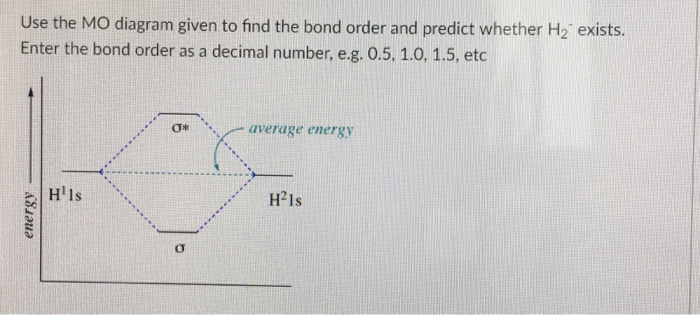
40 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Drop all the files you want your writer to use in processing your order. If you forget to attach the files when filling the order form, you can upload them by clicking on the “files” button on your personal order page. The files should be uploaded as soon as possible to give the writer time to review and use them in processing your order.
Chemistry questions and answers. Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists. Enter the bond order as a decimal number, eg. 0.5. 1.0, 1.5, etc ?* ???Y-average energy H2ls. Question: Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists.
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]` Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are gotten by joining the nuclear orbitals on the particles in the atom. Ensure you request for assistant if you can’t find the section. When you are done the system will automatically calculate for you the amount you are expected to pay for your order depending on the details you give such as subject area, number of pages, urgency, and academic level. After filling out the order form, you fill in the sign up details. Ensure you request for assistant if you can’t find the section. When you are done the system will automatically calculate for you the amount you are expected to pay for your order depending on the details you give such as subject area, number of pages, urgency, and academic level. After filling out the order form, you fill in the sign up details. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Give the Molecular Orbital Energy diagram of a) N2 and b) O2 . Calculate the respective bond order. Write the magnetic nature of N2 and O2 molecules.
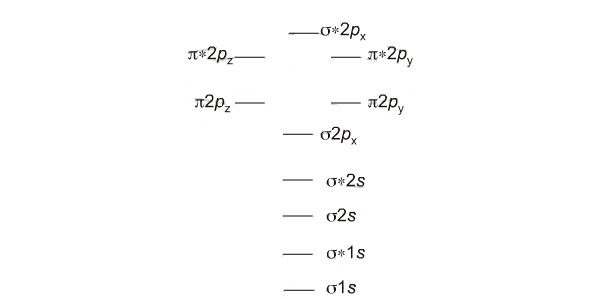
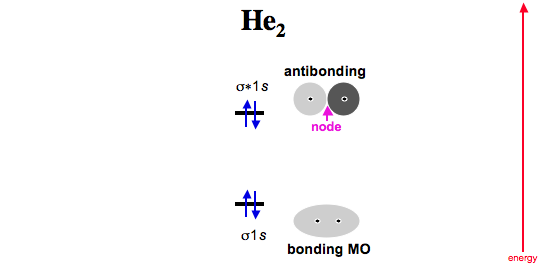
Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. diagram for CO2 in ... For this, we need to determine the bond order for each species. The bond order tells us the stability of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is more stable. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion. Answer (1 of 5): The total number of electron of CN- ion is ( 6+7+1) = 14 . According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration of CN - ion is as follows, From the above electronic configuration , it has been found that , the number of bonding electron is 10 and the the number of... Using the molecular orbital energy ordering for second-row homonuclear diatomic molecules in which the π2p orbitals lie at higher energy than the σ2p, predict the bond order in a molecule or ion with each of the following numbers of total valence electrons (by drawing MO energy diagrams).
Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. Question : Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. This problem has been solved! Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond. d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c. ) MO. The right image is of symmetry and has no node in the bonding region. It is the 1 u or u (2p x) MO. The lower two images : The left image shows out of phase AOs with no overlap. Therefore it is the 1 u * or u *(1s) MO. The right image has symmetry with no nodes in the bonding region. Therefore it is the 3 g or g (2p z) MO. 7. 8.
2 answersIn order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to ... By this trick you can find out the bond order of any molecules given in +2 ...
3 Feb 2021 — Figure 3: Schematic represenation of antibonding molecular orbital σ*(1s) ... Bond order = 1/2 (#e- in bonding MO - #e- in antibonding MO).
electronic state. Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 6 MO orbital energy level diagram for NO Sketch of the π MO
We have a convenient order form, which you can complete within minutes and pay for the order via a secure payment system. The support team will view it after the order form and payment is complete and then they will find an academic writer who matches your order description perfectly.
Show activity on this post. Theoretically electronic configuration and number of unpaired electron can be found out by using molecular orbital theory. But, practically I have seen only up to 20. For example, for Ne2. But for S2 (32 electrons) how to find out the electronic configuration and number of unpaired electrons. inorganic-chemistry.
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 . Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 ...
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. And if paramagnetic indicate the number of unpaired electrons. Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. In fact they do. A single covalent bond has a bond order of one. Example bdetermine the bond order and state whether you expect the species to be stable or unstable. The lewis ...
SOLVED:Apply molecular orbital theory to predict if each molecule or ion exists in a relatively stable form. a. H2 2- b. Ne2 c. He2 2+ d. F2 2-
The order of a covalent bond is a guide to its strength; a bond between two given atoms becomes stronger as the bond order increases (Table 1 in Chapter 8.1 Valence Bond Theory). If the distribution of electrons in the molecular orbitals between two atoms is such that the resulting bond would have a bond order of zero, a stable bond does not form.
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in ...
24.7.2021 · diabetes1type ⚡quotes. 2. Correct hyperglycemia: Continuous IV insulin infusion should be administered at 0.1 unit/kg/hr. No “bolus” or loading dose is necessary. When the serum glucose reaches 250 mg/dL, dextrose should be added to the IV fluids and insulin should be continued until the ketoacidosis completely resolves.
Ensure you request for assistant if you can’t find the section. When you are done the system will automatically calculate for you the amount you are expected to pay for your order depending on the details you give such as subject area, number of pages, urgency, and academic level. After filling out the order form, you fill in the sign up details.
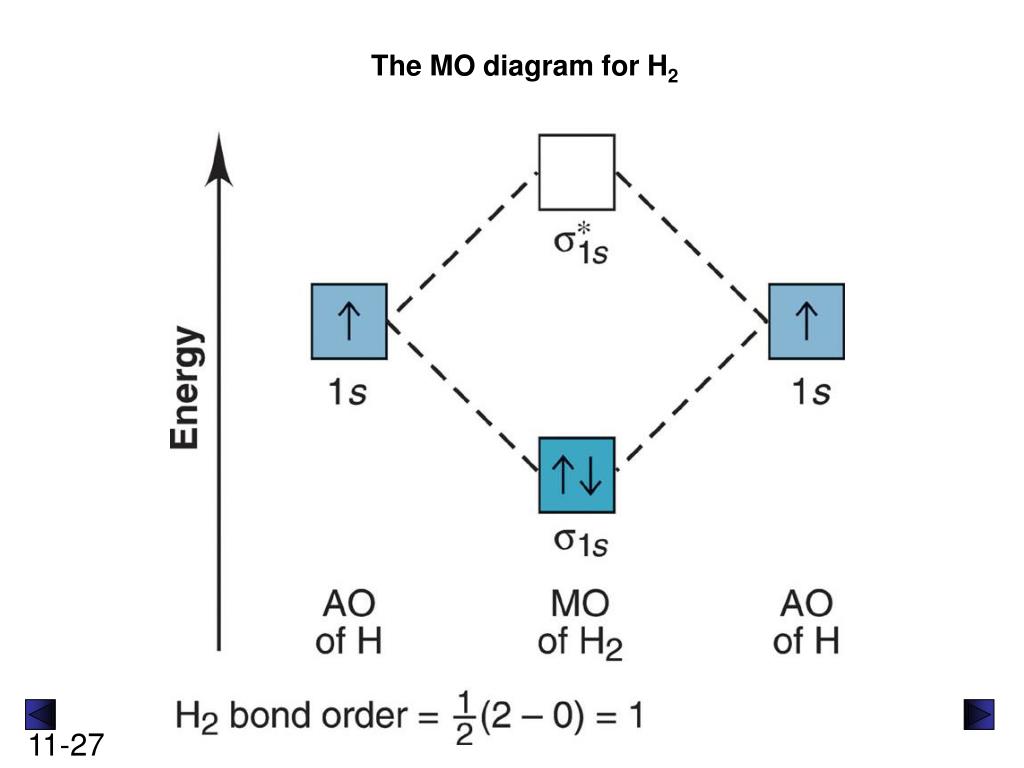
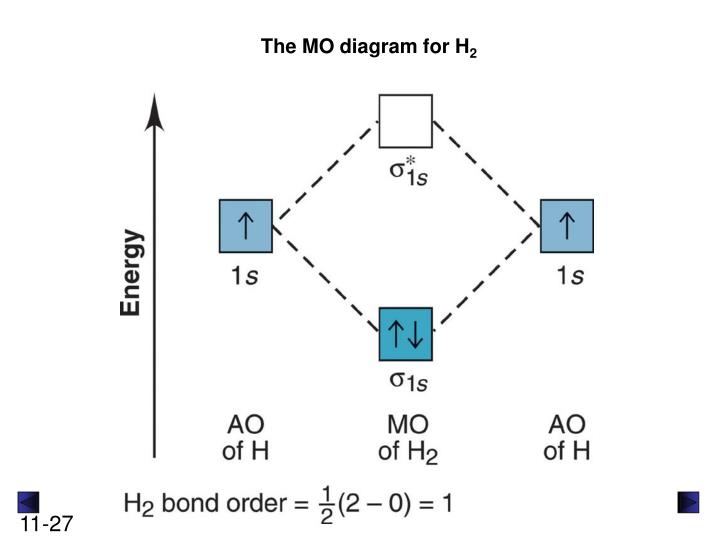
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
That is, the bond order for N2+ is 2.5. erroneous predictions of the MO method. This becomes clear if we recall the distance between nitrogen. distance between the nitrogen atoms in the N2 molecul ...
- The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict the stability of a species. - The MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electron in each MO. Molecular orbitals that lie along the internuclear axis are called _____ MOs because they are cylindrically symmetrical.
write molecular orbital configuration of c2 predict magnetic behaviour and calculate its bond order h7ch14qq -Chemistry - TopperLearning.com
To determine the bond order of a diatomic molecule such as H 2, CO or HCl, you simply look at the kind of bond involved and that is your answer. A molecule of hydrogen gas (H 2) has single bond and a bond order of 1. A molecule of oxygen gas (O 2) has a double bond and a bond order of 2. The triple bond of CN gives it a bond order of 3.
Problem Details. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H 2− exists. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems. Q. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN, and CN-. According to the Lewis model, which species is ...
Start studying chemistry online. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Given N22-, using molecular orbital and valence bond theory: a) Write the molecular orbital configuration. b) Determine the bond order. c) Determine the stability. d) Is it paramagnetic or diamagnetic? | Study.com
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. 8 2 2 62 3. Bond order number of electrons in bonding molecules number of electrons in antibonding molecules2. A the bond order of n2 b whether n2 is paramagnetic or diamagnetic c order of increasing bond strength for n2 n22 n2. Use an mo diagram to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. So the bond ...
Use The Mo Diagram Given To Find The Bond Order And Predict Whether H2 Exists - Wiring Site Resource
22 Aug 2018 — Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. Enter the bond ord. The lewis structure for h2 is h h ...
Determine the mass you will use of the MO and the HCl. Write a procedure that will determine the H for the reaction #1 above per mole of MO. Do the stoichiometry necessary to find the limiting reactant and amount of excess reagent remaining. Have your teacher approve both the stoichiometry and the procedure you wrote.
In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. For a straightforward answer: use this formula: Bond order = [(Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2.
If you're confident that a writer didn't follow your order details, ask for a refund. 25 + Subjects. From ... proofread, paraphrase, format, edit or rewrite your any paper, whether it’s a review or a term paper. High Quality. All the papers we deliver to clients are based on credible sources and are quality ... Please Use Our Service If You ...
2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero.
1 answerIf you write the sequence of molecular orbitals for the H2 molecule, the first two are a bonding sigma one and its antibonding equivalent.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Answer (1 of 4): Hi guys let me tell u one short trick for finding bond order… First of all for the given molecule add up the total no of electrons present in that molecule.. For example here in N2 we have 7+7 =14 electrons. Now remember this table.. ELECTRONS = BOND ORDER 10 = 1 11 = 1.5 ...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ...
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]`












0 Response to "40 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists."
Post a Comment