38 crystal field theory diagram
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) - Detailed Explanation with ... Crystal field theory was proposed which described the metal-ligand bond as an ionic bond arising purely from the electrostatic interactions between the metal ions and ligands. Crystal field theory considers anions as point charges and neutral molecules as dipoles. Crystal Field Theory - YouTube We are used to using a theory like VSEPR theory to predict molecular geometry, but unfortunately with coordination compounds, things are not so simple, becau...
Solved 1) Use crystal field theory to show d-orbital ... 1) Use crystal field theory to show d-orbital splitting diagram for [Co(OH2)6]2+ and [CoCl4]2-. Both complexes are high spin. Which complex has the largest delta? Why? ( there are two reasons). Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy for both. One of the compounds is red and one is blue. Which is which?

Crystal field theory diagram
Crystal Field Theory (CFT). An Introduction to Crystal Field Theory. The CFT approach can be easily extended to other geometries and the next most important case is the tetrahedron.To predict the splitting pattern of the energy of the d-orbitals under a tetrahedal crystal field you may once again find it convenient to consider how the ligands can fit into a cube to give a tetrahedron. Crystal field theory - SlideShare Crystal field theory takes the ionic approach and considers the ligands as point charges around a central metal positive ion, ignoring any covalent interactions. The negative charge on the ligands is repelled by electrons in the d-orbitals of the metal. Spectral Studies on Vanadyl Complexes. According to an electrostatic crystal field model, then, the resultant species may be regarded as a vanadium (IV) ion situated in a field of one oxide ion and five water dipoles. 17 As a result, Ballhausen and Gray propose the existence of four crystal field levels of increasing energy: t>2 (<^xy) * — 4Dq 2Ds ~ e ^xz'^yz^ : ~ 4^q — Ds + 4D^
Crystal field theory diagram. Crystal Field Theory -- from Eric Weisstein's World of ... Crystal Field Theory. An ionic theory which is an offshoot of electrostatic theory. It ignores all covalent bonding effects. It was developed by Hans Bethe in 1929 by applying group theory and quantum mechanics to electrostatic theory. It was further developed by physicists during the 1930s and 1940s. It can be used to predict chemical ... Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram ... Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment asked Aug 26, 2019 in Chemistry by Anup Agrawal ( 72.9k points) Crystal Field Theory: Postulates, Features, Limitations ... Crystal field splitting forms the basis of crystal field theory. Q.2.What are the main features of crystal field theory? Ans: The crystal field theory considers that the metal ion is situated in an electric field caused by the surrounding ligands. The attraction between the central metal and the ligand in a complex is purely electrostatic. Crystal Field Theory | Definition, Examples, Diagrams Crystal field theory The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to be ionic arising purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand. Ligands are treated as point charges in case of anions or dipoles in case of neutral molecules. definition Features of CFT
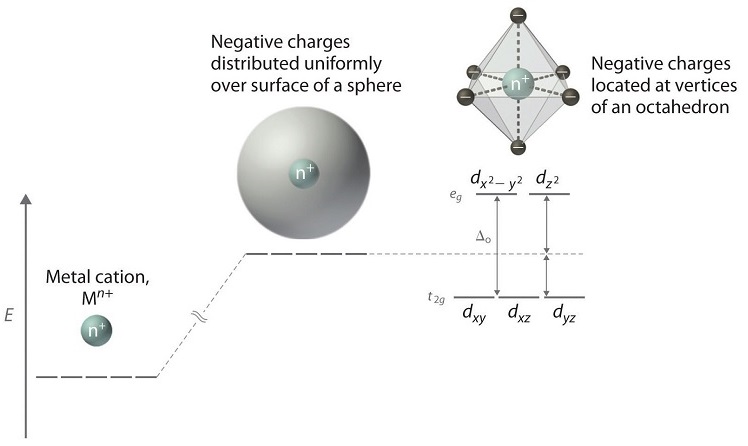
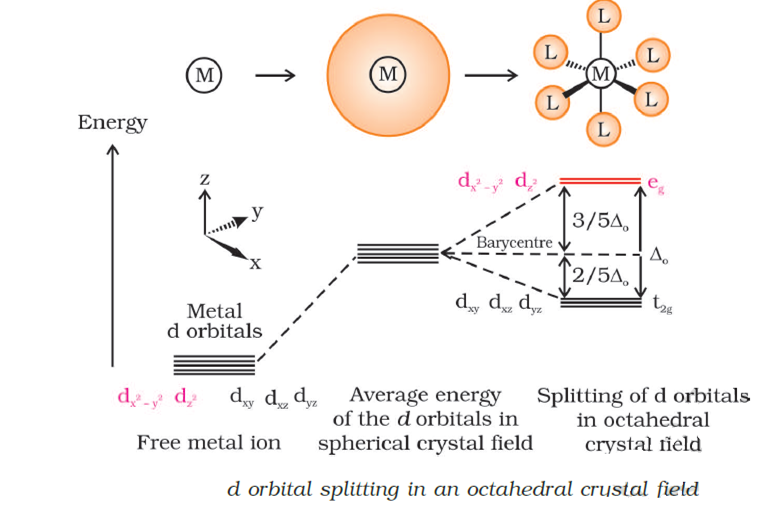
Crystal Field Theory - Purdue University Crystal field theory was developed by considering two compounds: manganese (II) oxide, MnO, and copper (I) chloride, CuCl. Octahedral Crystal Fields Each Mn 2+ ion in manganese (II) oxide is surrounded by six O 2- ions arranged toward the corners of an octahedron, as shown in the figure below. Crystal Field Theory - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The crystal field theory (CFT) was developed for crystalline solids by the physicist Hans Bethe in 1929. The model takes into account the distance separating the positively and negatively charged ions and treats the ions simply as point charges with the attractive and repulsive interactions between them as purely electrostatic/ionic ones. Ligand-Field Theory - Purdue University At the same time, this model generates a set of five orbitals in the center of the diagram that are split into t2g and eg subshells, as predicted by the crystal-field theory. As a result, we don't have to worry about "inner-shell" versus "outer-shell" metal complexes. In effect, we can use the 3 d orbitals in two different ways. Crystal Field Theory - YouTube This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into crystal field theory. It explains how to draw the crystal field splitting diagram of transi...
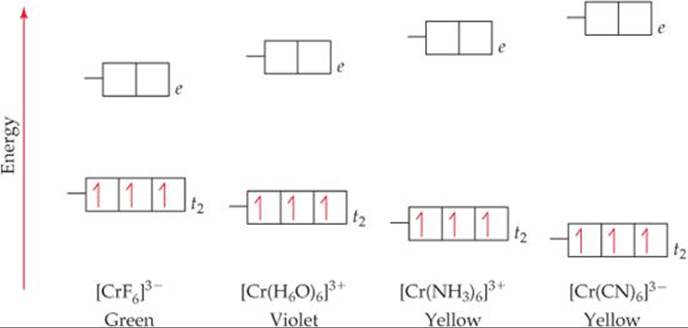
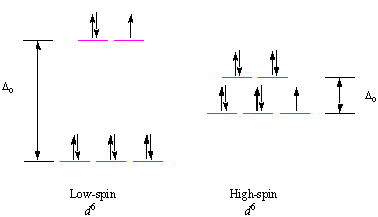
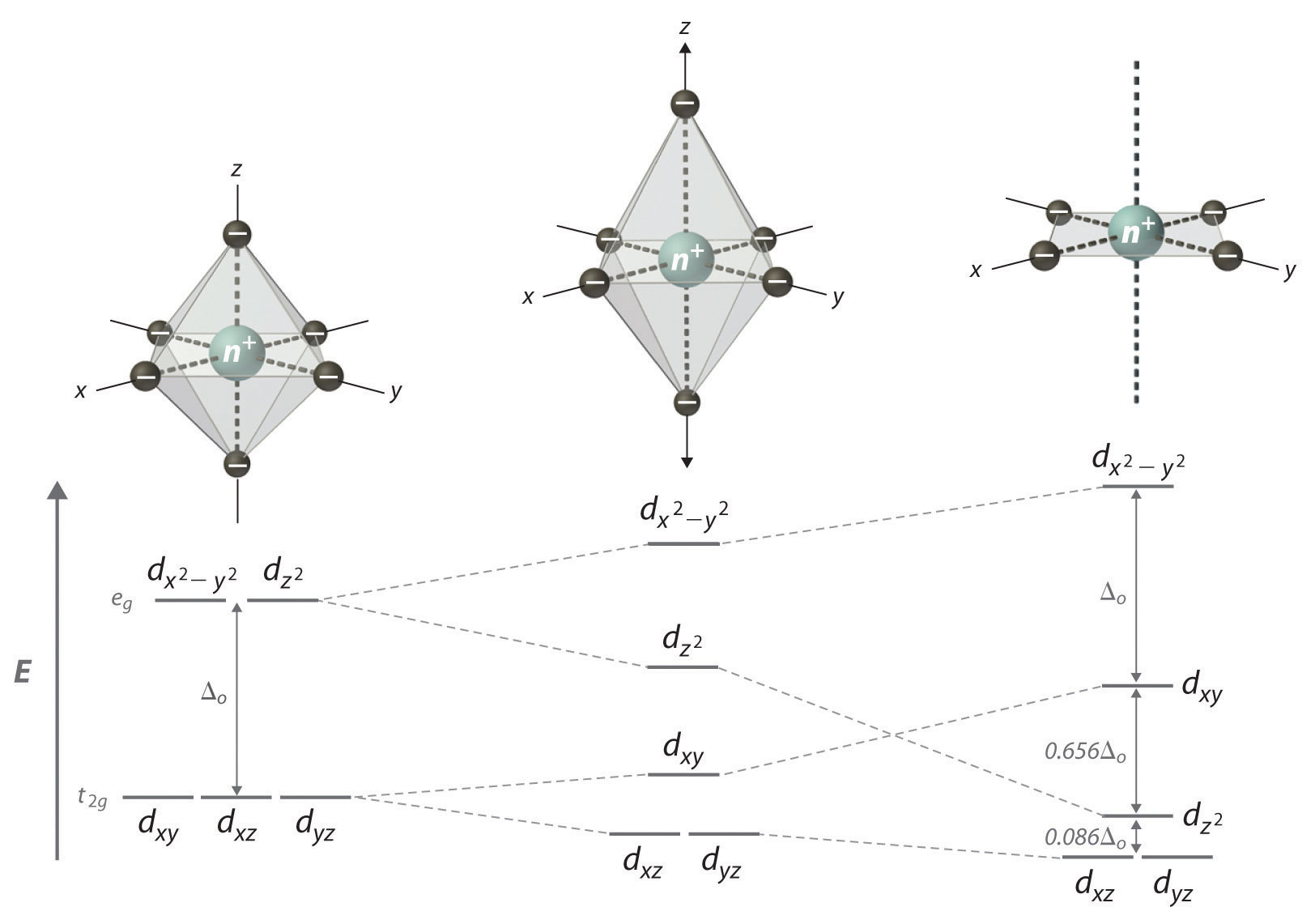
Bonding in Coordination Compounds: Crystal Field Theory ... Therefore, the crystal field splitting diagram for square planar geometry can be derived from the octahedral diagram. The removal of the two ligands stabilizes the d z2 level, leaving the d x2 -y 2 level as the most destabilized. Consequently, the d x2 -y 2 remains unoccupied in complexes of metals with the d 8 configuration. PDF Chemistry 1000 Lecture 26: Crystal field theory Crystal eld theory Crystal eld theory In an isolated atom or ion, the d orbitals are all degenerate, i.e. they have identical orbital energies. When we add ligands however, the spherical symmetry of the atom is broken, and the d orbitals end up having di erent energies. The qualitative appearance of the energy level diagram depends on Crystal field theory - Wikipedia Low Spin [Fe (NO 2) 6] 3− crystal field diagram Ligands which cause a large splitting Δ of the d -orbitals are referred to as strong-field ligands, such as CN − and CO from the spectrochemical series. In complexes with these ligands, it is unfavourable to put electrons into the high energy orbitals. Crystal Field Theory | Transition Metals - Nigerian Scholars This diagram shows the orientation of the tetrahedral ligands with respect to the axis system for the orbitals. Solution Since CFT is based on electrostatic repulsion, the orbitals closer to the ligands will be destabilized and raised in energy relative to the other set of orbitals.
Energy level diagrams crystal field - Big Chemical ... Energy-level diagram for C -3+ in an octahedral crystal field (L—S coupling not included) for the special choices and 30 (lowest doublet-levels only observed... Fig. 2. The simplified energy level diagram for Oj, 02, and 02 in their ground state. When a crystal field is present, the n, and nu levels are not degenerate.
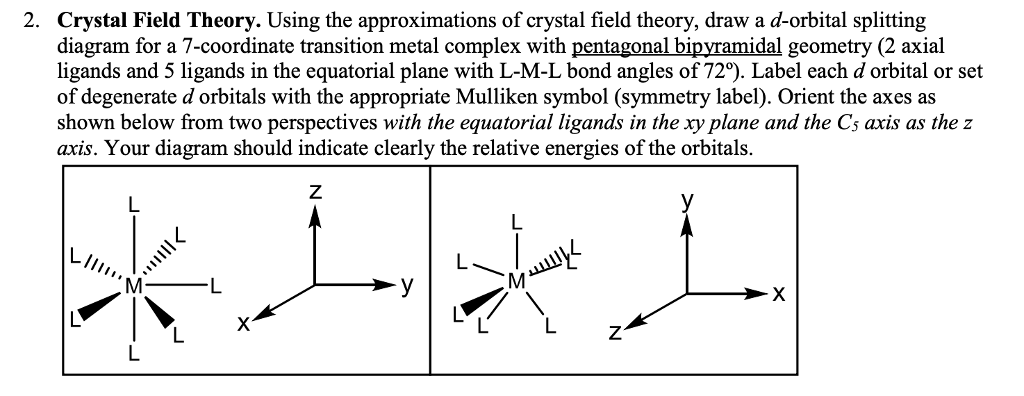
What does the crystal field splitting diagram for trigonal ... The most basic crystal field argument includes point-symmetric charges approaching the central metal in a way as the ligands would. Then, any orbitals that are symmetry-equivalent will end up at the same energy, and depending on how much these point towards the point-symmetric approaching charges they will be raised or lowered.
Crystal Field Theory (Theory) : Inorganic Chemistry ... Crystal Field Theory was developed to describe important properties of complexes (magnetism, absorption spectra, oxidation states, coordination,). The basis of the model is the interaction of d-orbitals of a central atom with ligands, which are considered as point charges.
Crystal Field Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Crystal Field Theory. Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of orbital degeneracy in transition metal complexes due to the presence of ligands. CFT qualitatively describes the strength of the metal-ligand bonds. Based on the strength of the metal-ligand bonds, the energy of the system is altered.
Square Planar D Orbital Splitting Diagram crystal field theory for tetrahedral and square planar complexes their ability to split the d-orbitals. . Lets look at some specific cases of d-orbital splitting for octahedral . tetrahedral coordination is the inverse of the diagram for octahedral .
PDF Crystal Field Theory History - University of Massachusetts ... Tetrahedral Crystal Field Splitting! The same considerations of crystal field theory can be applied to ML4 complexes with Td symmetry. •In Td, dxy, dyz, dxz orbitals have t2 symmetry and dx2-y2, dz2 orbitals have e symmetry. ! Relative energies of the two levels are reversed, compared to the octahedral case. " No d orbitals point directly ...
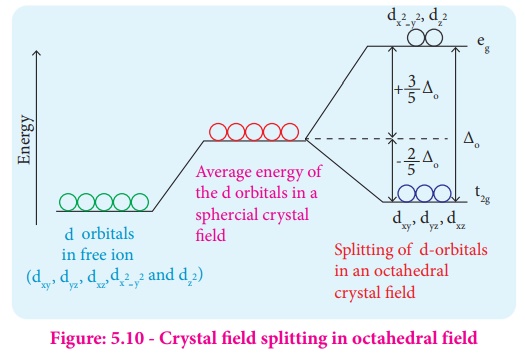
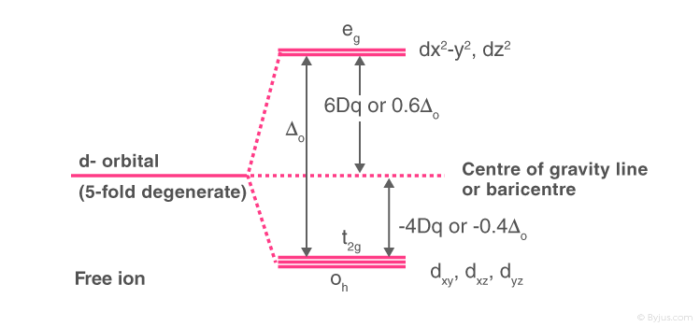
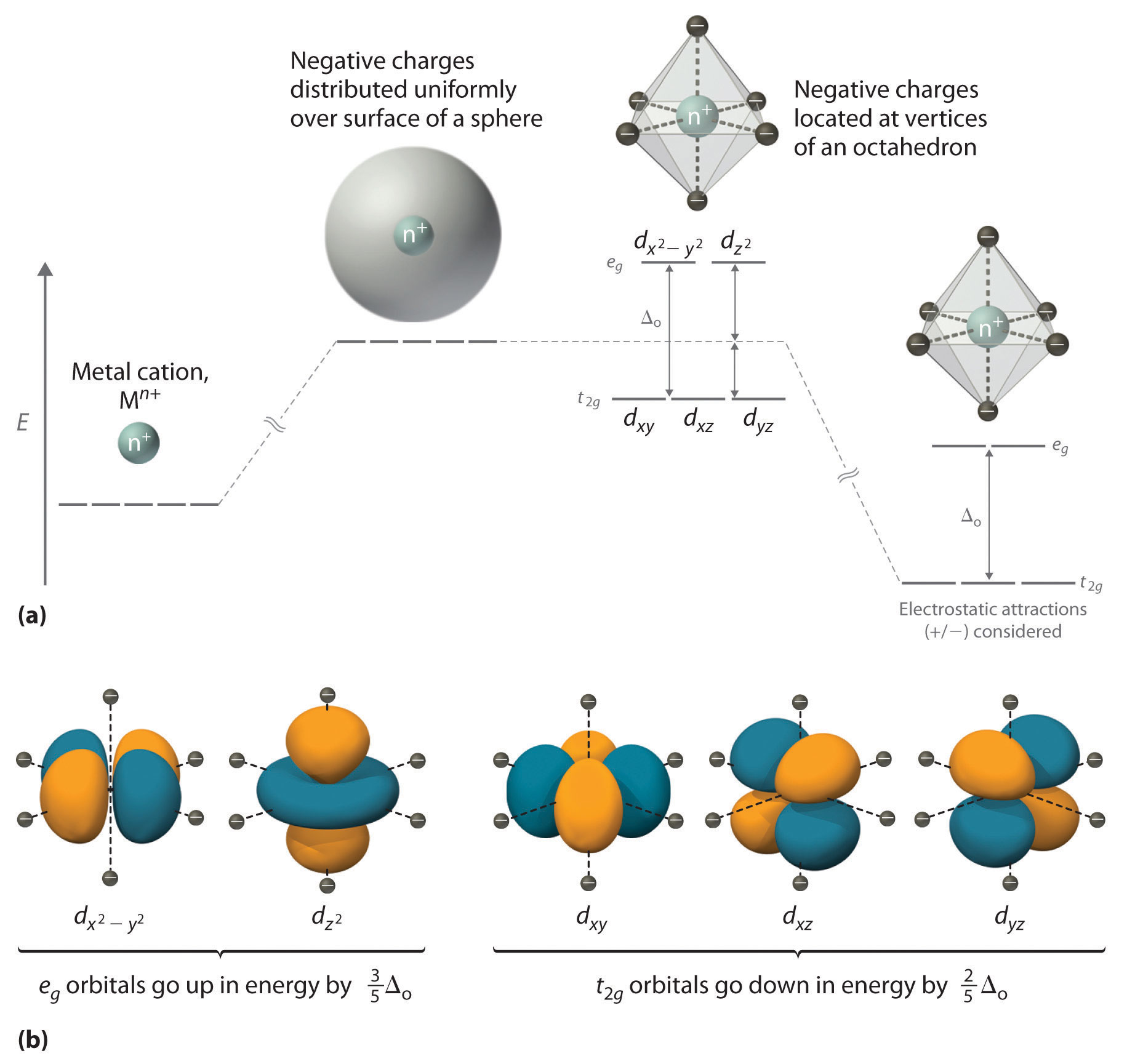
PDF Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
Crystal Field Theory | Introduction to Chemistry degenerateHaving the same quantum energy level. The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model for the bonding interaction between transition metals and ligands. It describes the effect of the attraction between the positive charge of the metal cation and negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
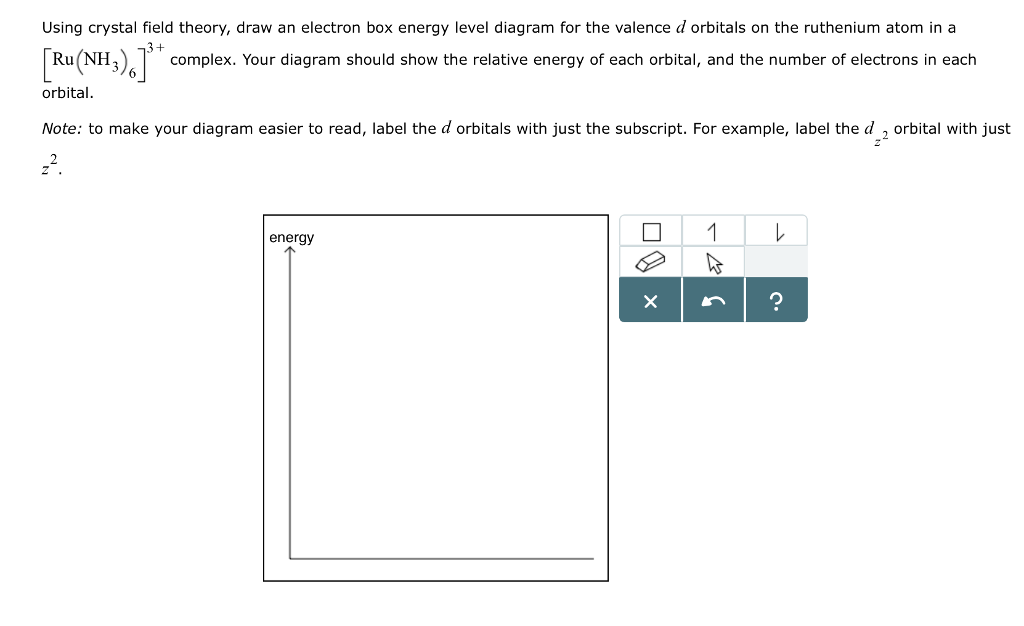
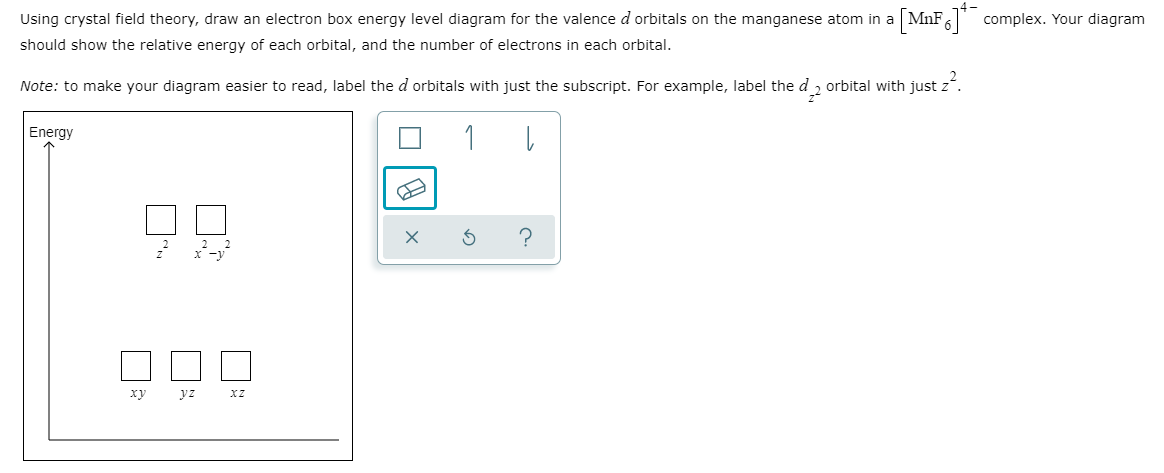
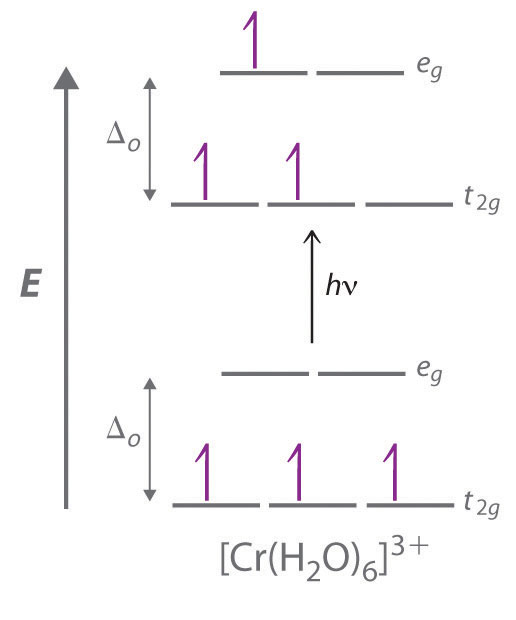
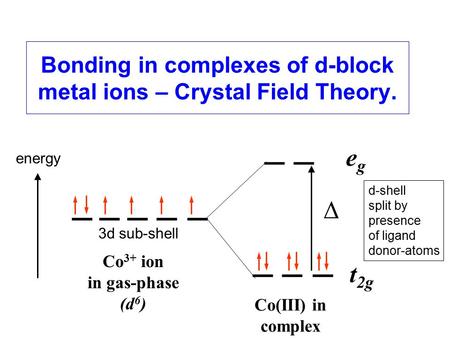
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram ... Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following. (i).[CoF 6 ] 3−,[Co(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+,[Co(CN) 6 ] 3− (ii).[FeF 6 ] 3−,[Fe(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+,[F(CN) 6 ] 4− Medium Solution Verified by Toppr Electronic configuration : Co 3+=Ar3d 6
Solved: Using crystal field theory, sketch the energy ... Using crystal field theory, sketch the energy-level diagram for the d orbitals in an octahedral field; then fill in the electrons for the metal ion in each of the following complexes. How many unpaired electrons are there in each case? a [V(CN) 6] 3− b [Co(C 2 O 4) 3] 4− (high-spin). c [Mn(CN) 6] 3− (low-spin)
Crystal_field_theory - chemeurope.com Crystal field theory (CFT) is a model that describes the electronic structure of transition metal compounds, all of which can be considered coordination complexes.CFT successfully accounts for some magnetic properties, colours, hydration enthalpies, and spinel structures of transition metal complexes, but it does not attempt to describe bonding. CFT was developed by physicists Hans Bethe and ...
Spectral Studies on Vanadyl Complexes. According to an electrostatic crystal field model, then, the resultant species may be regarded as a vanadium (IV) ion situated in a field of one oxide ion and five water dipoles. 17 As a result, Ballhausen and Gray propose the existence of four crystal field levels of increasing energy: t>2 (<^xy) * — 4Dq 2Ds ~ e ^xz'^yz^ : ~ 4^q — Ds + 4D^
Crystal field theory - SlideShare Crystal field theory takes the ionic approach and considers the ligands as point charges around a central metal positive ion, ignoring any covalent interactions. The negative charge on the ligands is repelled by electrons in the d-orbitals of the metal.
Crystal Field Theory (CFT). An Introduction to Crystal Field Theory. The CFT approach can be easily extended to other geometries and the next most important case is the tetrahedron.To predict the splitting pattern of the energy of the d-orbitals under a tetrahedal crystal field you may once again find it convenient to consider how the ligands can fit into a cube to give a tetrahedron.








/Octahedral_crystal-field_splitting-589932a85f9b5874ee4e3368.png)





![Valence Bond Theory & Crystal Field Theory Diagrams of [Co(NH3)6]3+](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/En7tzxclh5A/maxresdefault.jpg)







0 Response to "38 crystal field theory diagram"
Post a Comment