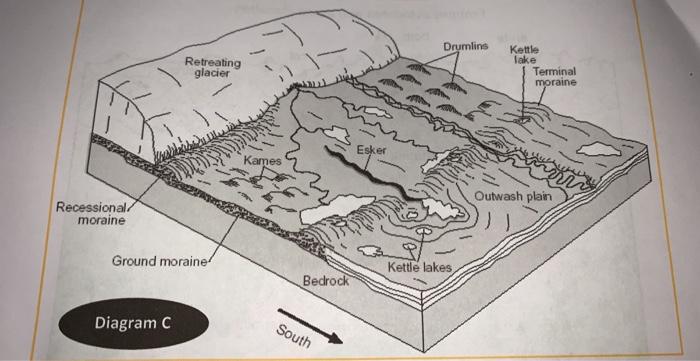
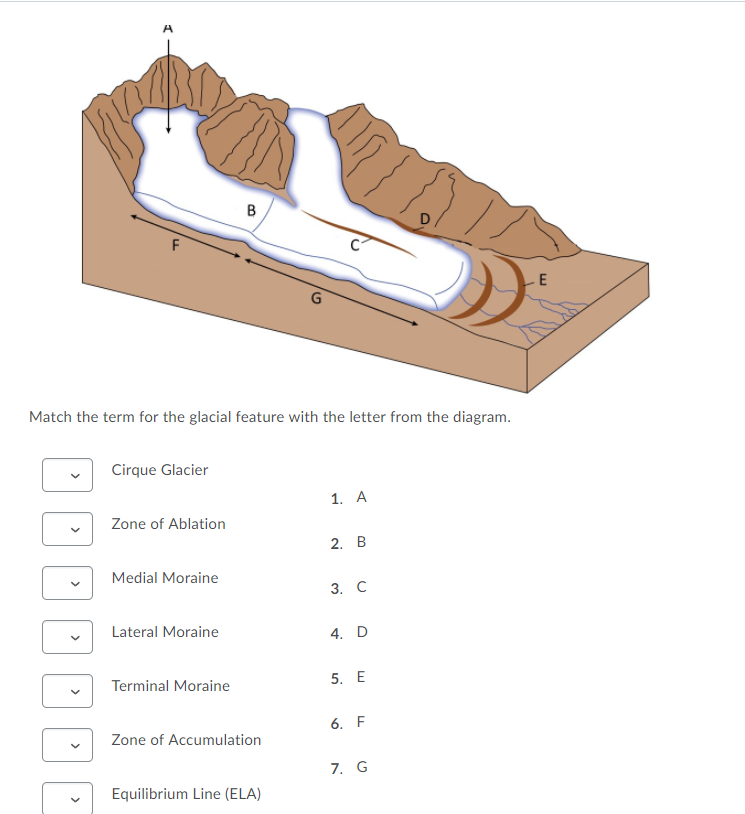
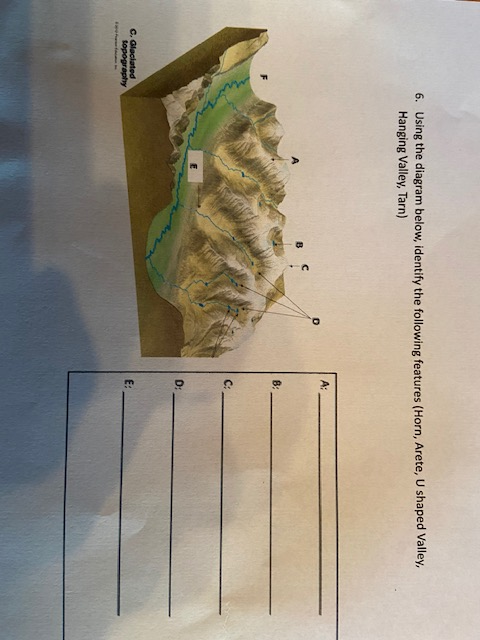
40 which feature on this diagram is a cirque?
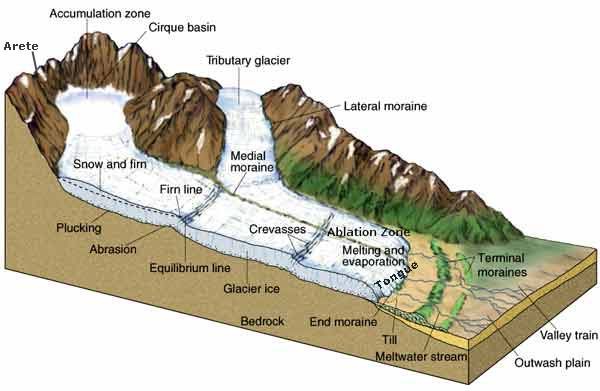
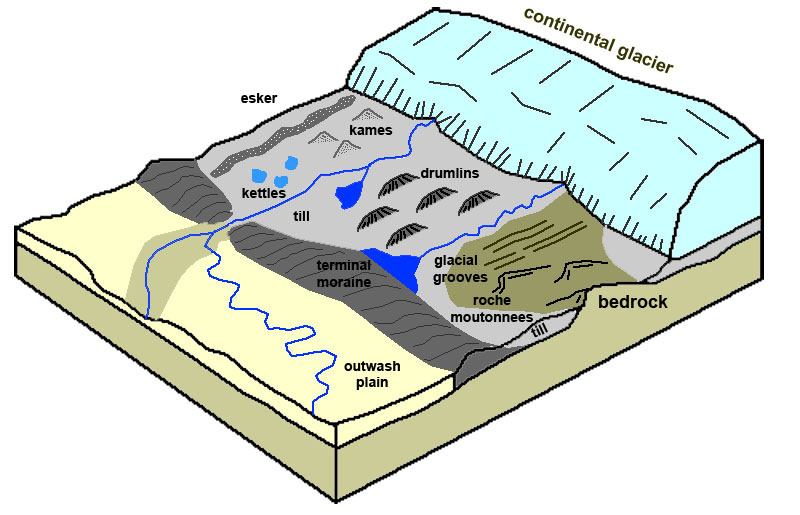
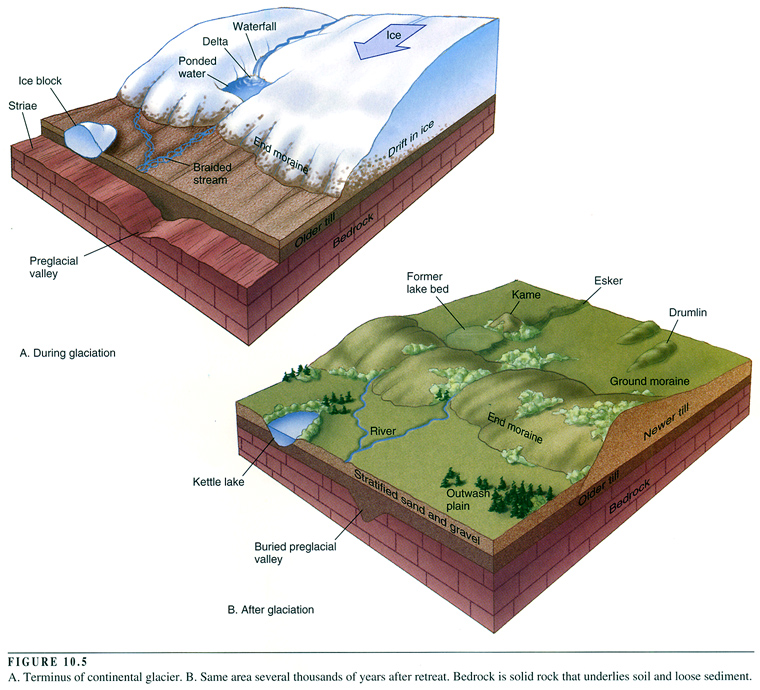
27) The type of glacial debris that can fall into a crevasse is A) subglacial debris. B) supraglacial debris. C) englacial debris. D) All of these are correct. 27) 28) The main reason that the deposits shown here are sorted and stratified is that the glacier that dropped them was A) moving very slowly. B) accompanied by running meltwater. Cirque True or False: mountain glaciation results in eroding flat-bottomed U-shaped troughs or valleys. True or False: a tarn is also known as a cirque lake 1-3. Review Fig. 13.6-13.7 on p. 336-337. List, sketch and briefly define the following: A) Three types of depositional features associated with alpine glaciers.
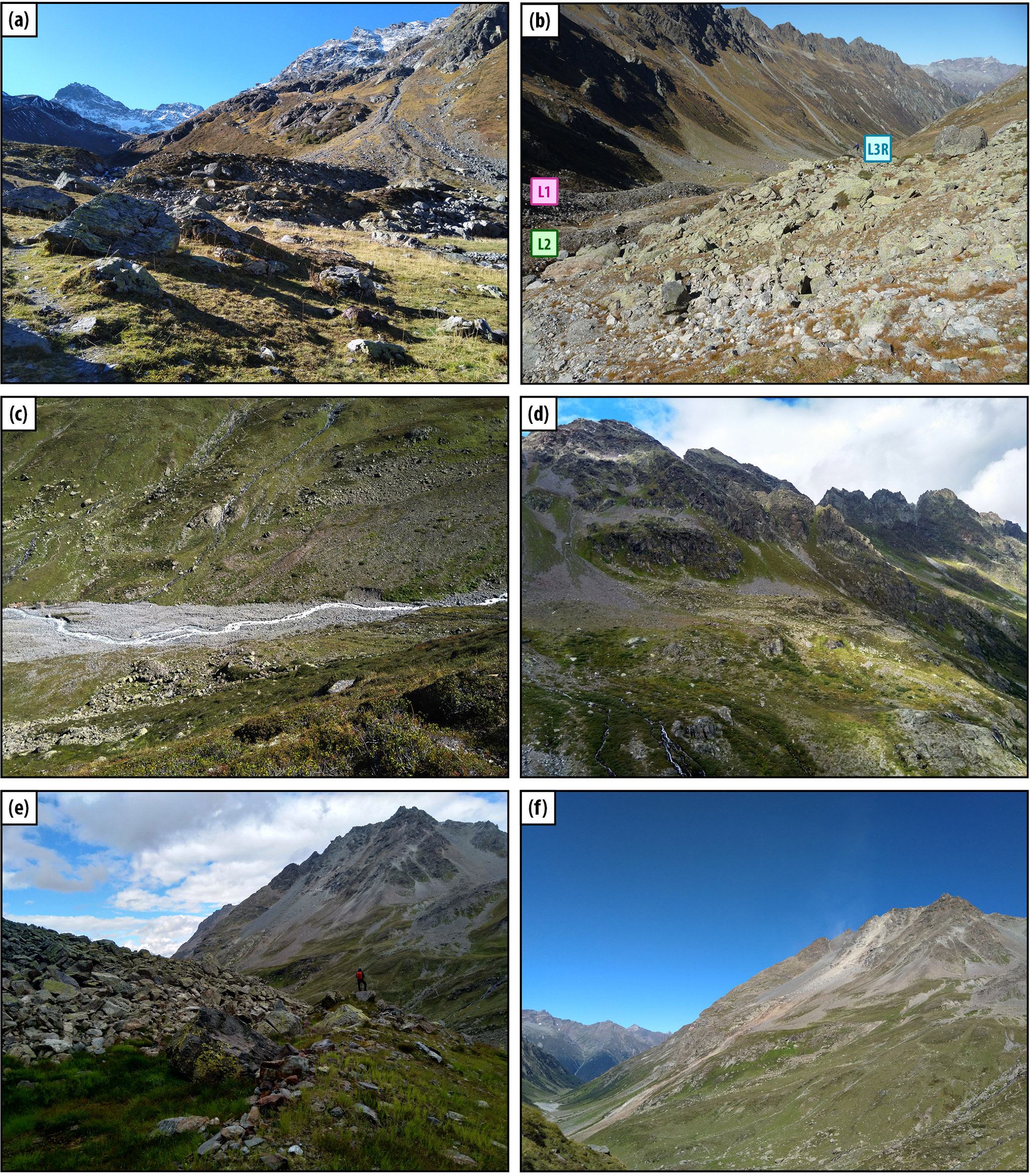
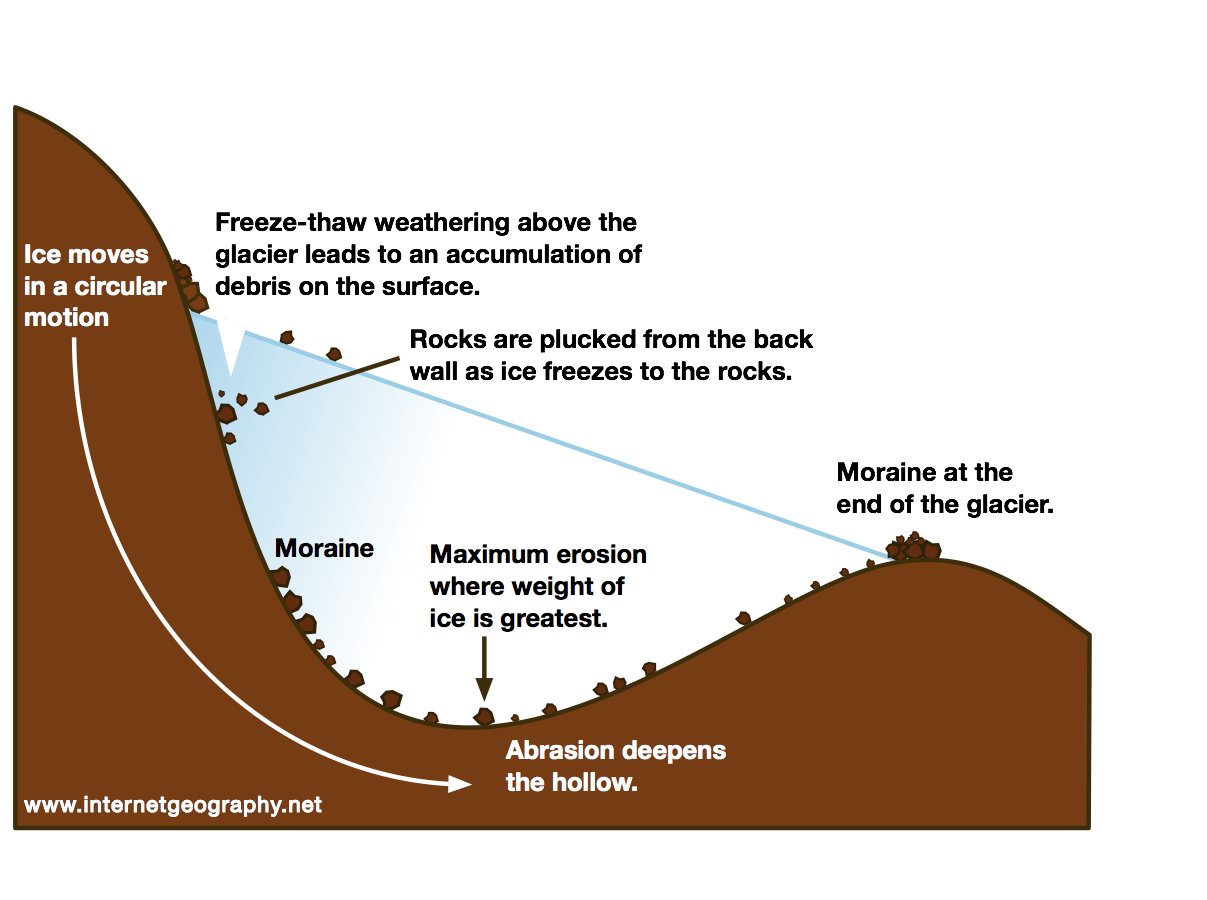
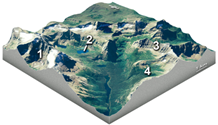
A cirque, or Corrie, is an amphitheater-like valley created by glacial erosion. The glacial cirque is opened on the downhill side while the cupped section is steep. The cliffs on the sides slope down and combine and converge from three or more higher sides.

Which feature on this diagram is a cirque?
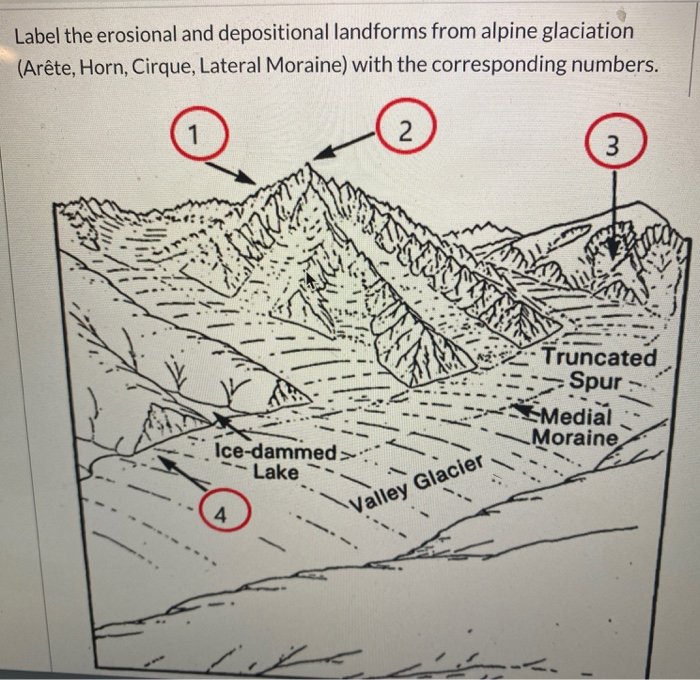
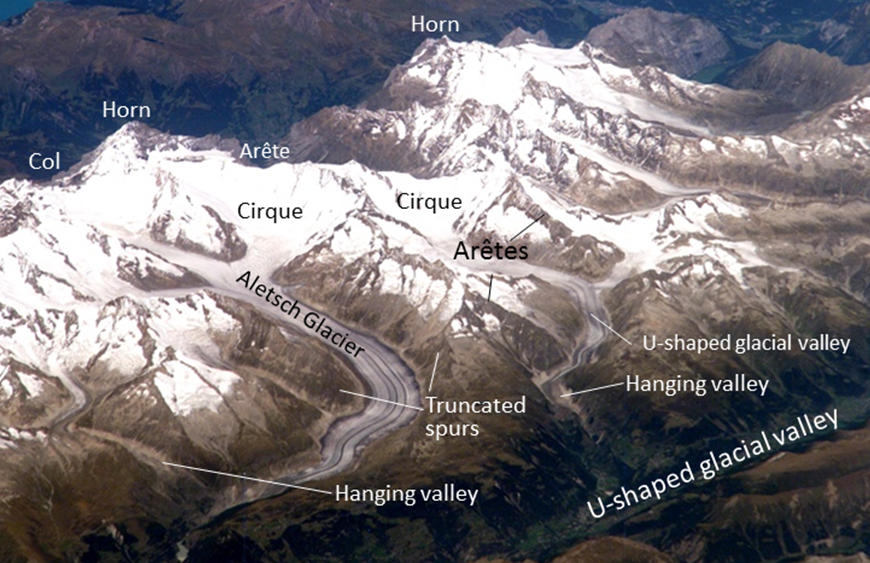
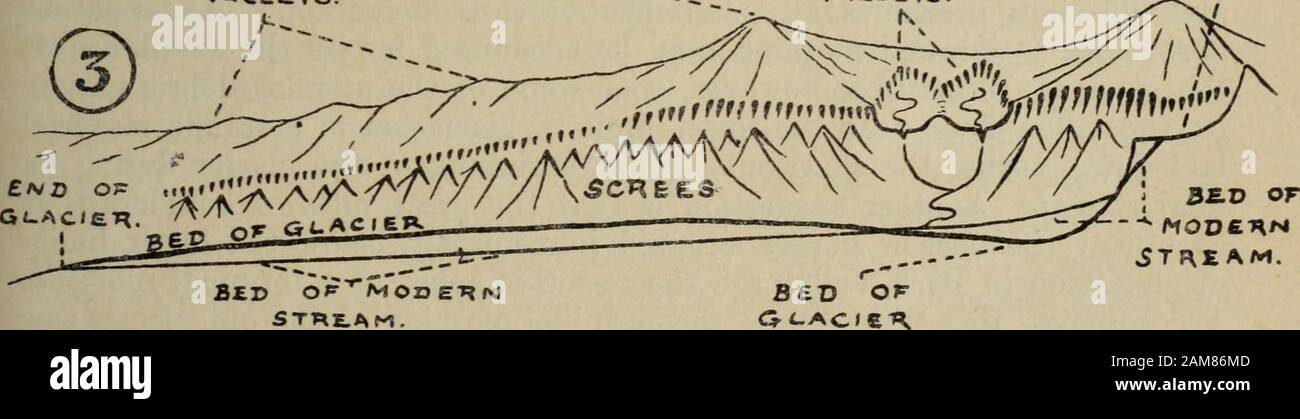
Erosional Glacial Features. A diagram showing erosional glacial features, as follows: 1 is a Pyramidal Peak; 2 is an Arête; 3 is a Corrie or Cirque; 4 is a Corrie Lochan or Tarn; 5 is an Alluvial Fan; 6 is a Ribbon Lake; 7 is a Truncated Spur; 8 is a Misfit Stream; 9 is a Hanging Valley; 10 is a 'U' Shaped Valley. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? asked Aug 28, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Fatboyslim. introductory-courses; Arête, horn, cirque, are features observed as a result of. asked Aug 22, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Carlos. environmental-geography-and-geology; Once formed, glaciers widen and deepen cirques by subglacial abrasion and quarrying of the hollow floor and lower headwall 3 (see diagram below). Cirques can also grow by backwards headwall erosion (wear back) due to frost-action, free-thaw, and mass movement 3,10.
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque?. Moraines- Moraines are formed by the build up of glacial till that isexposed to the elements after a glacier has retreated.This is a medial moraine, meaning that it is formed when two different glaciers merge and lateral moraines (formed on the sides of a glacier) combine to form a moraine in the middle of the combined glacier. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? 1: The circular depression at the head of the valley. Which feature on this diagram is an arete? 3: A steep ridge. What is the feature numbered 2 on this photograph? Medial moraine *know moraines. Which of the features labeled on this figure is a kettle? what feature on this diagram is a cirque. many beach areas are backed by costal dunes formed by wind. how are shorelines affected from the land side An arête is a thin, crest of rock left after two adjacent glaciers have worn a steep ridge into the rock. A horn results when glaciers erode three or more arêtes, usually forming a sharp-edged peak. Cirques are concave, circular basins carved by the base of a glacier as it erodes the landscape. The Matterhorn in Switzerland is a horn carved ...
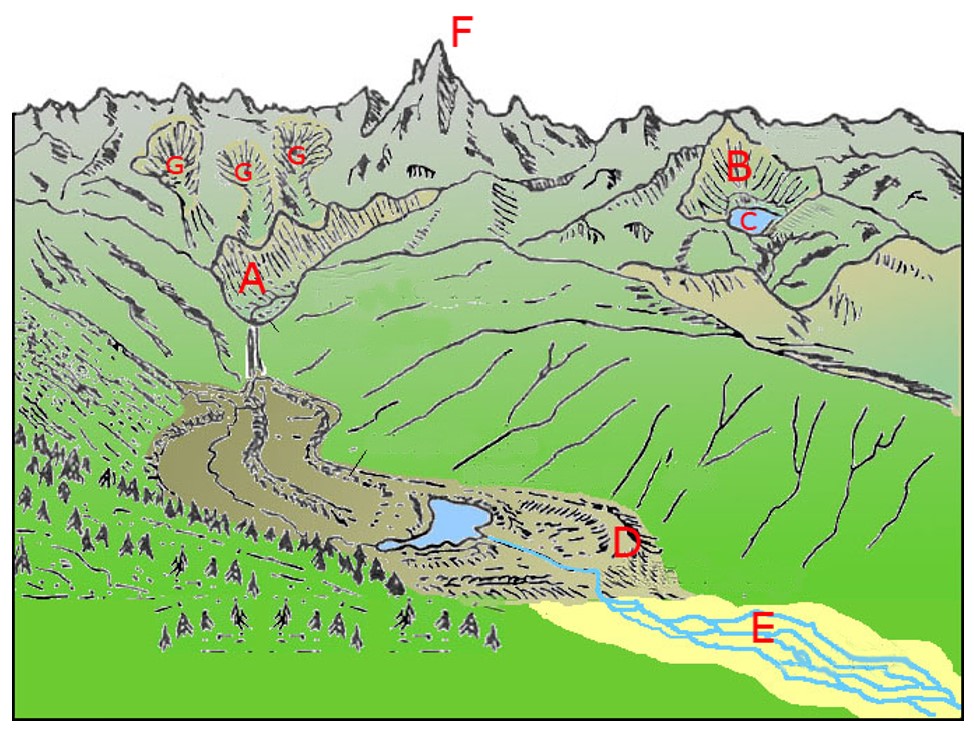
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? The frequency distribution for the weekly incomes of students with part-time jobs is given below. Construct the corresponding relative frequency distribution. Round relative frequencies to the Nearest hundredth of a percent; What are these sharp, glacially carved ridges? Ans 3. At point A, the feature shown is HORN Ans 4. Point B is a glacial trough Ans 5. Point C is tarn Ans 6. Point D is hanging valley Ans 7. These are …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Below are diagrams showing features typical of valley (mountain) glaciers. Arête Cirque Decrease Font Size Arête Tarn Horn Cirques Hanging ... Which feature on this diagram is a tarn? The following frequency distribution analyzes the scores on a math test. Find the class boundaries of scores interval 95-99. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? The frequency distribution for the weekly incomes of students with part-time jobs is given below. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? - 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley - 2, a lake in the upper valley - 3, a steep ridge - 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley
Which feature on this diagram is an arête? Which feature on this diagram is a tarn? The following frequency distribution analyzes the scores on a math test. Find the class boundaries of scores interval 95-99. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? The frequency distribution for the weekly incomes of students with part-time jobs is given below. Package: Exploring Geology with CONNECT Plus 1-semester Access Card (3rd Edition) Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 14 Problem 12MCQ: Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? A. 1, the circular depression at the head of the valleyB. 2, a lake in the upper valleyC. 3, a steep ridgeD. 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley … Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley. What is the origin of curved ridges (R on this figure) in the Great Lakes area? REVISIT. go back paths of ancient rivers. Which of the following is NOT a type of evidence left behind by glaciers? Cirque c. Hanging valley d. V-shaped valley ... Which statement correctly describes the landscape shown in the diagram. a. A is a lateral moraine, B is a medial moraine, and C is a terminal moraine. ... Which features form by deposition from glacial meltwater? a. Kettles, kames, and eskers b. Moraines, erratics, and drumlins c. Tarns, hanging ...
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? A. 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley B. 2, a lake in the upper valley C. 3, a steep ridge D. 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley
Which feature on this diagram is an arête? Which feature on this diagram is a tarn? The following frequency distribution analyzes the scores on a math test. Find the class boundaries of scores interval 95-99. Which feature on this diagram is a cirque?
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? Page 8 of 23 → 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley 2, a lake in the upper valley 3, a steep ridge 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley Bloom's: 3.
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? asked Jan 20, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Messi1031. general-geography; Welcome to Sciemce, where you can ask questions and receive answers from other members of the community. Recent Packs. Child Psych Chapter 5 Sections 2&3.
Cirque is a type of glacial erosional landform. It is also known as a corrie. They are deep, long and wide troughs or basins with very steep concave to vertically dropping high walls at its head as well as sides. A cirque is basically a bowl-shaped depression formed by the erosional activity of a glacier.
cirque glacier. When the upper surface of the open ocean freezes, the feature produced is called sea ice, composed mostly of fresh water. The exposed bedrock in the background of the figure below, to the right, formed as particularly resistant rock and/or thin ice left the rock above the ice surface An interglacial period is
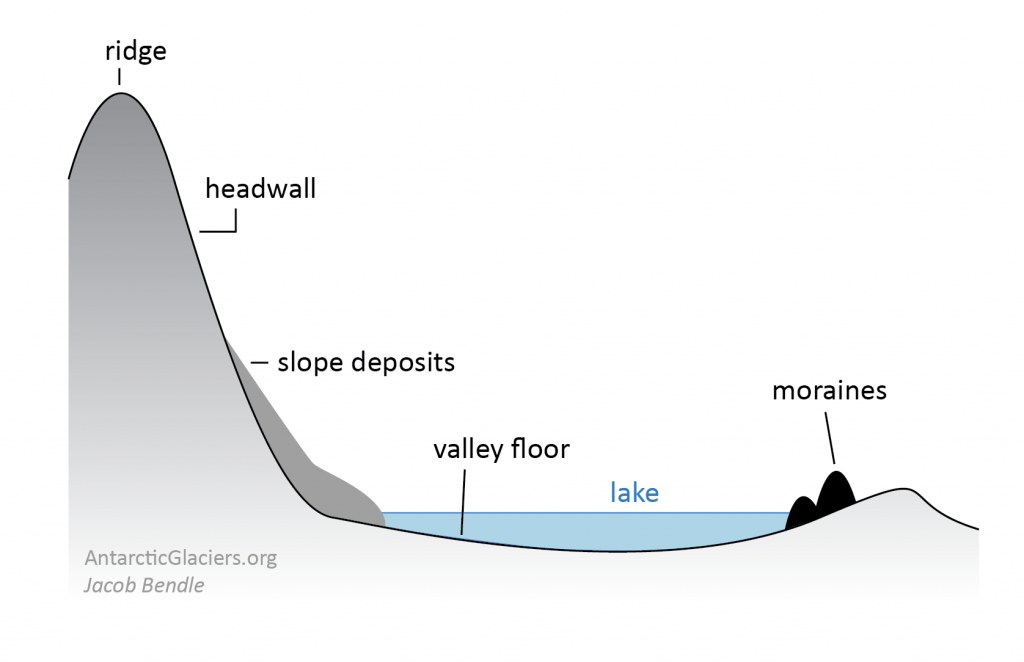
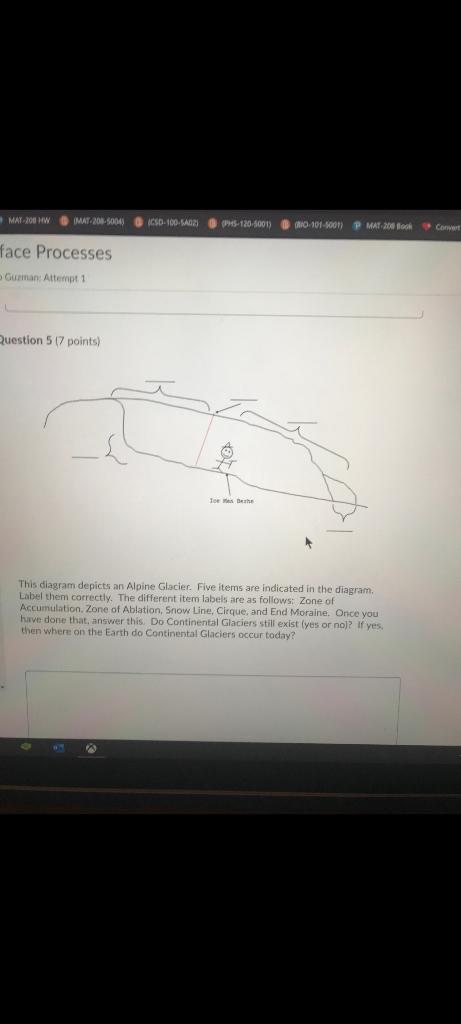
Question 2 1 / 1 pts Identify the feature at #38 on the accompanying diagram that has a characteristic of a lake in a cirque. pater noster arete tarn lake horn peak hanging valley Question 3 1 / 1 pts The boundary between the zone of ablation and the zone of accumulation is called equilibrium line moraine ablation zone terminus
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? A) 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley B) 2, a lake in the upper valley C) 3, a steep ridge D) 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley. Categories Questions. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published.
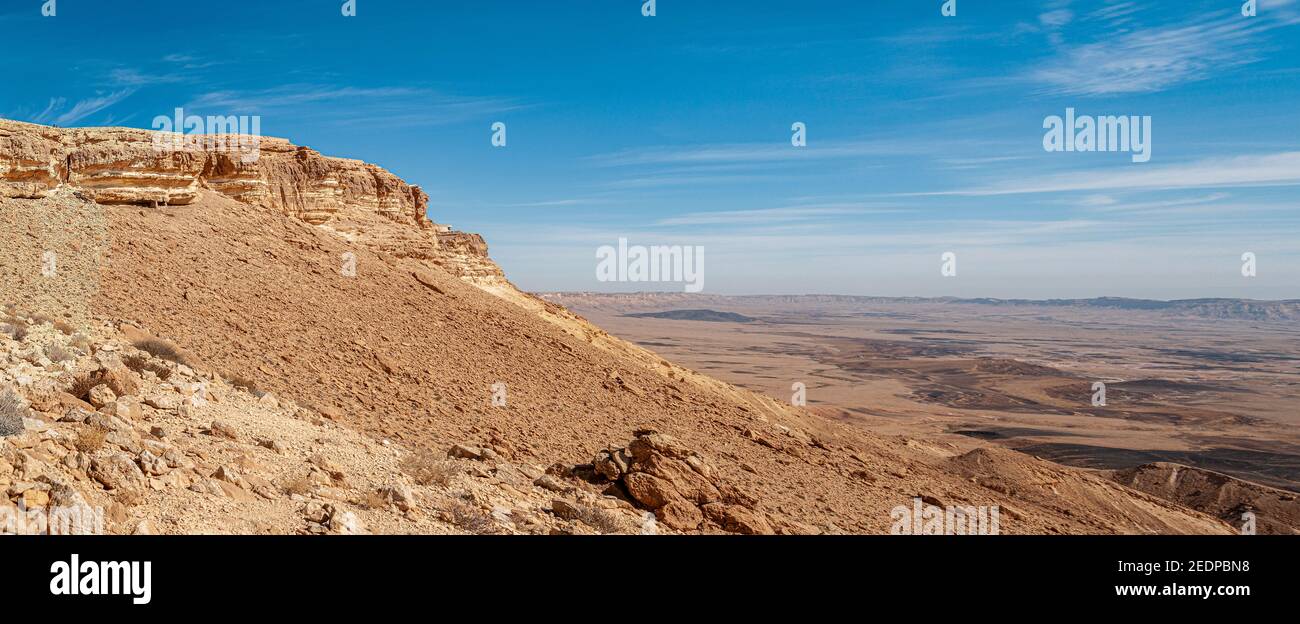
The fluvial cirque or makhtesh, found in karst landscapes, is formed by intermittent river flow cutting through layers of limestone and chalk leaving sheer cliffs. A common feature for all fluvial -erosion cirques is a terrain which includes erosion resistant upper structures overlying materials which are more easily eroded. Contents 1 Formation
Once formed, glaciers widen and deepen cirques by subglacial abrasion and quarrying of the hollow floor and lower headwall 3 (see diagram below). Cirques can also grow by backwards headwall erosion (wear back) due to frost-action, free-thaw, and mass movement 3,10.
Which feature on this diagram is a cirque? asked Aug 28, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Fatboyslim. introductory-courses; Arête, horn, cirque, are features observed as a result of. asked Aug 22, 2019 in Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences by Carlos. environmental-geography-and-geology;
Erosional Glacial Features. A diagram showing erosional glacial features, as follows: 1 is a Pyramidal Peak; 2 is an Arête; 3 is a Corrie or Cirque; 4 is a Corrie Lochan or Tarn; 5 is an Alluvial Fan; 6 is a Ribbon Lake; 7 is a Truncated Spur; 8 is a Misfit Stream; 9 is a Hanging Valley; 10 is a 'U' Shaped Valley.



















0 Response to "40 which feature on this diagram is a cirque?"
Post a Comment