39 action potential diagram labeled
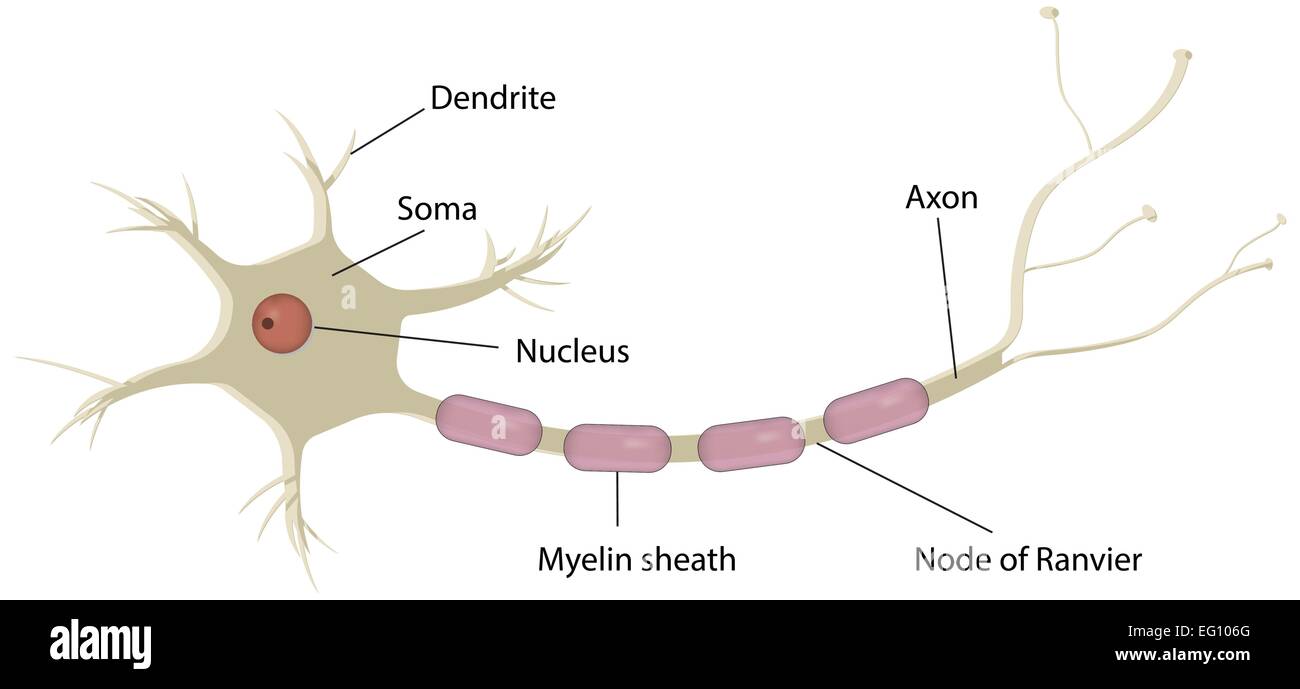
The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. Conduction Velocity Depends on Diameter and Myelination of the Axon • Conduction velocity is the speed with which an action potential is propagated. An action potential is a rapid rise and fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane. Explore action potential chart/graph for more ...
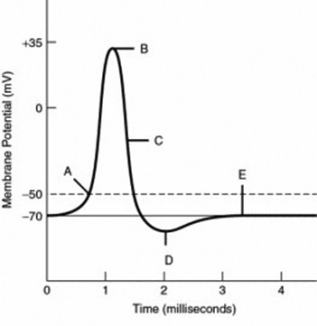
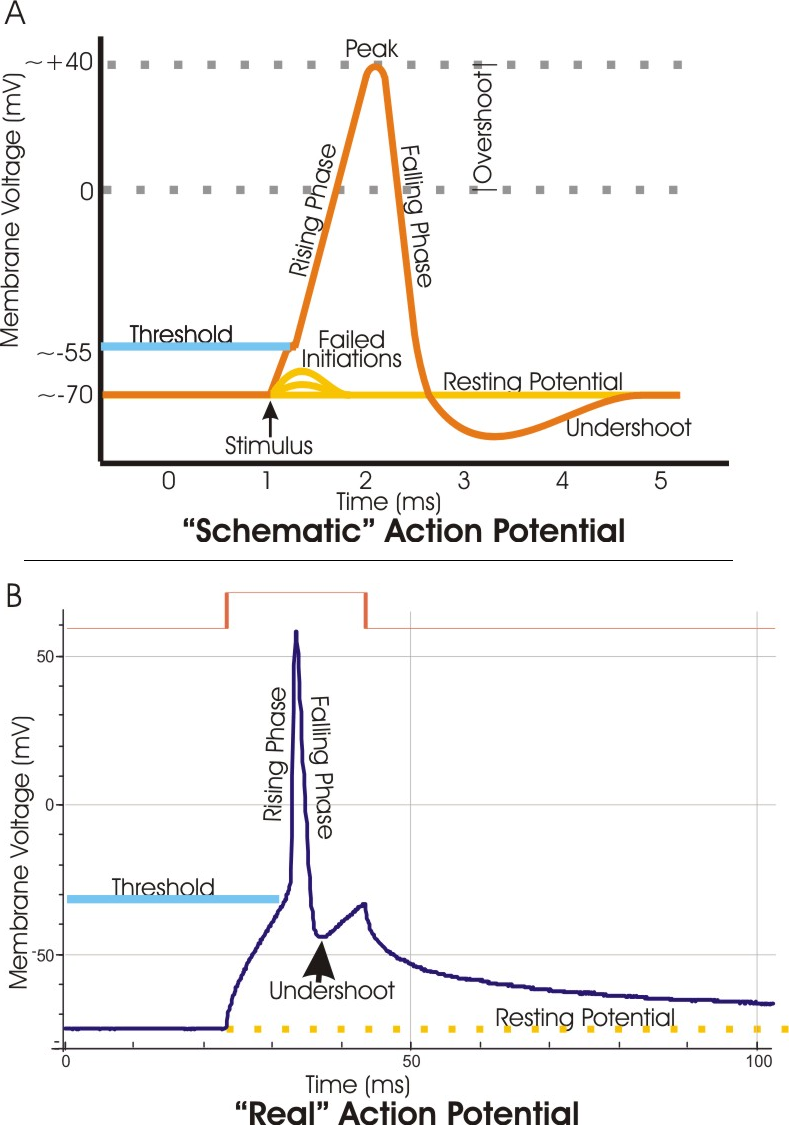
What has been described here is the action potential, which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 12.5.7. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to +30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change.
Action potential diagram labeled
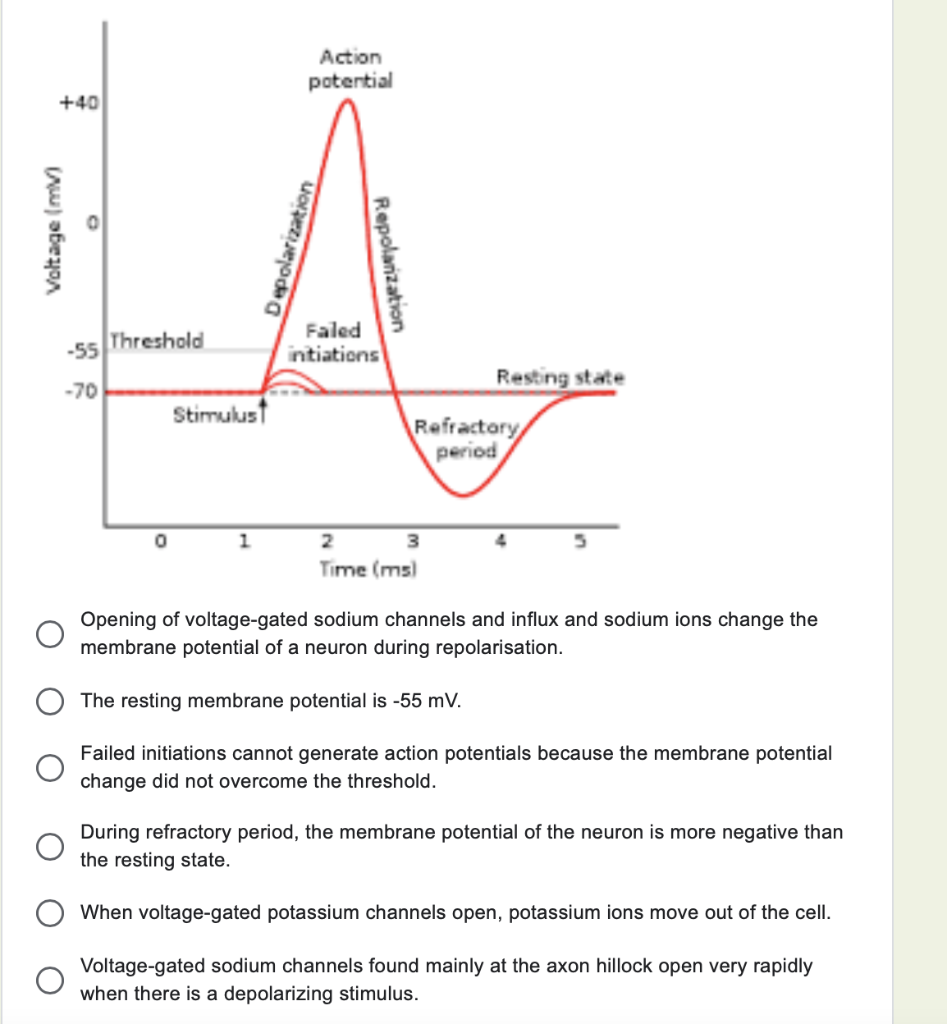
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... If depolarization reaches -55 mV, then the action potential continues and runs all the way to +30 mV, at which K + causes repolarization, including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. Also, those changes are the same for every action potential, which means that once the threshold is reached, the exact same thing happens. When that voltage becomes less negative, the channel begins to allow ions to cross the membrane (Figure 4). This is a two part diagram. Both diagrams show a ...
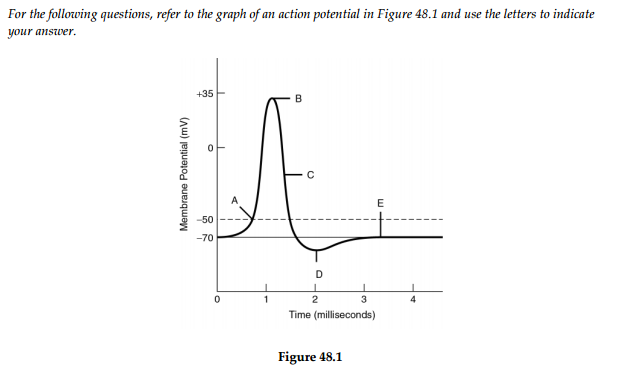
Action potential diagram labeled. If we look at a graph, we can see there is a starting point where the line is flat. This is the resting potential. Resting potentials vary between cells, but usually are around -70 millivolts (mV). Label and explain steps 1-7 in the action potential diagram below. 0 -55 -70 Time ; Question: 6. Label and explain steps 1-7 in the action potential diagram below. 0 -55 -70 Time . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a How action potentials work · A triggering event occurs that depolarizes the cell body. · Depolarization - makes the cell less polar (membrane potential gets ...
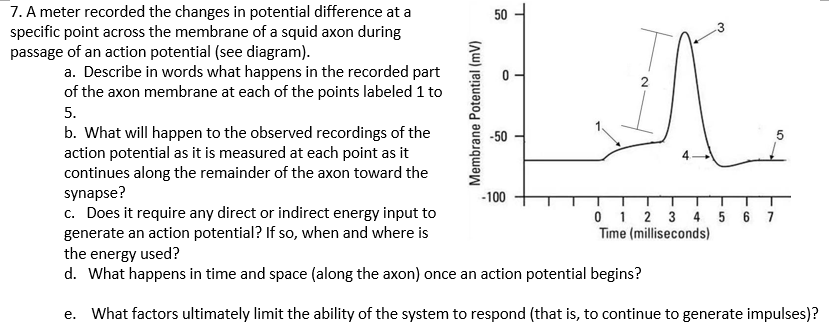
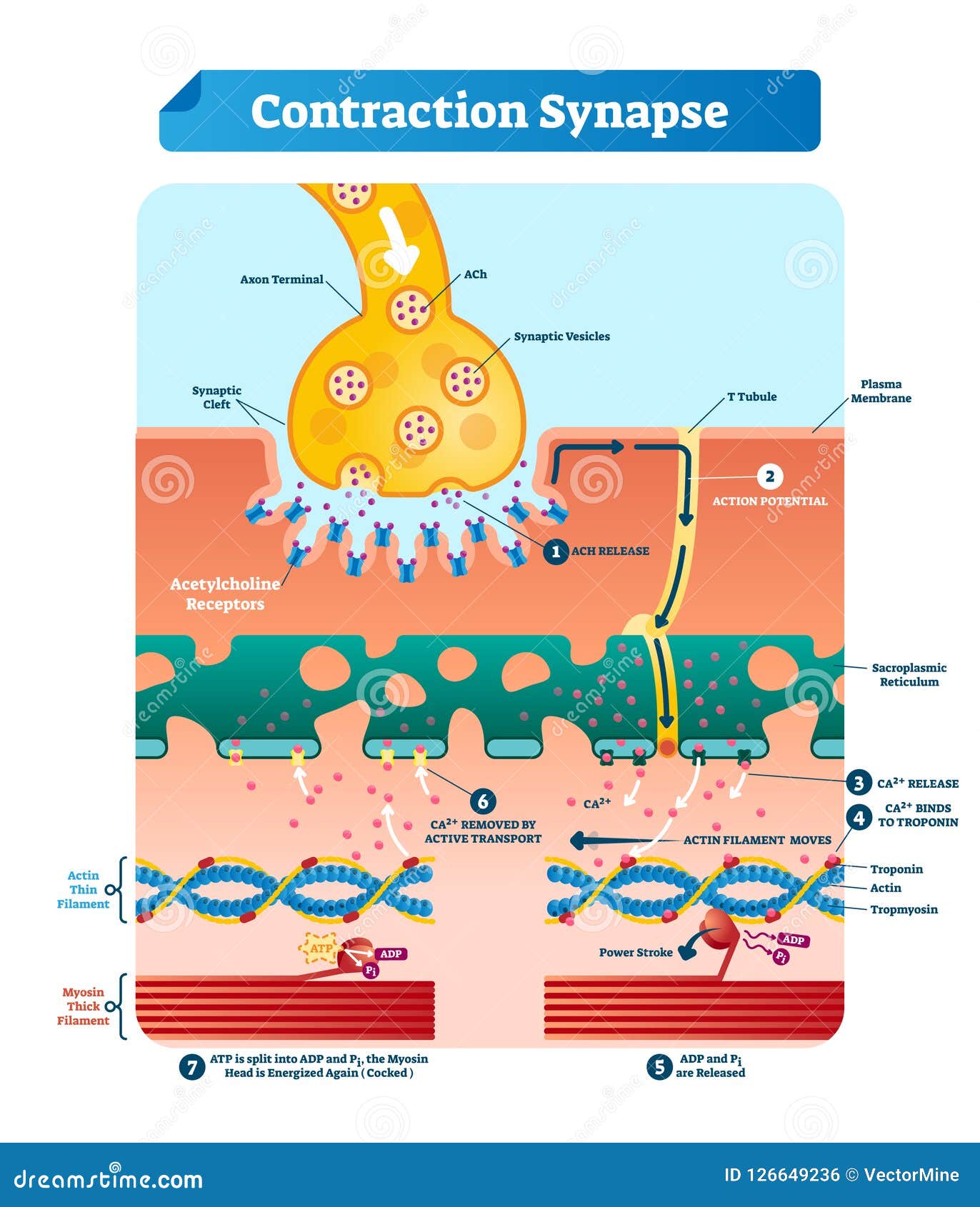
Expert Answer. 100% (1 rating) Action Potential: When impulse is initiated by stimulation of sensory nerve ending, movement of ions across the cell membrane indicate action potential. Polarised membrane: The nerve in the resting st view the full answer. Previous question Next question. heart; blood. sarcoplasmic reticulum is more extensive in smooth muscle fibers than in skeletal muscle fibers. false. the sinoatrial (sa) node, or the ______________, sets the rate of the hearts contractions by sending action potentials through the specialized conduction fibers to the atria and ventricle. pacemaker. Diagram of the relationship between AI and machine learning . What is a neural network? An artificial neural network (ANN) is modeled on the neurons in a biological brain. Artificial neurons are called nodes and are clustered together in multiple layers, operating in parallel. When an artificial neuron receives a numerical signal, it processes it and signals the other neurons connected to it ... 13 Aug 2020 — Key Terms · action potential.: A brief reversal of membrane potential. · repolarization: Also called the falling phase, · absolute refractory ...
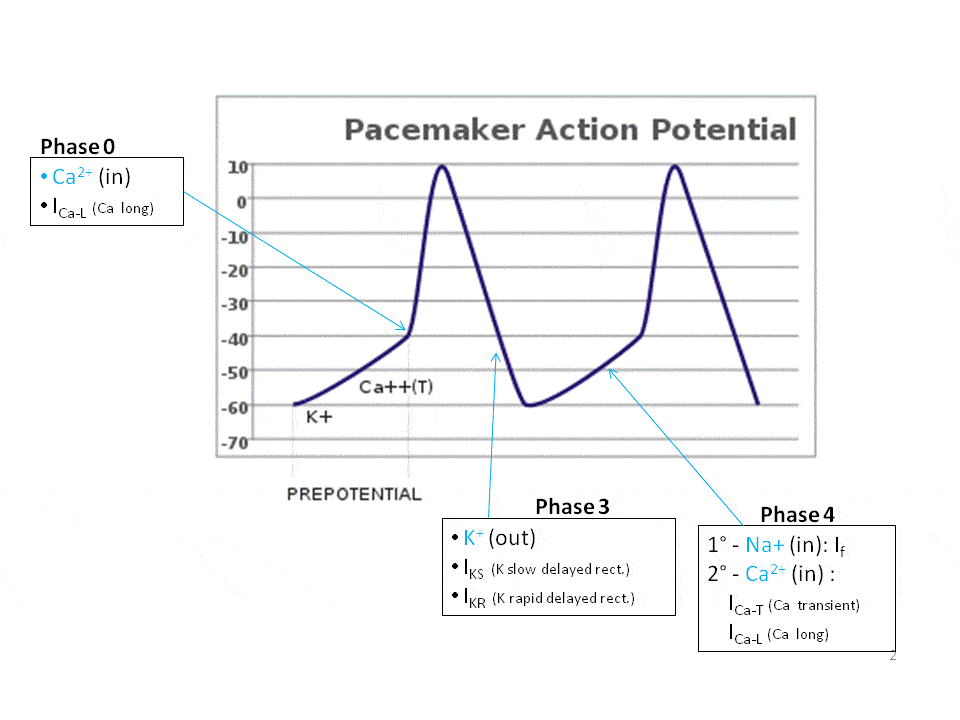
In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then ...Membrane potential · Threshold potential · Cardiac action · Saltatory conduction • Initiation of action potential in autorhythmic cells: 1. Pacemaker Potential due to influx of sodium and reduced efflux of potassium. 2. Depolarization and reversal of the membrane potential due to influx of calcium. 3. Repolarization due to efflux of potassium. • Initiation of action potential in contractile cells: 1. The ions, in this case, are cations of sodium, calcium, and potassium. These two diagrams each show a channel protein embedded in the cell membrane. In the. A ... Action potential curve and phases (diagram) Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential.The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions.
Solved Draw An Action Potential And Label With Numbers 1 6 The Phases Noted Below 30 1 Depolarizing Local Potential Na Ligand And Voltage 0 Course Hero
When that voltage becomes less negative, the channel begins to allow ions to cross the membrane (Figure 4). This is a two part diagram. Both diagrams show a ...
If depolarization reaches -55 mV, then the action potential continues and runs all the way to +30 mV, at which K + causes repolarization, including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. Also, those changes are the same for every action potential, which means that once the threshold is reached, the exact same thing happens.
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
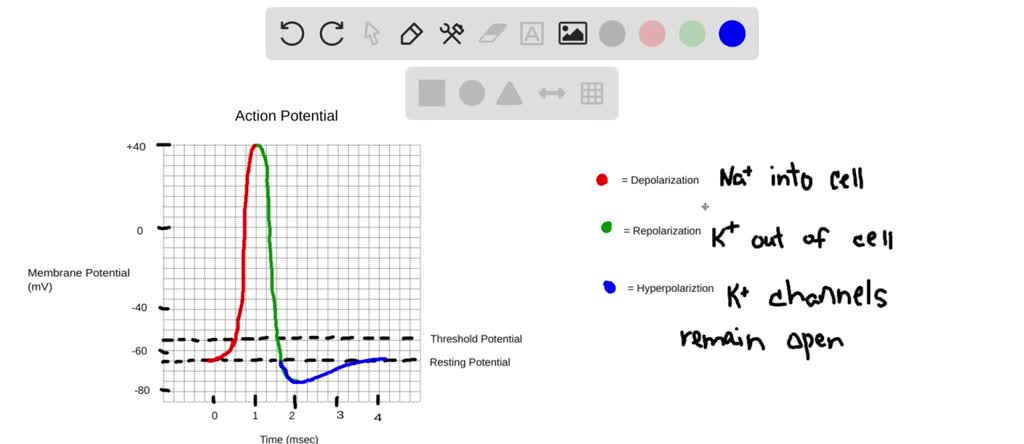
Solved Draw And Label An Action Potential Including Which Ions Are Moving Through The Membrane And In Which Direction They Are Flowing In Each Phase How Does Each Iona S Conductance Change With Each

Nerve Action Potential Nerve Signals Are Rapid Changes In The Membrane Potential That Spread Rapidly Along The Nerve Fiber Membrane By Action Potential Ppt Download

Diagram Of Synaptic Transmission Okinawa Institute Of Science And Technology Graduate University Oist
:format(jpeg)/images/article/en/action-potential/pJRivfYxfsvi7mIh8xRQg_Action_potential_curve.png)
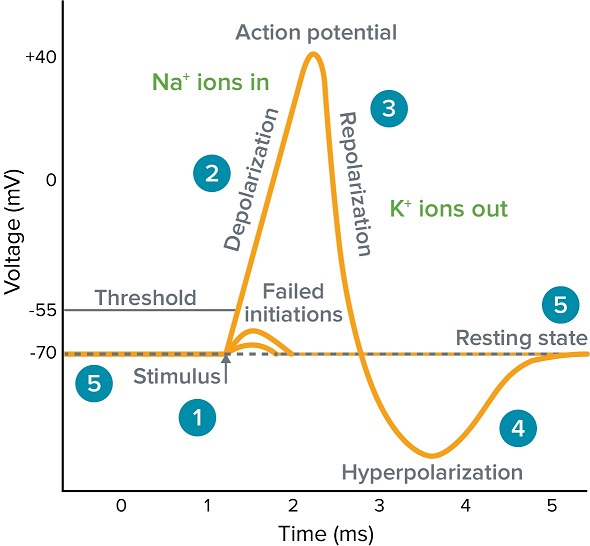















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)

0 Response to "39 action potential diagram labeled"
Post a Comment