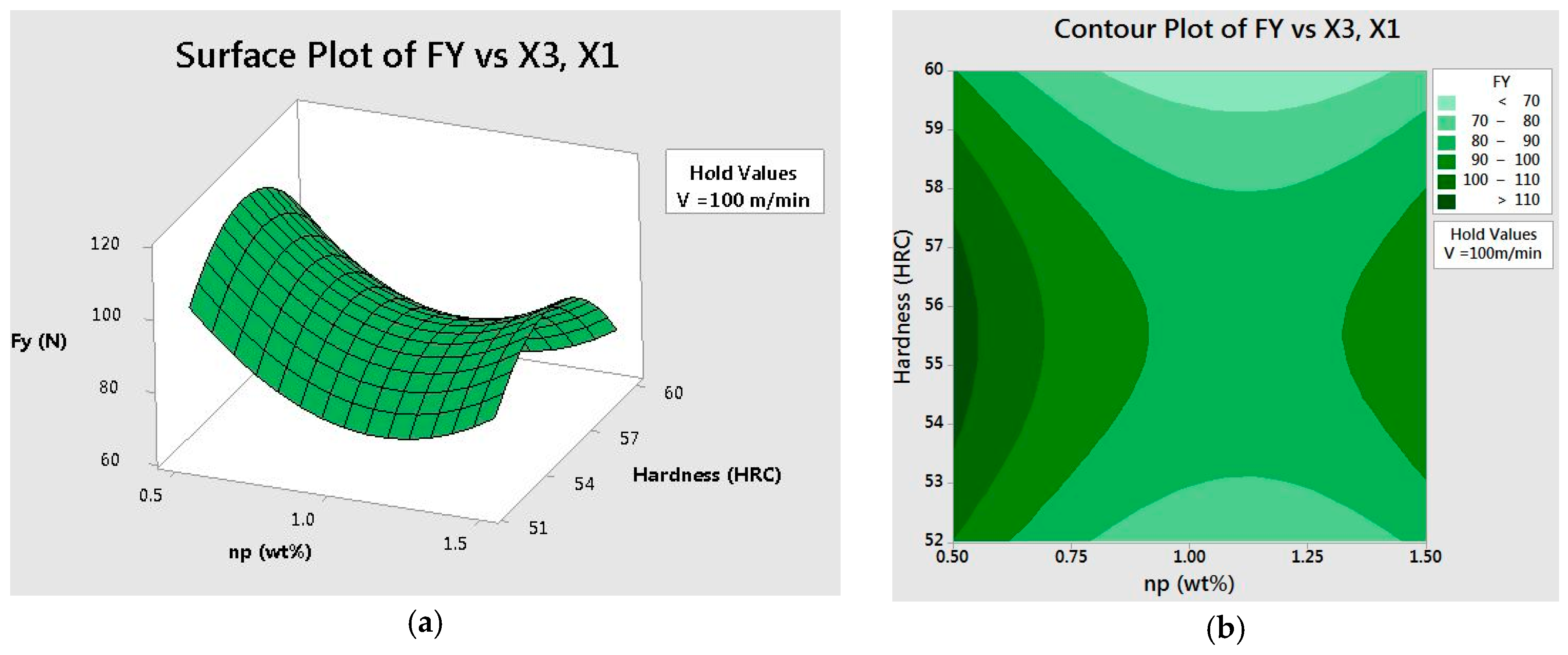
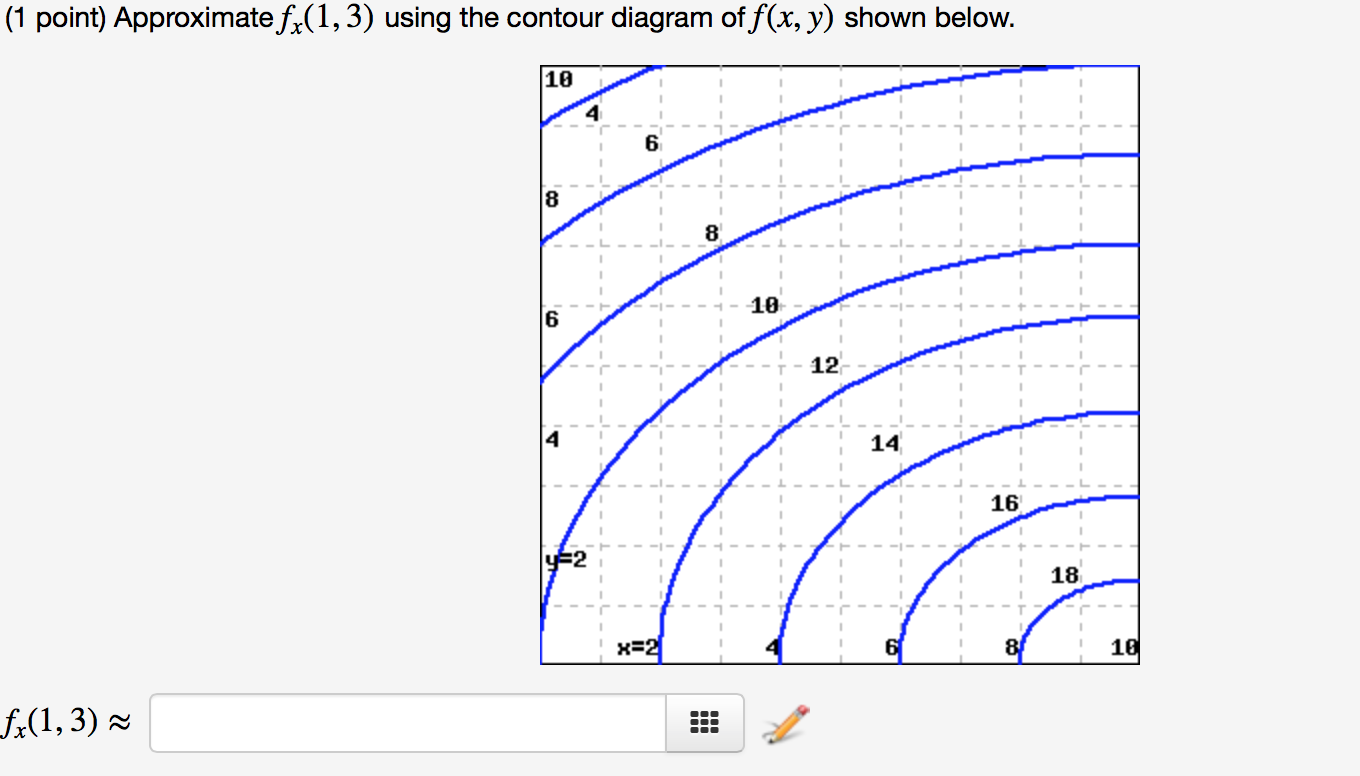
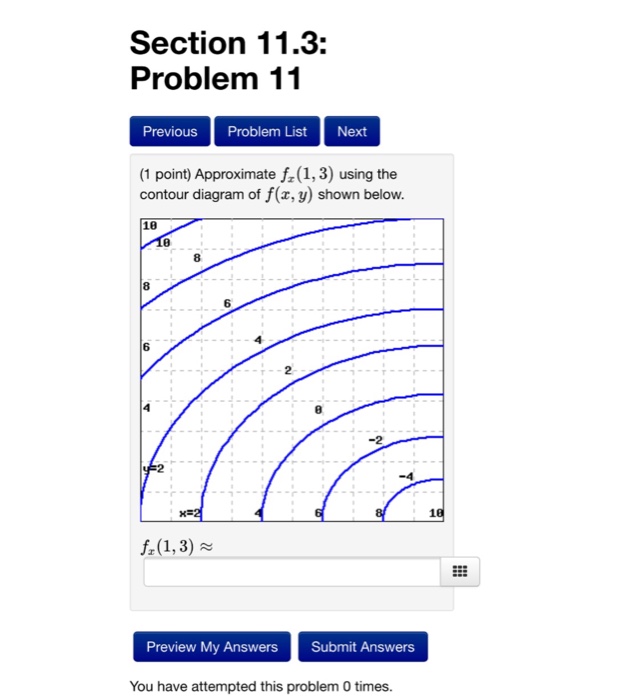
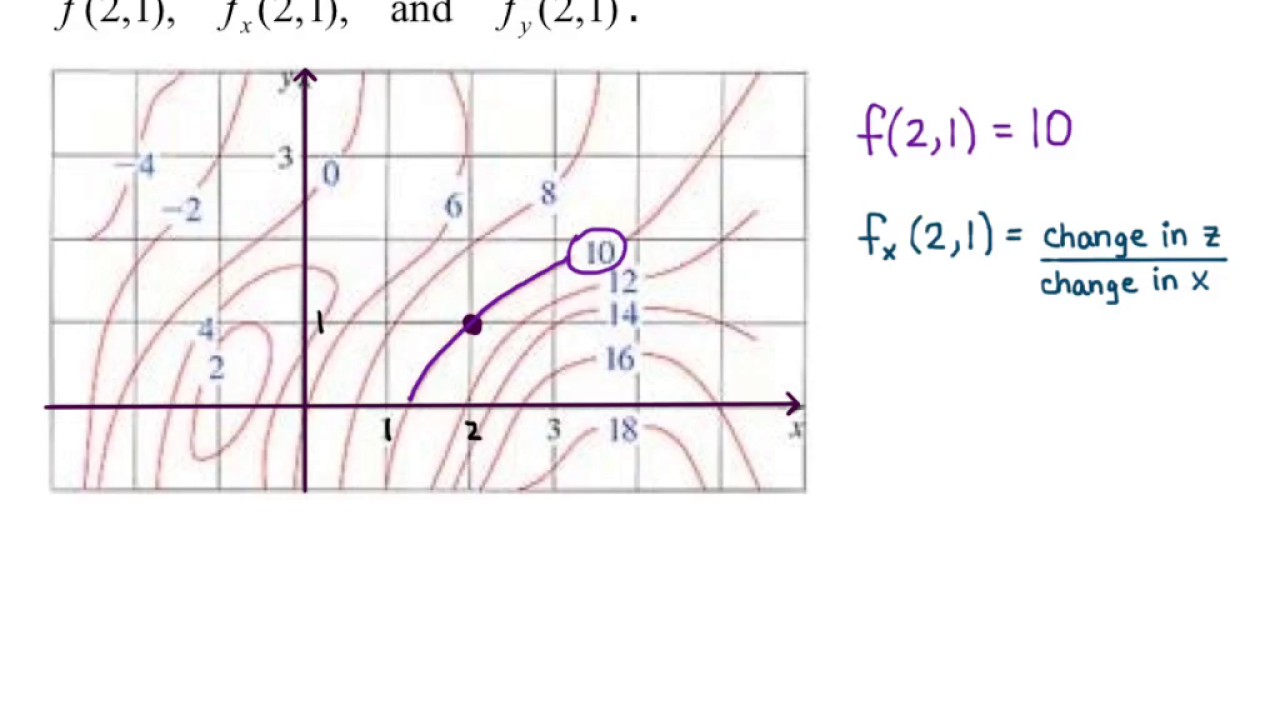
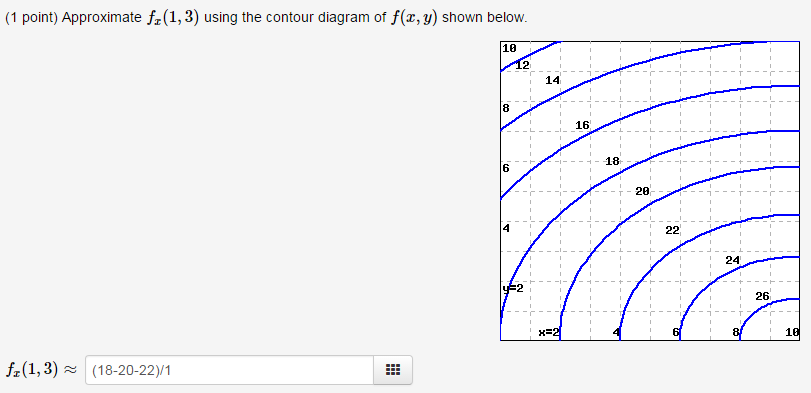
42 approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
PDF SOLUTIONS - University of California, San Diego sponding point (1;0) is one of the corners, and we will consider it separately below. the line y= 0: f(x;0) = x2 2x: Computing the derivative and setting it to 0 we find 2x 2 = 0 =)x= 1. This gives the corner (1;0) as before. the line y= 2: f(x;2) = x2 +2x+4 with critical point x= 1 which is again a corner. Finally, we check the four corners b Is P r positive or negative Suppose that your bank tells ... (1 pt) Approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. For both parts of this problem, be sure you can explain what • negative • negative • negative 4. (1 pt) Approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. f y (1, 3) ≈ Correct Answers: • (16 - 18)/2.5
PDF To learn how to use and interpret contour diagrams as a ... Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables.

Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
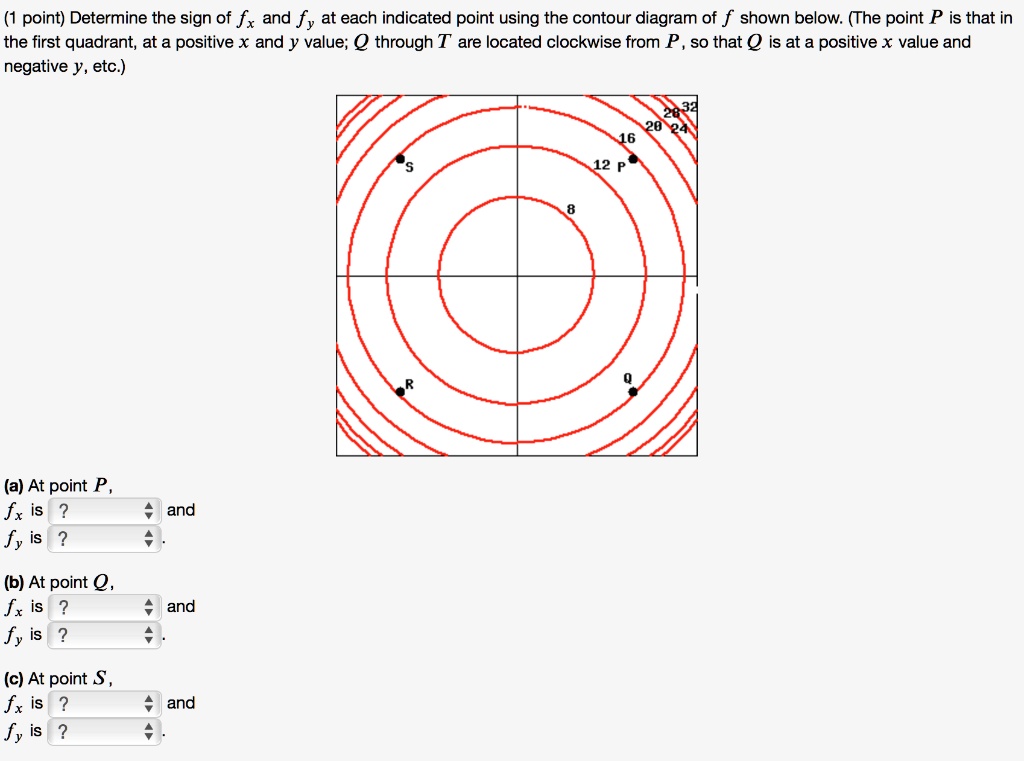
PDF Mathematics 205 HWK 11 Solutions Section 14.7 p687 Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated PDF Line Integrals and Green's Theorem Jeremy Orlo Gradient. For a function f(x;y): gradf= rf= (f x;f y). Curl. For a vector in the plane F(x;y) = (M(x;y);N(x;y)) we de ne curlF = N x M y: NOTE. This is a scalar. In general, the curl of a vector eld is another vector eld. For vectors elds in the plane the curl is always in the bkdirection, so we simply drop the bkand make curl a scalar. PDF Problem Set - Chapter 3 Solutions c. U(x, y) = x2/3 y1/3 Since the indifference curves are bowed towards the origin, they do obey the assumption of diminishing MRS. y x 8 8 1 1 512 512 . Economics 3070 d. U(x, y) =min(2X, 3Y) This is an example of perfect complements. The MRS is undefined at the vertex where 2X=3Y. But lets graph the indifference curve, remember they L shaped.
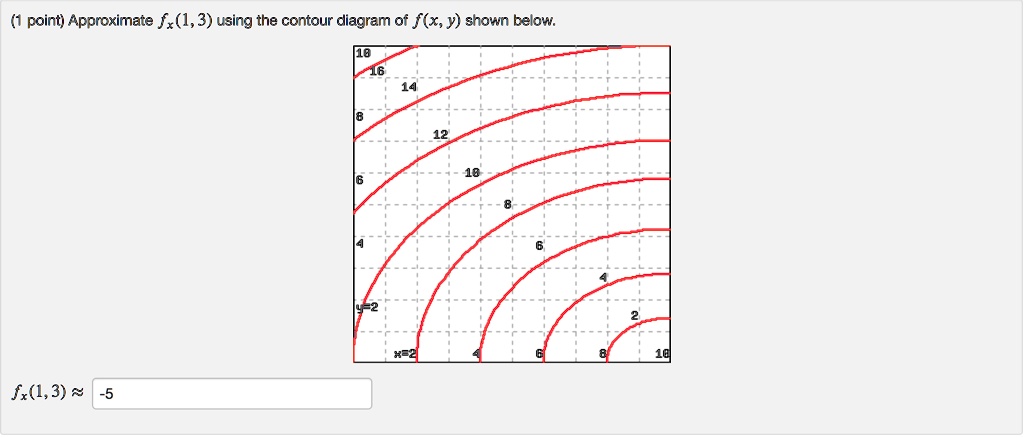
Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.. PDF Front Door - Valencia College Front Door - Valencia College PDF Unit #18 - Level Curves, Partial Derivatives Contour Diagrams c. (G) (III) - Identical reasoning as the other two ex-amples. 12.Below is the contour diagram of f(x;y). x y 1 2 31 1 2 3 2 2 1 1 0 0-1-1-2-2 Sketch the contour ... Program for Simpson's 1/3 Rule - GeeksforGeeks In Simpson's 1/3 Rule, we use parabolas to approximate each part of the curve.We divide. the area into n equal segments of width Δx. Simpson's rule can be derived by approximating the integrand f (x) (in blue) by the quadratic interpolant P (x) (in red). In order to integrate any function f (x) in the interval (a, b), follow the steps ... Solved Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram ... See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (23 ratings)
Solved Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: (1 point) Approximate fx (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. Fx (3,5). Answered: Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour… | bartleby Question. Approximate fx (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Transcribed Image Text: 10 18 16 8 14 12 6 18 8 6 4 x=2 10. 4.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient - Calculus ... Using f (x, y) = x 2 ... When using a topographical map, the steepest slope is always in the direction where the contour lines are closest together (see Figure 4.44). This is analogous to the contour map of a function, assuming the level curves are obtained for equally spaced values throughout the range of that function. ... (10 x − 2 y + 3 z ... PDF Tuesday,September17 Solutions Partial ... (c) fxx ˘ @x (fx), so if we fix y and allow x to vary, fxx is the rate of change of fx as x increases.Note that at points to the right of P the level curves are closer together (in the x-direction) than at points to the left of P, demonstrating that f increases more quickly with respect to x to the right of P.So as we move through P in the positive x-direction the (positive) value
PDF ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION - University of California, Berkeley ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1. Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f Function table (2 variables) Calculator - High accuracy ... determine whether y is a function of x and if the function is one-to-one. [4] 2021/11/20 10:34 Under 20 years old / Elementary school/ Junior high-school student / Not at All / Purpose of use First-Order Partial Derivatives - Active Calculus Once again, the derivative gives the slope of the tangent line shown on the right in Figure 10.2.3.Thinking of the derivative as an instantaneous rate of change, we expect that the range of the projectile increases by 509.5 feet for every radian we increase the launch angle \(y\) if we keep the initial speed of the projectile constant at 150 feet per second. PDF Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector f(x+u1h,y)− f(x,y) h = fy. Example 1.3. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, ... Drawing a vector out from the point (1,1) in the direction of ~u =~i+~j, we can use a difference quotient to approximate the rate of change. Specifically, the vector ~u ...
PDF Partial Differentiation - Whitman College 352 Chapter 14 Partial Differentiation k; in general this is called a level set; for three variables, a level set is typically a surface, called a level surface. EXAMPLE 14.1.5 Suppose the temperature at (x,y,z) is T(x,y,z) = e−(x2+y2+z2). This function has a maximum value of 1 at the origin, and tends to 0 in all directions.
PDF Section 14.5 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and ... Section 14.5 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview: The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x- and y-directions.Rates of change in other directions are given by directional
PDF Solutions to HW7 Problem 4.1 - IUPUI ECE302 Spring 2006 HW7 Solutions March 11, 2006 4 Problem 4.4.1 • Random variables X and Y have the joint PDF fX,Y (x,y) = ˆ c x+y ≤ 1,x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0, 0 otherwise.
PDF Vector Calculus - Whitman College a function f(x,y), recall that the gradient is hfx(x,y),fy(x,y)i, a vector that depends on (is a function of) x and y. We usually picture the gradient vector with its tail at (x,y), pointing in the direction of maximum increase. Vector fields that are gradients have some particularly nice properties, as we will see. An important example is F ...
Ex: Estimate the Value of a Partial Derivative Using a ... This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site:
[Solved] Contour map problem? - Course Hero Solved by verified expert. All tutors are evaluated by Course Hero as an expert in their subject area. Answer. -2/3. Pls find solution by graph. Step-by-step explanation. 1 Attachment. jpg.
PDF 14.6 the Gradient Vector - United States Naval Academy 27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉.
Answered: Exponential Function: f(x) = 2^(x)… | bartleby Q: Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. A: We can estimate fx by observing that as x goes from 0 to 2, with y = 3 fixed, fseems to go from abou... question_answer
PDF Section 14.1: The Partial Derivative - University of Arizona 3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below.
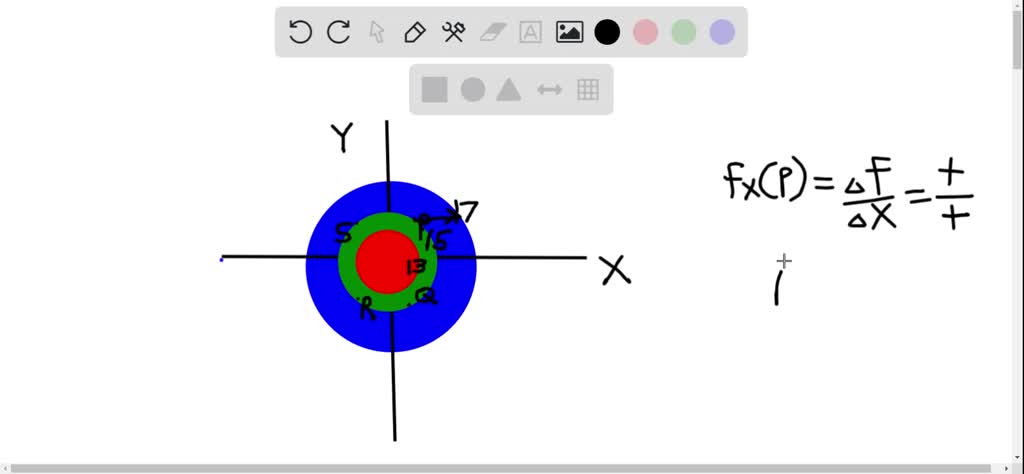
From the contour map of f shown below decide whether fx ... From the contour map of f shown below decide whether fx and fy are positive, negative, or zero at P. fx > 0, fy > 0 fx > 0, fy ... Given The Contour Diagram Answer The Questions (Green Is Lower Red Is Higher) -2 -1) 1 -1 -3 15 A A -2° B-1-1 -1 -2 Circle The Appropriate Answer. A) Fx(A) Is POSITIVE NEGATIVE ZERO B) Fy(B) Is POSITIVE NEGATIVE ...
(Solved) - Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram ... 1 Answer to Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. ... Show transcribed image text Use the contour diagram for f(x, y) shown below to estimate the directional derivative of f in the direction v at the point R (a) At the point p = (2, 2) in the direction v = i, the directional derivative is approximately ...
PDF Problem Set - Chapter 3 Solutions c. U(x, y) = x2/3 y1/3 Since the indifference curves are bowed towards the origin, they do obey the assumption of diminishing MRS. y x 8 8 1 1 512 512 . Economics 3070 d. U(x, y) =min(2X, 3Y) This is an example of perfect complements. The MRS is undefined at the vertex where 2X=3Y. But lets graph the indifference curve, remember they L shaped.
PDF Line Integrals and Green's Theorem Jeremy Orlo Gradient. For a function f(x;y): gradf= rf= (f x;f y). Curl. For a vector in the plane F(x;y) = (M(x;y);N(x;y)) we de ne curlF = N x M y: NOTE. This is a scalar. In general, the curl of a vector eld is another vector eld. For vectors elds in the plane the curl is always in the bkdirection, so we simply drop the bkand make curl a scalar.
PDF Mathematics 205 HWK 11 Solutions Section 14.7 p687 Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated














0 Response to "42 approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment