41 upper airway anatomy diagram
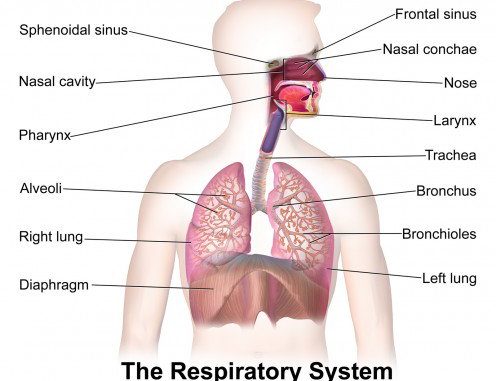
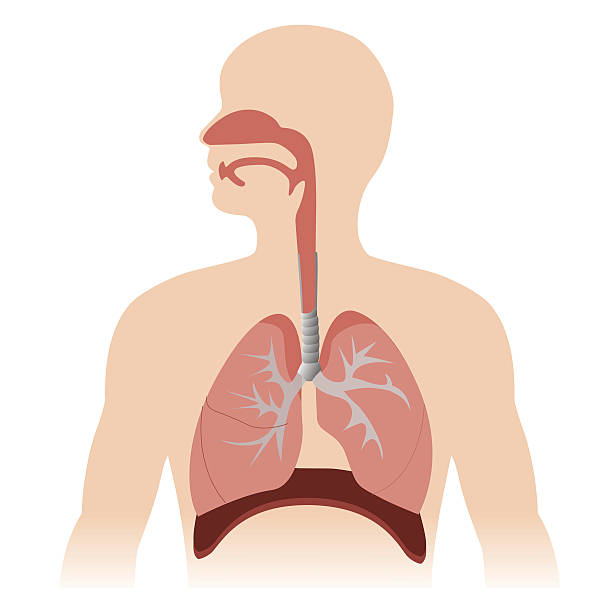
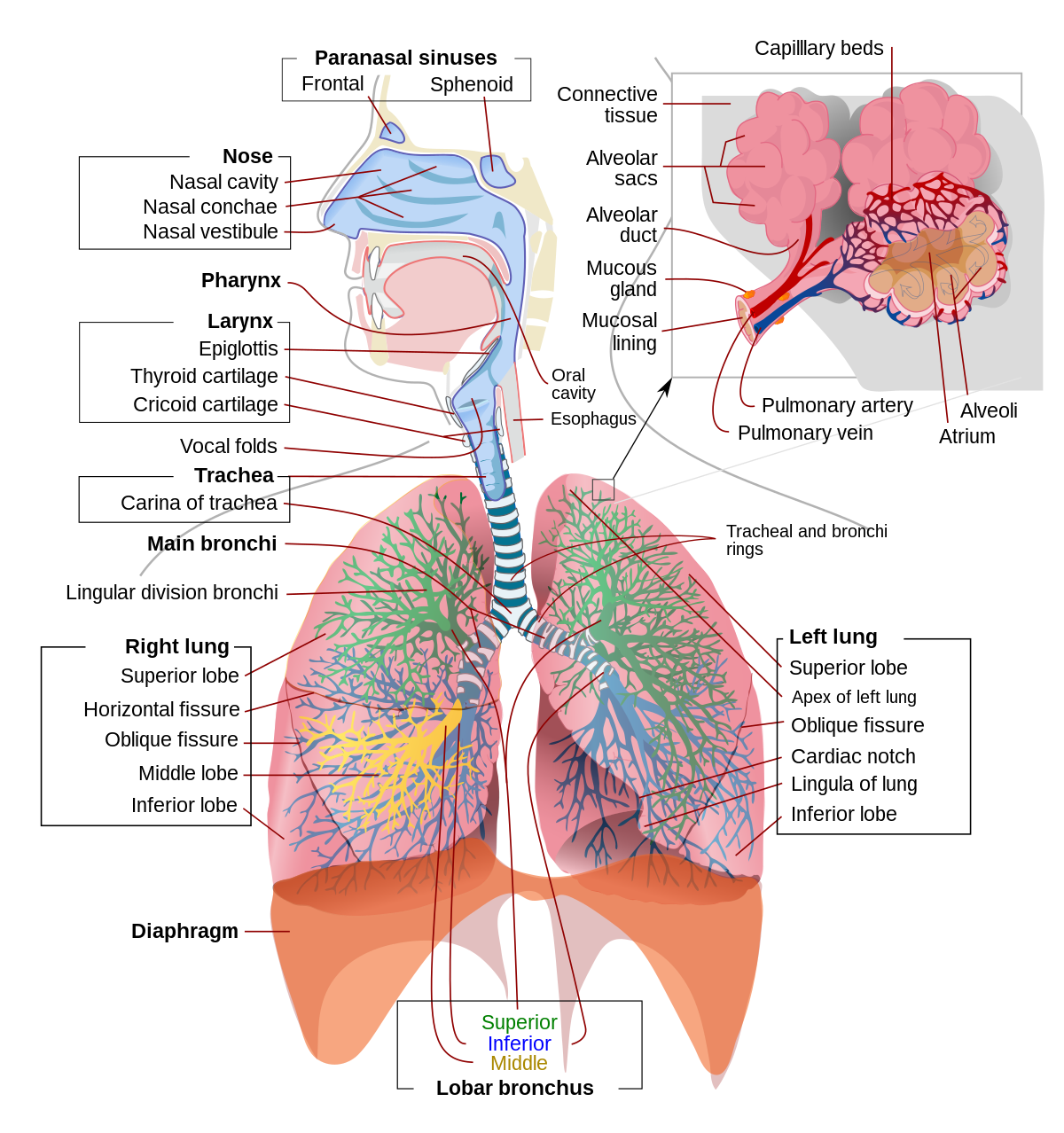
Mar 13, 2015 · The respiratory system, which includes air passages, pulmonary vessels, the lungs, and breathing muscles, aids the body in the exchange of gases between the air and blood, and between the blood ... The airway, or respiratory tract, describes the organs of the respiratory tract that allow airflow during ventilation. [1][2][3]They reach from the nares and buccal opening to the blind end of the alveolar sacs. They are subdivided into different regions with various organs and tissues to perform specific functions. The airway can be subdivided into the upper and lower airway, each of which ...
The nose is the major portal of air exchange between the internal and external environment. The nose participates in the vital functions of conditioning inspired air toward a temperature of 37°C and 100% relative humidity, providing local defense and filtering inhaled particulate matter and gases. It also functions in olfaction, which provides ...
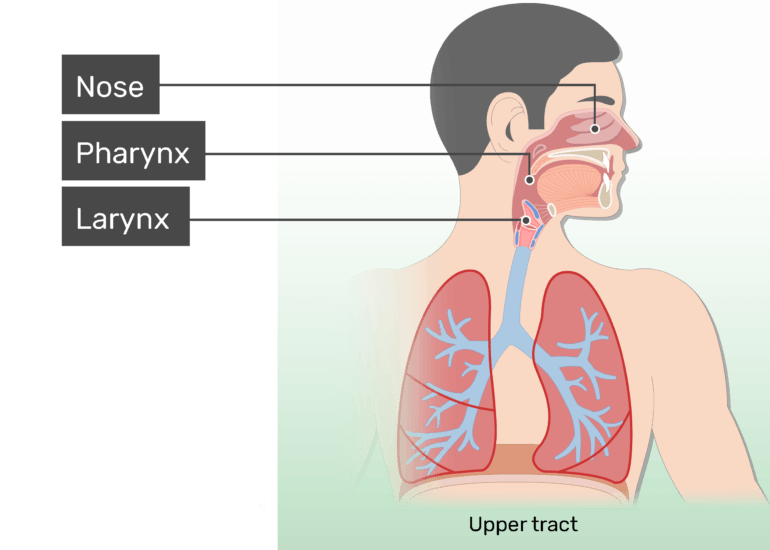
Upper airway anatomy diagram
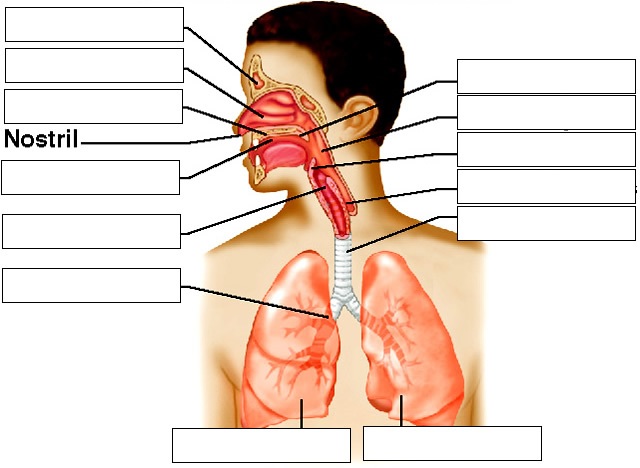
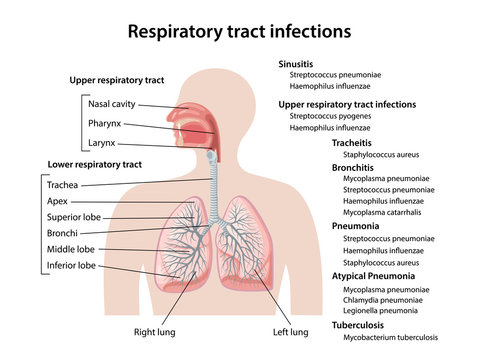
Basic Airway Anatomy Upper Airway. The upper airway is the "A" of the ABC's. As the entry point for oxygen any damage to, or blockage of, the structures in the upper airway can rapidly result in unconsciousness or death. The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose, mouth, and throat. Nov 18, 2021 · The main function of the trachea is to transport air from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. Air that enters the trachea is warmed and moisturized before moving on to the lungs. Mucus on the trachea walls can catch debris or particles. This debris is then transported upward by cilia, tiny hair-like structures that remove it from the airway. ANATOMY OF RESPIRATORY TRACT •Anatomically Respiratory tract is divided into upper and lower tract in relation to vocal cord. Upper: nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and mainstem bronchi. Lower: bronchioles , terminal bronchioles, Respiratory bronchioles , alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli.
Upper airway anatomy diagram. Jan 21, 2018 · The nose is the body's primary organ of smell and also functions as part of the body's respiratory system. Air comes into the body through the nose. As it passes over the specialized cells of the ... The upper airway system comprises the nose and the paranasal cavities (or sinuses), the pharynx (or throat), and partly also the oral cavity, since it may be used for breathing.The lower airway system consists of the larynx, the trachea, the stem bronchi, and all the airways ramifying intensively within the lungs, such as the intrapulmonary bronchi, the bronchioles, and the … Nov 28, 2016 · What is the Larynx. The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is a 2-inch long cartilaginous tube connecting the back of the nose and the windpipe with each other.It is one of the most important structures of the respiratory system, also playing a crucial role in the production of speech in humans [1].. Where is the Larynx (Voice Box) Located Mar 15, 2017 · Trachea is the medical name for the windpipe, the largest airway in the respiratory system, about 4-5 inches in length and 1 inch in diameter that extends from the lower end of the larynx or voice box [1]. An integral part of the human airway, the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli together make up the lower respiratory tract [2, 3].
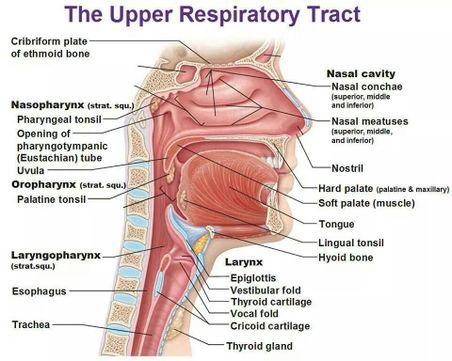
Upper airway impairment manifested in combination with breathing pattern disorders (e.g., vocal cord dysfunction) Functional DB (a subdivision of thoracic and extrathoracic DB) No structural or functional alterations directly associated with the symptoms of DB (e.g., phrenic nerve palsy, myopathy, and diaphragmatic eventration ((one leaf of ... The upper airway consists of the pharynx and the nasal cavities; however, some authors include the larynx and trachea as well. The pharynx is can be divided into the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. The nose is composed of bone and cartilage, which are in turn attached to the facial skeleton. It is a pyramidal structure that is ... Anatomy and Physiology (A&P) of the Upper Airway. The airway begins at the tip of the nose and the lips and ends at the alveolocapillary membrane, through which gas exchange takes place between the air sacs of the lung (the alveoli) and the lung’s capillary network. The airway consists of chambers and pipes, which conduct air with its 21% ... Airway anatomy 1. Anatomy of theAnatomy of the Upper AirwayUpper Airway Dr. Saurabh Barde, Anaest hesiology, GMCH, Nagpur. 2. Dr. Saurabh Barde, Anaest hesiology, GMCH, Nagpur. The Upper Airway is a Continuation of the Respiratory System 3.
Nov 09, 2021 · Upper respiratory tract. The upper respiratory tract refers to the parts of the respiratory system that lie outside the thorax, more specifically above the cricoid cartilage and vocal cords.It includes the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx and the superior portion of the larynx.Most of the upper respiratory tract is lined with the pseudostratified ciliated columnar … Nov 23, 2020 · Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nose and Nasal Cavity. The nose and nasal cavity form the main external opening for the respiratory system and are the first section of the body’s airway—the respiratory tract through which air moves. The nose is a structure of the face made of cartilage, bone, muscle, and skin that supports and protects ... Anatomy of infant and adult. Sagital section of the head and neck in (A) infant and (B) adult human. The food way and the airway are shaded in dark and light grey, respectively. (A) In infant human, the oral cavity is small, the tongue and palate … Anatomy and physiology of the upper airway Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011 Mar;8(1):31-9. doi: 10.1513/pats.201007-050RN. Authors Asli Sahin-Yilmaz 1 , Robert M Naclerio. Affiliation 1 Umraniye Education and Research Hospital, Department of Otolaryngology, Istanbul, Turkey. PMID: 21364219 DOI: 10.1513 ...
Upper Airway Anatomy Pediatric vs Adult Upper Airway Larger tongue in comparison to size of mouth Floppy epiglottis Delicate teeth, gums More superior larynx Funnel shaped larynx due to undeveloped cricoid cartilage Narrowest point at cricoid ring before ~8 years old. Upper Airway Anatomy.
An understanding of these structures is important to the clinician involved in maintaining or reestablishing the normal airway. The fol … Anatomy and physiology of the upper airway Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2002 Dec;20(4):733-45, v. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8537(02)00017-2. ...
ANATOMY OF RESPIRATORY TRACT •Anatomically Respiratory tract is divided into upper and lower tract in relation to vocal cord. Upper: nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and mainstem bronchi. Lower: bronchioles , terminal bronchioles, Respiratory bronchioles , alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli.
Nov 18, 2021 · The main function of the trachea is to transport air from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. Air that enters the trachea is warmed and moisturized before moving on to the lungs. Mucus on the trachea walls can catch debris or particles. This debris is then transported upward by cilia, tiny hair-like structures that remove it from the airway.
Basic Airway Anatomy Upper Airway. The upper airway is the "A" of the ABC's. As the entry point for oxygen any damage to, or blockage of, the structures in the upper airway can rapidly result in unconsciousness or death. The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose, mouth, and throat.






:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13894/Respiratory_system.png)
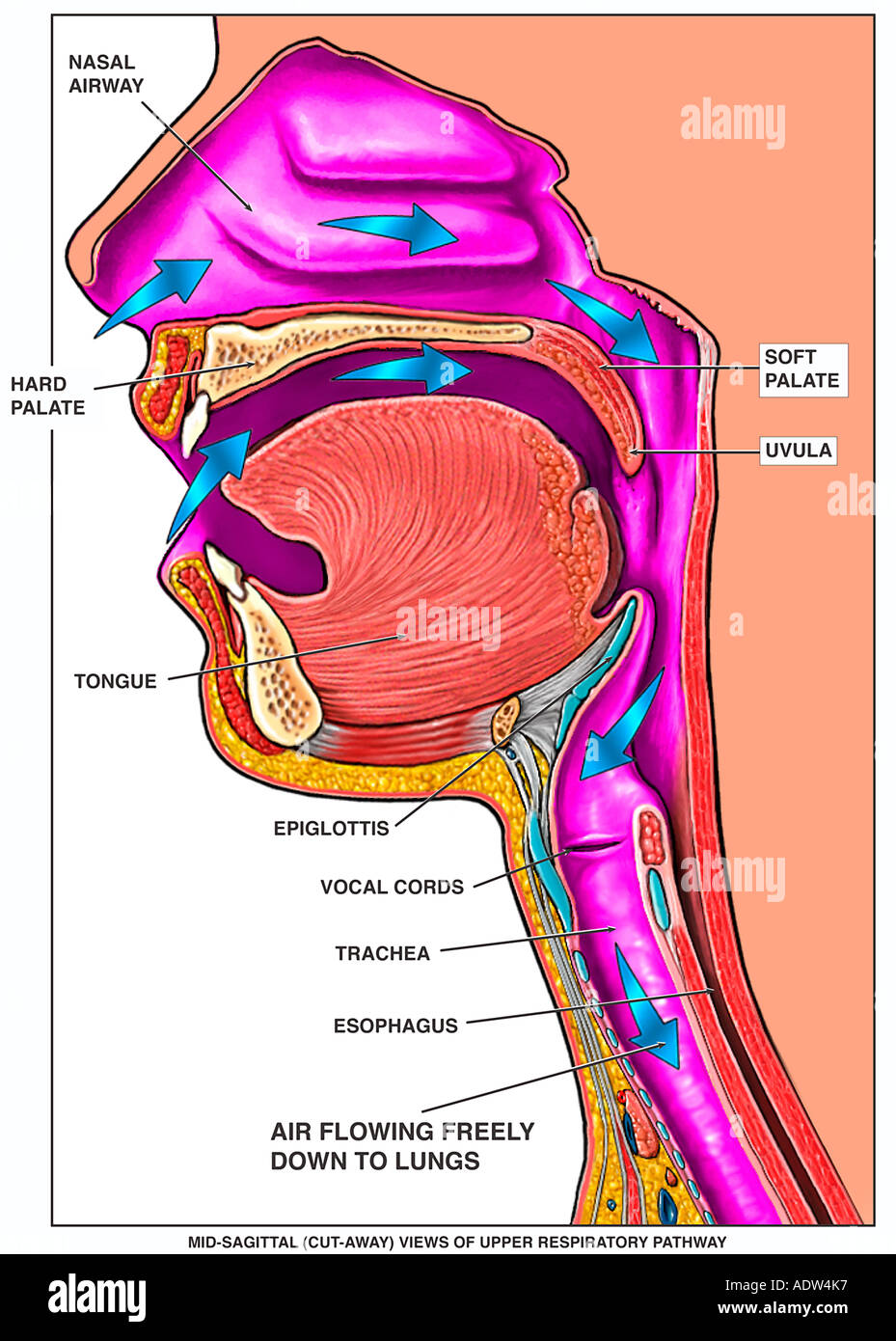

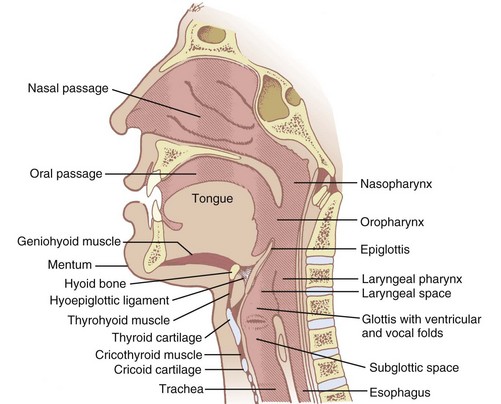




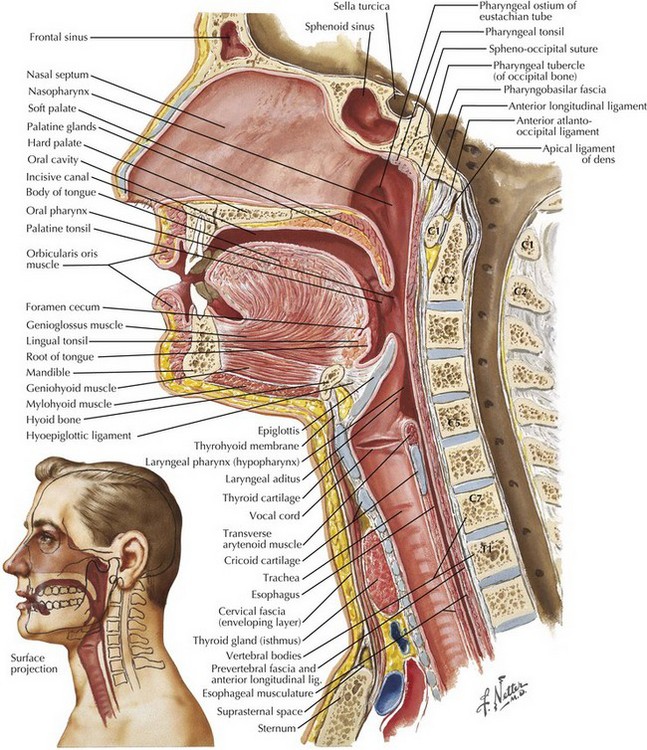








:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/6716/Overview_of_the_.png)






0 Response to "41 upper airway anatomy diagram"
Post a Comment