41 ray diagram convex lens
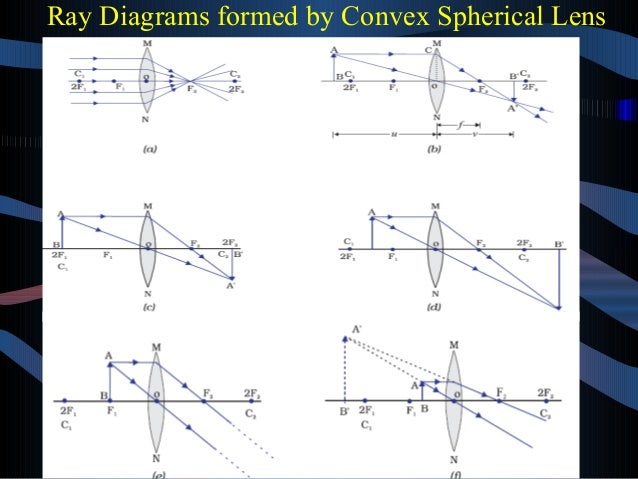
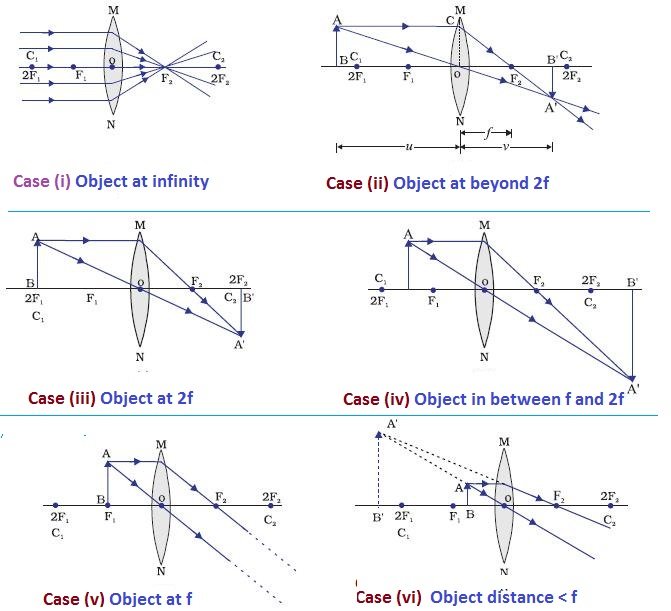
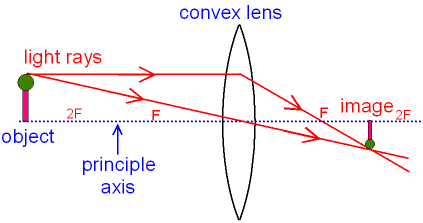
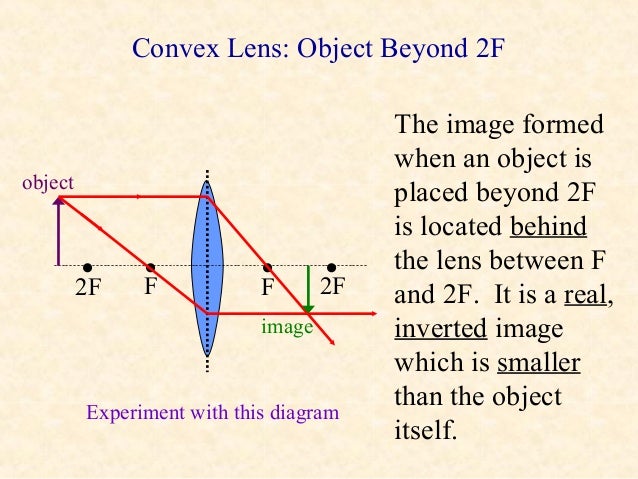
Hey guys, so after hours of study/confusion (idk maybe I'm just like...physics challenged and had trouble...that happens often to me with topics)...I've boiled it down to the following. Hopefully, it can help you all solve these kinds of problems; NS Content review goes over how to draw the diagrams, etc., but I really doubt any of us will be drawing diagrams on test day. Things to be aware of that don't have to do with the 5 steps: --> Snell's Law and refraction/reflection (i.e. what ... Jul 22, 2021 · This gives the approximate focal length of the convex lens. The corresponding ray diagram is shown below. When the position of object is beyond 2F 1, the image formed is real, inverted, and smaller in size and lies in between F 2 and 2F 2. The corresponding ray diagram is shown in figure (b) in experiment 1(b).
1896, X-rays, translation of German X-strahlen, from X, algebraic symbol for an unknown quantity, + Strahl (plural Strahlen) "beam, ray." Coined 1895 by German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1845-1923), who discovered them, to suggest that the exact nature of the rays was unknown. As a verb by 1899. Meaning "image made using X-rays" is from 1934, earlier in this sense was X-radiograph (1899).
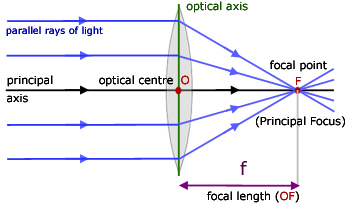
Ray diagram convex lens
1955, proprietary name of a type of wide-screen lens, a word formed from elements of panorama + vision. A convex lens has a focal length of 1 0 c m.At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it gives a real and inverted image 2 0 c m away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if the object is 2 c m high? With the help of a ray, the diagram show the formation of the image by the lens in this case. I know 1/f=1/d^i +d^o . But How do I find lenses type image and draw the ray diagram? D^o =60cm D^i =? F=15 H^i =15 Convex lens
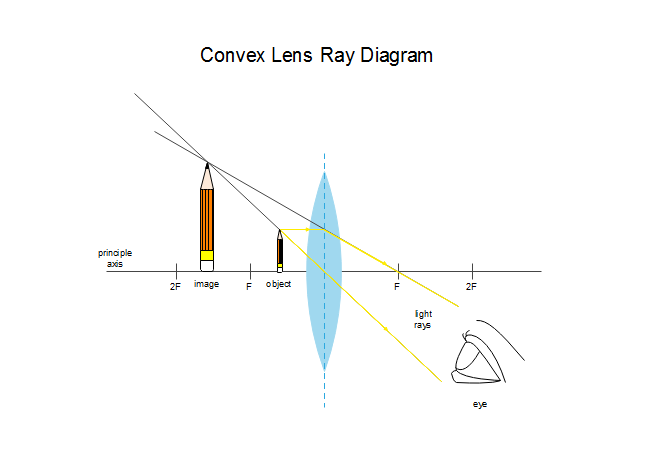
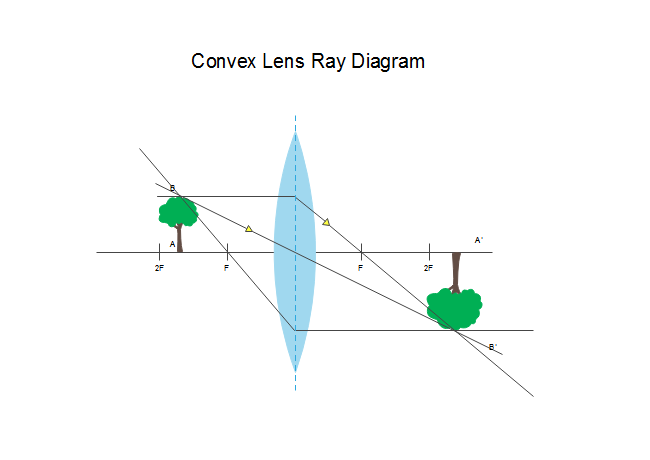
Ray diagram convex lens. An is object placed 8 cm from a converging lens and the focal length of the converging lens is 4 cm, and it is placed 4 cm left from a convex mirror which has an 8 cm focal length. Draw a ray diagram of an image of the object formed by the converging lens and call it A. What is the position of the Image A on the central axis (x=0 at the position of the object) is it A virtual or real? Upright or inverted? what is the magnification? Draw a ray diagram of an image of the Image A formed by the c... "a skate, type of fish related to sharks and noted for its broad, flat body," early 14c., raie, from Old French raie (13c.) and directly from Latin raia. De Vaan describes this as a word of unknown origin but with apparent cognates in Germanic (Middle Dutch rogghe, Old English reohhe), perhaps a loan-word from a substrate language. The old etymology (Century Dictionary, etc.) was that the fish was so called from its resemblance to the rays of a fan and from the source of ray (n.1). Hi all. I have always been a studious guy without much artistic skills or hobbies and I am a pretty smart guy who had straight As in most of the high school and college classes. I can help you understand and excel in several topics via: 1. suggesting trusted and verified sources, books, youtube videos, links, blogs 2. private doubt solving sessions (however I would be able to do these either on weekends bcoz I work a full-time job or on weekdays after 7 PM IST (Indian Standard time) till 12 PM... A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find ...
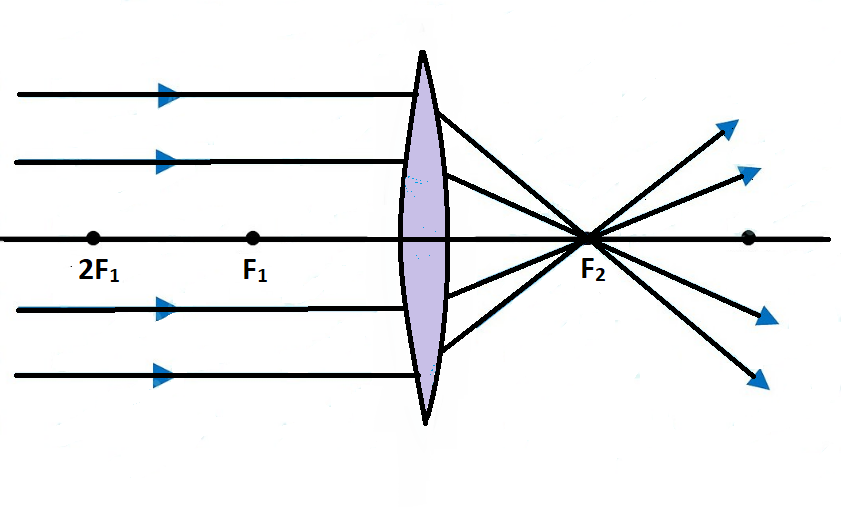
TL;DR *I am farsighted and recently had an eye exam. Optometrist said I needed a progressive lens. I asked a plethora of questions but didn't get an answer I was satisfied with. I'm worried I got taken advantage of, but before I shell out MORE money for a second opinion I wanted to run it by you folks* Now, I am a curious chap and I ask a lot of questions. I pestered the optometrist with questions until he was annoyed - but still didn't get an explanation that satisfied me. As best I coul... also sting ray, 1620s, from sting + ray (n.2). First in Capt. John Smith's writings: "Stingraies, whose tailes are very dangerous ...." I know in physics classes we often use the thin lens approximation for ray diagrams and stuff, but I was wondering what would happen if you had a lens so thick and convex that it focused light within itself - like the focal point was no longer outside the lens. Is that possible? Edit: To elaborate on "What happens?" I mean like... Could you make a lens that could hollow itself out by focusing intense light in its center? Or a lens with two focal points, since it focuses after one interface but... Nov 18, 2021 · For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
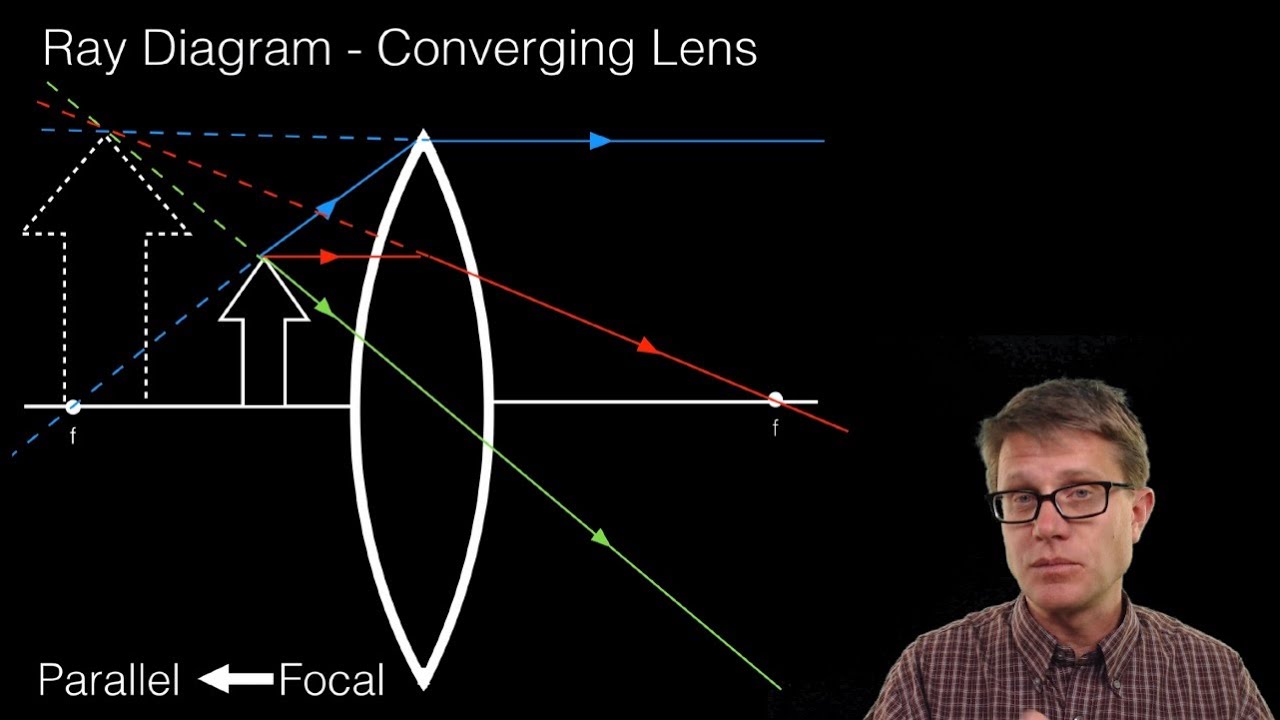
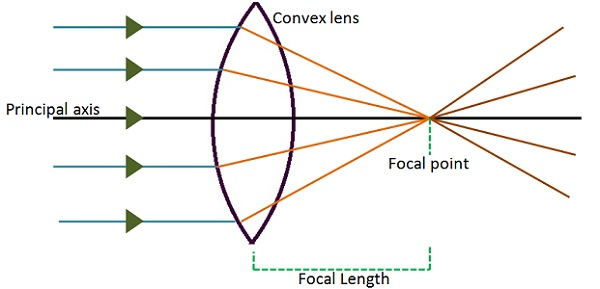
"beam of light, light emitted in a given direction from a luminous body," early 14c., rai, from Old French rai (nominative rais) "ray (of the sun), spoke (of a wheel); gush, spurt," from Latin radius "ray, spoke, staff, rod" (see radius). Not common before 17c. [OED]; of the sun, usually in reference to heat (beam being preferred for light). Ray is usually distinguished from beam, as indicating a smaller amount of light; in scientific use a beam is a collection of parallel rays. In ordinary language ray is the word usually employed when the reference is to the heat rather than the light of the sun .... [OED] Science fiction's ray-gun is recorded by 1931 (in Amazing Stories; electric ray gun as an imaginary weapon is from 1924; death-ray gun from 1926 as a prop in a vaudeville act), but the Martians had a Heat-Ray weapon in "War of the Worlds" (1898). Parrallel rays of light (consisting of one Red, one Green and one Blue wavelength) enter a single thin converging lens; I have to draw three diagrams- one demonstrating spherical abberation, one demonstrating chromatic abberation, and the final demonstrating both. Spherical aberration comes from the fact that a spherical lens doesnt focus parallel rays at a single point. The closer the rays are to the axis of the lens, the better job the lens does of focusing them at one point, but it is never... Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the ... If those surfaces are bent outwards, the lens is called a biconvex lens or simply convex lens. These types of lenses can converge a beam of light coming from outside and focus it to a point on the other side. This point is known as the focus and the distance between the center of the lens to the focus is called the focal length of convex lens.
A Convex Lens Of Focal Length 15 Cm Forms An Image 10 Cm From The Lens How Far Is The Object Placed From The Lens Draw The Ray Diagram. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Here is the system I'm working with: https://imgur.com/W3K5ClC Here is the ray tracing I have done: https://imgur.com/V5HXmO7 I've draw the ray traces to image the object. I'm fairly confident that it is correct. My next task is to determine the aperture stop of the system. I've drawn in the black aperture stop labeled "AS" in the diagram but I'm not confident that this is correct. My thought process is that the aperture stop only lets in light that makes it to the image so I put the AS on the...
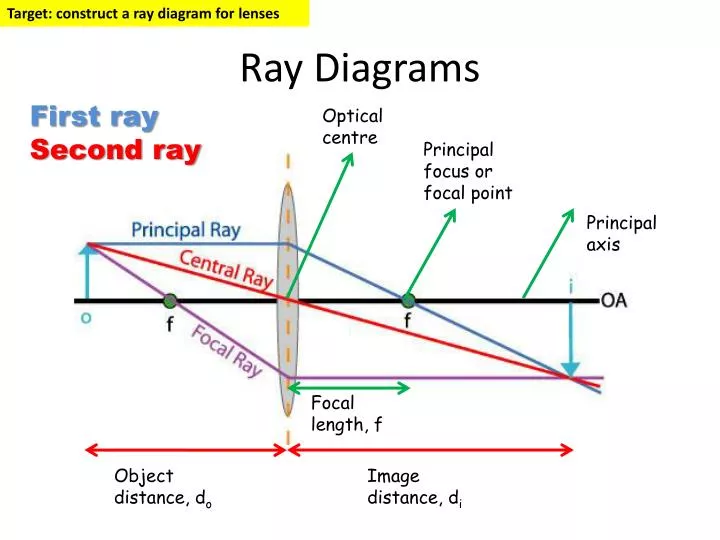
Tutorial: Ray Diagram for Convex Lenses. Here we describe the method of drawing a ray diagram for a convex lens, for which the object is.
A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak diverging lens is placed between the converging lens and the image, where is the new image ...15 pages
"lens-shaped, having the form of a double-convex lens," early 15c., from Late Latin lenticularis "lentil-shaped," from lenticula "a small lentil," diminutive of Latin lens "a lentil" (see lentil). Related: Lenticularity (1890).
"curved like a circle or sphere when viewed from outside," 1570s, from French convexe, from Latin convexus "vaulted, arched," past participle of convehere "to bring together," from assimilated form of com "with, together," or "thoroughly" (see com-) + vehere "to bring, carry, convey" (from PIE root *wegh- "to go, move, transport in a vehicle"). Possibly the notion is of vaults "carried together" to meet at the point of a roof. Related: Convexity. Convex lens is from 1822.
I finally understand ray diagrams, but I have another problem. When plotting the ray diagram of a convex lens refraction with the object sitting between F' and O (lens), the description says the refracted image should be at 2F' and beyond. Mine sits at F', and I do not know why it changed, or how it happened. Hopefully someone can answer. Thank you in advance
1610s, "an illustrative figure giving only the outlines or general scheme of the object;" 1640s in geometry, "a drawing for the purpose of demonstrating the properties of a figure;" from French diagramme, from Latin diagramma "a scale, a musical scale," from Greek diagramma "geometric figure, that which is marked out by lines," from diagraphein "mark out by lines, delineate," from dia "across, through" (see dia-) + graphein "write, mark, draw" (see -graphy). Related: Diagrammatic; diagrammatically. The verb, "to draw or put in the form of a diagram," is by 1822, from the noun. Related: Diagrammed; diagramming.
The word lens comes from lēns, the Latin name of the lentil, because a double-convex lens is lentil-shaped.The lentil plant also gives its name to a geometric figure.. Some scholars argue that the archeological evidence indicates that there was widespread use of lenses in antiquity, spanning several millennia. The so-called Nimrud lens is a rock crystal artifact dated to the 7th century BC ...
Parrallel rays of light (consisting of one Red, one Green and one Blue wavelength) enter a single thin converging lens; I have to draw three diagrams- one demonstrating spherical abberation, one demonstrating chromatic abberation, and the final demonstrating both. Spherical aberration comes from the fact that a spherical lens doesnt focus parallel rays at a single point. The closer the rays are to the axis of the lens, the better job the lens does of focusing them at one point, but it is never...
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length.
Lens and Mirror Inquiry Lab ... Lens and Mirror Lab. Category Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick! Recommended Lab: Lens and Mirror Inquiry Lab PDF Version MS …
1690s, "glass to regulate light rays," from Latin lens (genitive lentis) "a lentil," on analogy of the double-convex shape. See lentil. Anatomical use, of the eye part, from 1719. Lens-cap is from 1857. In the vernacular of the photographer, anyone crowding to the front of a group, staring into the lens, or otherwise attracting attention to himself is known as a "lens louse." ["American Photography," vol. xl, 1946; the term dates from 1915]
1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881).
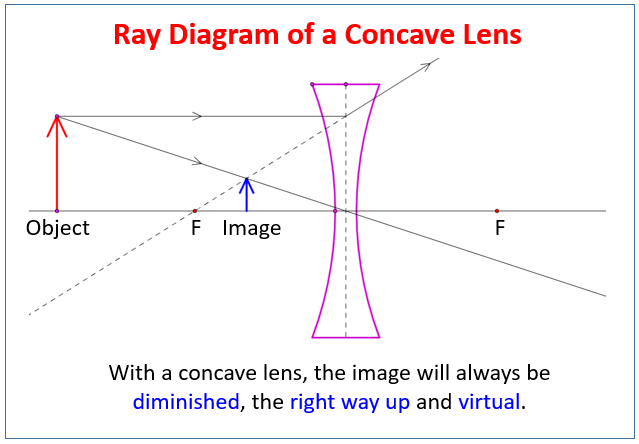
Oct 08, 2021 · For a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction For a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation
Guidelines for rays falling on the concave and convex lenses · When a ray strikes concave or convex lenses obliquely at its pole, it continues to follow its path ...
Having studied the journals of Heirgen Delamere, which are contained in Moonsmoth Museum, I find myself more interested in obscure German urban legends. By these accounts, there was held to be, in certain maps of old, a city near Bavaria, some few miles North of the Black Forest. Writing in the year 1850, H.Delamere was born in Hamburg to an estranged mother, and secretive father. Moreover, his recorded annals, indicate his preoccupation with looking into his ancestral lineage around this time...
I know 1/f=1/d^i +d^o . But How do I find lenses type image and draw the ray diagram? D^o =60cm D^i =? F=15 H^i =15 Convex lens

Image from page 222 of "A high-school astronomy: in which the descriptive, physical, and practical are combined .." (1859)
A convex lens has a focal length of 1 0 c m.At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it gives a real and inverted image 2 0 c m away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if the object is 2 c m high? With the help of a ray, the diagram show the formation of the image by the lens in this case.
1955, proprietary name of a type of wide-screen lens, a word formed from elements of panorama + vision.

Image from page 40 of "Optical projection : a treatise on the use of the lantern in exhibition and scientific demonstration" (1906)

Image from page 41 of "Optical projection : a treatise on the use of the lantern in exhibition and scientific demonstration" (1906)

Image from page 67 of "A compendium of astronomy; containing the elements of the science, familiarly explained and illustrated, with the latest discoveries. Adapted to the use of schools and academies, and of the general reader" (1850)

















0 Response to "41 ray diagram convex lens"
Post a Comment