perfectly elastic.
February 24, 2021 - Most demand curves are relatively elastic in the upper-left portion because the original price: from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small.
In the above diagram, D' is the demand curve, which represents inelastic demand. Even though price changes from OP to OQ or from OQ to OP, demand for the commodity is same i.e. OM. Thus in this case demand is not at all responding to change in price and i.e. why elasticity of demand is equal to zero (el = 0). Less Elastic Demand
The pure monopolist's demand curve is: A. identical with the industry demand ... Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3.
(a) demand was inelastic (b) demand was infinitely elastic (c) demand was elastic (d) none of the above. 197. On typical straight line demand curve, the elasticity of demand at a point where it meets the price axis is-(a) 2 (b) 0.75 (c) 1 (d) infinite. 198. On a straight line demand curve the elasticity of demand at the mid-point of the curve ...
Inelastic segment as price decreases These two segments are based on the fact that the decisions of oligopolistic firms are interdependent. Because of the fact that competing firms are unlikely to match the increases in the price of an oligopoly, there is a tendency for the firm to lose its customers and market share to the competition.
B) When there are many firms in the market and the demand curve faced by each firm is relatively inelastic. C) When there are few firms in the market and the demand curve faced by each firm is relatively elastic. D) When there are many firms in the market and the demand curve faced by each firm is relatively elastic. Answer: A. Diff: 2. Section ...
Perfectly inelastic demand (A limiting case) Perfectly elastic demand (A limiting case) Relatively inelastic demand (Quantity stretches less than price) 1. Price elasticity (we also have cross-elasticity and income elasticity of demand) ... diagram for yourself. The author’s latest book is Going to University: the Secrets of Success,
Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic: A. in the P2P1 price range. B. in the 0P1 price range. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. only at price P2. in the P2P4 price range. 25. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3. B. at any price below P2. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. in the P2P3 price ...
Refer to the diagram. Assuming Q2 hits demand at its midpoint, demand is relatively inelastic: at any price below P2.
larger burden of a sales tax if Will bear a OA) demand is relatively elastic and supply is relatively inelastic. B) demand is relatively inelastic and supply is relatively elastic C) both demand and supply are relatively inelastic. D) both demand and supply are relatively elastic. ... P MC PA ATC P3 AVC P2 A P1 23 Refer To The Diagram.
More change in the price of the goods but less change in demand for the goods. See the graph, price of the goods increased from P1 to P2 and eventually the demand for the goods decreases from Q1 to Q2. The proportionate change in price is more than the proportionate change in demand. For
D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 4. In the market for "White Russian" mixed-drinks, you observe price decrease by 50% and quantity demanded increase by 20%. The elasticity of demand in this case is: A. perfectly elastic. B. elastic (relatively) C. unit elastic. D. inelastic (relatively) E. perfectly inelastic. 5.
Elasticity refers to the degree of responsiveness in supply or demand in relation to changes in price. If a curve is more elastic, then small changes in price will cause large changes in quantity consumed. If a curve is less elastic, then it will take large changes in price to effect a change ...
B. in the 0P1 price range. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. only at price P2. 36. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively inelastic: A. at price P3. B. at any price below P2. C. in the P2P4 price range. D. in the P2P3 price range. 10-9 Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 37.
February 24, 2021 - (Straight-line demand curve) Refer to the above diagram. In the P1P2 price range demand is: ... In the P3P4 price range demand is: B. relatively inelastic. The total-revenue test for elasticity. C. does not apply to supply because price and quantity are directly related.
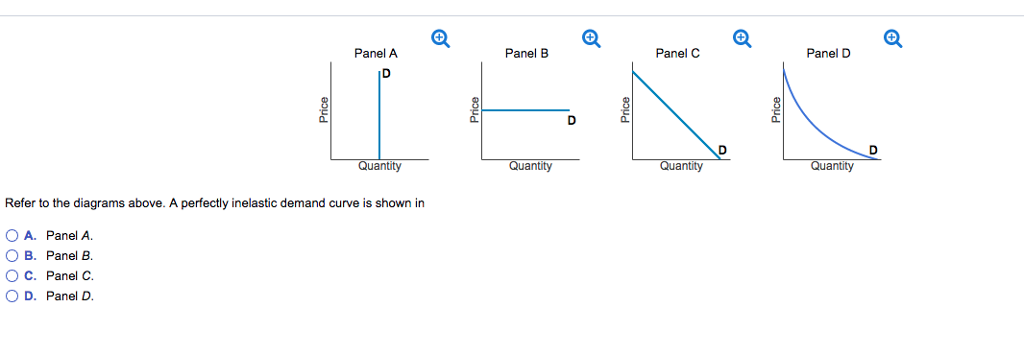
Refer to the graphs above. Which demand curve is relatively most elastic between P1 and P2? A) D1 B) D2 C) D3 D) D4 Refer to the graph above. Which demand curve is perfectly inelastic? A) D2 B) D3 ...






/inelastic-demand-definition-formula-curve-examples-3305935-final-5bc4c3c14cedfd00262ef588.png)










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Price_Elasticity_Affect_Supply_Feb_2020-04-859fb2e0ea774bf88da48c4405d76a29.jpg)


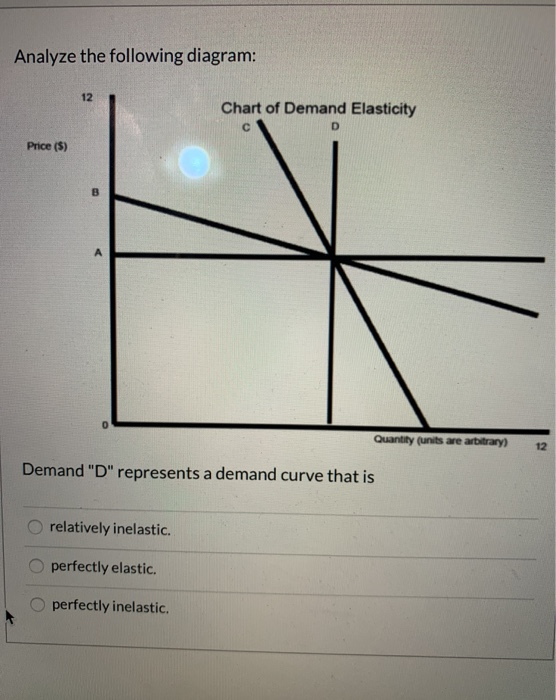
0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. demand is relatively inelastic:"
Post a Comment